Contents
Electrical engineering
See also: Software, signal processing, batteries, sound.
History
- 1745. Leyden jar stores a high-voltage electric charge.
- 1777. Coulomb invents the torsion balance.
- 1785. Coulomb’s law.
- 1798. Cavendish experiment measures the gravitational constant based on an experiment by geologist John Michell.
- 1831. Faraday’s law of induction. 1836 Faraday cage.
- 1838. Samuel Morse invents the telegraph and Morse code.
- 1861. Western Union builds the first transcontinental telegraph.
- 1910. Telegraph teleprinters increase productivity by 15x.
- 1850. John Tyndall discovers diamagnetism.
- 1864. Maxwell’s equations.
- 1869. Tyndall effect: light scattering by particles causes blue color. Intensity is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength.
- 1875. Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone.
- 1877. Thomas Edison invents the phonograph. Improved by Bell to a graphophone using wax-coated cylinders and then to flat records in 1894.
- 1879. Thomas Edison invents the lightbulb using carbonized bamboo filament.
- 1892. General Electric founded from Edison Electric.
- 1884 Steam turbine by Charles Parsons makes electricity possible and makes shipping much faster.
- 1885. William Stanley invents the first AC transformer at Westinghouse.
- 1886. First DC motor.
- 1887. Nikola Tesla invents an AC induction motor.
- 1887. Heinrich Hertz discovers electromagnetic waves and observes the photoelectric effect.
- 1888. Lord Kelvin invents the Ampere balance to measure current, and a quadrant electrometer.
- 1891. Tesla coil is a resonant transformer circuit that produces high voltage low current discharge.
- 1897. Guglielmo Marconi invents radio.
- 1900. Knob-and-tube wiring: copper wires supported by insulating porcelain knobs and tubes. No safety ground conductor. Soldered and taped junctions.
- 1905. Michelson-Morley experiment is evidence against the luminiferous aether thought to carry light waves.
- 1905. Albert Einstein Annus Mirabilis papers: photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, special relativity, and mass-energy equivalence (E=mc^2). 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Special relativity: Maxwell’s equations imply a constant speed of light for all observers. Pursue a beam of light with the velocity c, observe an electromagnetic field at rest though spatially oscillating.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Einstein's_thought_experiments
- 1920. Sodium-vapor lamp produces yellow light. Needed borosilicate glass to resist sodium corrosion.
- 1927. First quartz clock at Bell Labs.
- 1927. Vannevar Bush invents the differential analyzer, an analog computer, at MIT using torque amplifiers. As We May Think (1945) introduces the memex, a hypertext filing system.
- 1939. Television.
- Terrestrial television or over-the-air (OTA) via radio waves from a TV station to a TV receiver.
- Cable television headend receives television signals from geosynchronous satellites.
- Satellite television.
- low-noise block downconverter (LNB) converts to intermediate frequency.
- Outside plant is the cable network to subscriber homes.
- 1939. Hewlett-Packard is founded by by Bill Hewlett and David Packard.
- 1941. Motorola introduces the walkie-talkie.
- 1947. Transistor radio changes popular music. 1957 Sony TR-63 sells the most.
- 1955. First accurate atomic clock using caesium-133.
- 1957. Sony portable radio (1957), home video tape recorder (1965), Walkman radio (1979), CD player (1983).
- 1963. Cassette tape: magnetically coated polyester plastic tape. Flip to switch between the two tracks, which wind in opposite directions.
- 1970. Fax machine.
- 1970. Residual-current device circuit breaker detects ground faults. 1980s GFCI (ground fault circuit interruptor) outlets protect against 5 mA within 25 ms.
- 1975. Kibble balance measure electric current.
- 1980. Pagers become popular.
1980 Information Age, Third Industrial Revolution, or Digital Revolution. Knowledge workers, cognitive-cultural economy, new service-based economy.
- Software history
- 1981. IBM PC with Microsoft MS-DOS. By Bill Gates and Paul Allen.
- Internet culture: History
- Economic impact: Econ
- Advertising and attention economy.
- Platform economy deriving value from user-generated content (imagination age) and sharing economy.
- Smart manufacturing with distributed smart sensors, industrial robots, 3D printing.
- AI era with large language models.
Electricity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dielectric_loss
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corona_discharge
The charge of an electron (-e) is 1.6e-19 C.
Point charge
- Coulomb’s law. Electric force F = qQ/(4π ε_0 r^2) for two charges q and Q.
- Electric field E = Q/(4π ε_0 r^2), so F = qE.
- Electric potential V = Q/(4π ε_0 r) is the work done to bring a charge from infinity to its current location at r.
- V = Ed.
- The Lorentz force or electromagnetic force is F = q(E + v × B).
- The magnetic field causes a radial force on a moving charge, which does not do work.
Torque on a magnet in a magnetic field: τ = m × B.
Maxwell’s equations describe electromagnetic fields.
- Φ_E = 1/ε_0. Gauss’s law is equivalent to Coulomb’s law.
- Φ_B = 0. Gauss’s law for magnetism: there is no magnetic monopole.
- ∮E∙dl = -dΦ_B/dt or ∇×E = -∂B/∂t.
- Lenz’s law. A changing magnetic field causes an induced current that opposes the change.
- Faraday’s law of induction (1831). The back emf in a wire loop equals the negative rate of change of the magnetic flux enclosed by the path.
∇×B = μ_0 (J + ε_0 ∂_t E)- Ampere’s circuital law.
- Oersted’s law: electric current creates a magnetic field. ∮B dl = μ_0 I.
- Current density J
- Vacuum permittivity ε_0
- Vacuum magnetic permeability μ_0 = 1e-6 N/A^2.
- Flux Φ_B = ∫∫ B∙dS is the amount of field passing through a surface S. Φ = BA for an orthogonal field through area A.
- Divergence is the outward flux at any point.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_group
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Helmholtz_decomposition
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Divergence_theorem
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_dipole_moment
Piezoelectricity convert between electric field and mechanical strain.
- Occurs in crystals with no inversion symmetry.
- A crystal oscillator, typically quartz, oscillates elastically with a very high Q factor. Synthesized in the hydrothermal process.
- lead zirconate titanate (PZT) crystals
- polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is 20 pC/N. Semi-crystalline.
- stretched to orient the molecular chains
- strong electric field induces a net dipole moment
Thermoelectric effect. A thermocouple converts between temperature differences and voltage differences. Seebeck effect: temperature to voltage. Peltier effect: voltage to temperature (low efficiency).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kirchhoff%27s_circuit_laws
Impedance is resistance and reactance.
- Impedance matching helps avoid reflections.
An LC circuit combines an inductor and capacitor. It can generate or pick out signals at its resonant frequency. The capacitor discharges current through the inductor, building up its magnetic field. The inductor opposes changes, and recharges the capacitor. The LC circuit will amplify an AC input at its resonant frequency.
- Inductors are often made from magnet wire, which is copper or aluminum coated with a polymer insulation.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage_source
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Current_source
- Dissipative or thermodynamically passive elements do not produce energy and are not sources.
A voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series, with the output terminal in between them. The voltage difference is dissipated as waste heat.
- Often used to bias op-amp inputs or FET gates with minimal load.
- Only works correctly if current through the load leg is much less than the current to the ground, leading to high waste current.
- A potentiometer or pot is an adjustable voltage divider. The slider or wiper controls the graphite resistance and output voltage.
A linear regulator is a nonlinear component that continuously adjusts a voltage divider to maintain a constant output voltage. It needs an internal voltage reference, typically from a Zener diode, which has a fixed voltage drop independent of input voltage.
A switching regulator uses pulse-width modulation to control the average output voltage, achieving around 80% efficiency.
A trimmer or preset is a circuit-mounted pot that is set once with a screwdriver and not user-adjusted.
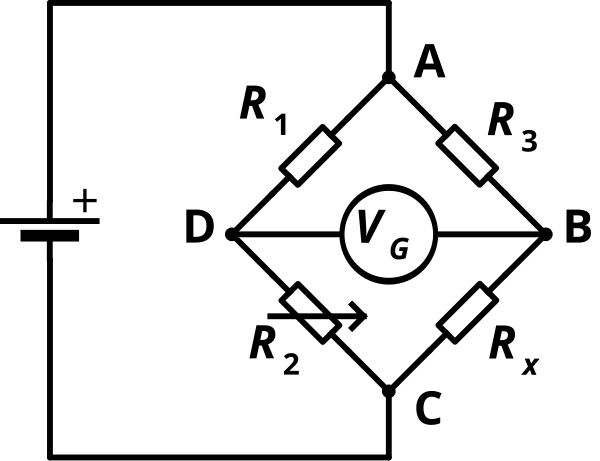
1833. A Wheatstone bridge measures an unknown resistance Rx.
- The two legs of a bridge circuit can be balanced by adjusting R2 so that VG = 0 and R2/R1 = Rx/R3.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_analysis_(electrical_circuits)
- A port consists of two terminals where the current entering one terminal equals the current exiting the other.
- Matching network for impedance.
- Two-port network
- Transfer function can be expressed in impedance z-parameters: V = Z I for vectors V and I.
- Most passive networks are reciprocal, meaning that the current at port A from a voltage at B equals the current at B from a voltage at A. A reciprocal network has a symmetric transfer function.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_circuit
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Current%E2%80%93voltage_characteristic
Switch
- A 2-pole switch controls two independent circuits.
- A single-throw switch can be open or closed.
- A double-throw switch has a contact that can be connected to either of two other contacts.
- A relay is an electrically operated switch.
Analytic representation. The Fourier transform of a real-valued function \(A\cos(\omega t+\theta)\) has Hermitian symmetry, so the negative frequency components can be discarded.
- An analytic signal is a complex-valued signal with no negative frequencies. It can be produced by adding \(A\sin(\omega t+\theta) i\).
- A phasor is a complex number representing an analytic signal \(Ae^{i(\omega t+\theta)}\).
- The Hilbert transform relates the real and imaginary parts of an analytic signal. It shifts every frequency by 90°. It convolves the input u(t) with the Cauchy kernel 1/(πt), though this is not integrable across t = 0 and requires a definition as the Cauchy principal value.
Any signal decomposes into amplitude-modulated in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components.
- The quadrature phase is offset by 90 degrees.
- Angle sum identity: cos(x + φ) = cos(x) cos(φ) + cos(x + π/2) sin(φ).
Alternating current
- Three-phase AC
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small-signal_model
Active electronics produce power gain.
- An amplifier increases voltage amplitude.
- Operational amplifier. Uses negative feedback. Gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth.
- Negative-feedback amplifier.
- Signal-flow graph analyses gain. By Claude Shannon.
- A differential amplifier outputs A(V+ - V-) for gain A.
- Can be created by feeding differential input to an op amp.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage_regulator
- Shunt regulator
Power electronics
- Inverter converts DC to AC.
- Gallium nitride (GaN) is used for power switching and voltage conversion such as AC adapters. Bad p-channels, so mostly nmos logic.
- silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET chips. delaminating gate oxide
- Rectifier converts AC to DC. Uses a capacitor to smooth pulses.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diode_bridge
- Silicon diodes are used at low voltage.
- Germanium diode has a lower forward voltage (0.3 V versus 0.7 V)
- Thyristor has two extra layers of semiconductor. Used for high voltage.
- Insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is the second-most common power transistor.
- DC-DC converter
- Charge pump: charge a capacitor to the supply voltage, then connect it in series to double voltage across the load. Switching at 1 MHz reduces capacitance required.
- https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=41507879
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Switched-mode_power_supply
1936. Printed circuit board (PCB) by Paul Eisler.
- Replaces point-to-point construction or manual soldering, and wire wrapping.
- A lead or pin forms electrical connections.
- Surface-mount technology (SMT) via pick-and-place machines.
- Replaces insertion mount machine and through-hole technology, where leads inserted through holes in a PCB and soldered to pads on the backside.
- Dual in-line package is a rectangle with two rows of pins.
- A chip carrier is a rectangle with leads on all four sides.
- A quad flat package has longer leads extending on all sides.
- Ball grid array (BGA) is high density and low inductance. Solder balls and reflow oven.
- Flip chip: add solder balls directly on the wafer (wafer bumping).
Work tools
- Multimeter measures voltage, resistance, and current.
- A potentiometer measures voltage by comparing against a known reference produced from a calibrated voltage divider.
- Oscilloscope shows voltage waveforms over time.
- Inductive amplifier can detect AC current within 10 cm.
- Logic analyzer to analyze signals.
- Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) Test Access Port (TAP) for scan testing
- Boundary scan tests interconnects
- Prototyping
- Breadboard and jumper wires.
- Crocodile clips and banana connectors.
- Soldering iron
- Heat-shrink tubing used to join wires.
- Wiring pencil uses a reel of 38 SWG copper wire insulated with polymer lacquer which burns away with a soldering iron. Uncommon.
Solder is a fusable metal alloy, melting at 190 °C. Brazing joins metal with hard solder with a melting point above 450 °C. Tin-lead solder is most common. Tin improves wetting (maintaining contact), has higher tensile and shear strength, and is more expensive. Lead prevents the growth of tin whiskers which cause short circuits. 63/37 Sn-Pb is the eutectic alloy with minimum melting point.
- Flux core is a reducing agent to improve electrical connection and mechanical strength. Electronics solder has 2% rosin, which is a mixture of resin acids. Rosin flux requires polluting hydrocarbon solvents, so industry is shifting to water-soluble flux which can be removed with detergent. Plumbing uses acid flux, applied using the fluxuator.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Strain_gauge
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resistance_thermometer
Magnetism
A dielectric medium is an insulator with high permittivity, meaning that it can be polarised by an electric field. A higher permittivity allows a greater stored charge at a given voltage.
A magnetic field can be described as magnetic flux density B (tesla or N/m/A) or magnetic field strength M (A/m), related by the magnetic permeability μ of the material: B = μM.
A particle with magnetic moment m (Am^2) experiences a torque 𝜏 = m × B.
Lorentz reciprocity. Current density J1 produces electric field E1 and magnetic field H1 with time dependence exp(-iωt). Current J2 produces E2 and H2. Then for a surface S enclosing a volume V, int_V (J1∙E2 - E1∙J2) dV = int_S (E1×H2 - E2×H1) dS. The surface term is 0 for localized currents.
In magnetic materials, an external field H induces an internal field M depending on the magnetic susceptibility χ: M = χH. The flux density B = μ_0 (H + M) = (1 + χH) = μH.
Ferromagnetic materials spontaneously form many magnetic domains due to the exchange interaction, which favors aligned local spins. Their atoms have unpaired electrons. Remanence is the process of magnetization, a hysteresis where the domains are aligned through an external field. Ferromagnets demagnetize above the Curie temperature, becoming diamagnetic.
A neodymium magnet or rare-earth magnet has more unpaired elections and a high magnetic anisotropy which gives high remanence (1 T) and high coercivity, or resistance to being demagnetized. Ferrite is 0.35 T.
In paramagnetic materials, an external magnetic field induces a very weak aligned field, causing attraction. Induced field strength is linear with the external magnetic field.
In diamagnetic materials, an external magnetic field induces an opposing field, causing repulsion and allowing levitation. An external field induces an opposing field. All electrons in their atoms are paired.
Superconductors have zero electrical resistance due to Cooper pairs, which prevents scattering of electrons.
Meissner effect causes repulsion due to screening currents. If there is some penetration then the superconductor is pinned in place through flux tubes.
An electromagnet is a coil of wire which creates a magnetic field when current is applied.
- Field coil generates a magnetic field. Wound on an iron magnetic core with a stator and a rotor. Field lines loop through stator and rotor.
- At a pole, magnetic field lines pass from stator to rotor. Usually one field coil per pole.
- A magnetic core concentrates magnetic flux, increasing the magnetic field by 100x. However, alternating current transformers and inductors have core losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. The core consists of soft magnetic materials such as silicon steel or ferrite with low coercivity and hysteresis.
- A solenoid is longer than wide and can operate the contacts in a relay.
- A galvanometer or moving coil ammeter measures current down to ten microamperes. An electric current deflects a rotating coil and pointer against a stationary permanent magnet.
- A voice coil is wound with flat copper ribbon wire coated with an electric insulator. The coil produces a magnetic field opposing a stationary permanent magnet to move a speaker cone. The coil must be lightweight to minimize inertia damping at high frequencies, and reaches temperatures over 100°C. A voice coil motor is also used in hard disk drives.
Hall effect. Magnetic field applied to a current-carrying conductor causes a Lorentz force which deflects the electrons and induces a Hall voltage. Can be used to measure magnetic fields, current, or position.
A Helmholtz coil uses a pair of wide magnetic coils carrying the same current on the same axis to produce a nearly uniform magnetic field. A third larger magnetic coil on the outside can improve uniformity, producing a Maxwell coil.
- A magnetic mirror sets the coils further apart so that the field expands in the middle, trapping charged particles in the diverging field lines.
- An anti-Helmholtz coil uses opposite currents to produce a nearly uniform magnetic gradient. A cusp trap spaces the coils futher apart.
- Magnetic confinement fusion also uses stellarator and z-pinch machines.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_motor
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Switchgear
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distribution_board

Generator and electric motor
- A coil generates a magnetic field.
- The brush transfers current between stationary and rotating components.
- A commutator reverses the direction of the current in the rotating coil at specific points, ensuring continuous rotation of the armature in a DC motor.
- A split-ring commutator is a segmented copper ring or cylinder attached to the armature.
- Dynamo generates pulsing DC using a commutator.
- Homopolar generator (1831): metal disk rotating perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field creates a radial potential difference.
- Homopolar motor: radial current spins the disk. No commutator needed!
- Brushed DC motor.
- Brushless DC motor uses electronic commutation.
- Alternator generates AC.
- Armature produces power. Armature winding carries AC. Usually stationary, with a rotating magnetic field.
- Magneto generates AC using permanent magnets. Most alternators use field coils.
- Turbo generator
- Universal motor
- Induction motor
- Servo
- Rotary encoder measures shaft position.
- A linear variable differential transformer can also measure positin.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Electric_machines
- A linear motor has its stator and rotor unrolled, producing a linear force instead of a torque.
- Linear induction motor uses a three-phase winding and a passive conductor plate.
- Linear synchronous motor uses alternate-pole stators and are low-acceleration. Used in the Shanghai maglev train.
- Railgun. Sliding projectile contacts completes a single loop of current with no windings. Delievers 5 MA for a few milliseconds, producing 10 T fields, 2,000 m/s, and 10 MJ energies.
- A coilgun uses windings to accelerate the projectile.

An H-bridge switches the polarity of an input voltage, allowing DC motors to run backwards. Can be implemented with a double pole double throw (DPDT) relay.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-power_electronics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zero-energy_building
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-energy_house
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Building_envelope
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_Star
Power engineering
The electric grid or power grid delivers electric power via transmission between power plants to electrical substations at 500 kV and distribution to individual consumers at 120 V to 13 kV. Substations transform voltage from 220 kV to 66 kV.
- Energy demand management: time-of-use pricing (TOU) and real-time pricing
- Generation
- Dispatchable generation can output energy on demand, while variable renewable energy (VRE) cannot. Grid batteries dispatch in milliseconds, hydro in seconds, natural gas in tens of minutes, coal in hours, and nuclear in days. Base load power plants usually operate at maximum output, a load-following power plant varies its output, and peaking power plants run only at high demand.
- Merit order ranks sources by marginal cost (including environmental factors). Economic dispatch starts the sources with highest merit first.
- A grid-tie inverter converts generator DC to AC.
- Duck curve or Nessie curve plots the supply of power from dispatchable sources. Peak demand occurs in the evening when VRE is offline, while there is a sharp drop in midday prices due to solar.
- Transmission is mostly three-phase along uninsulated aluminum, which is cheap and light, though it needs a 1.6x cross section for the same conductivity. Bundle conductors are used because AC current only penetrates to skin depth (1 cm). Three wire delta connection and four wire Y or star connection. Y connection has a neutral point and less line current. Delta connection can tolerate a winding failure.
- High voltage DC is better for lines over 100 miles. DC current penetrates the entire conductor, reducing resistance and power loss.
A wide area synchronous grid or interconnection is a three-phase grid that connects generators to many consumers at a synchronized utility frequency. The synchronous grid of Continental Europe has 860 GW at 50 Hz. The Northern Chinese State Grid has 1,700 GW at 50 Hz.
North America has four grids at 60 Hz. They are operated by six regional entities overseen by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). Regional transmission organizations (RTO) and independent system operators (ISO) operate markets for wholesale power. RTOs are larger and have more responsibility over grid reliability. Some areas of the US use power purchase agreements instead of wholesale markets. - Eastern Interconnection (610 GW). Midwest Reliability Organization (MRO), Northeast Power Coordinating Council (NPCC), ReliabilityFirst (RF) in the east, SERC (Southern Electric Reliability Corp). Southwest Power Pool (SPP) and Midcontinent ISO in the midwest, ISO New England, NY ISO, and PJM Interconnection (PJM) in the east.
- 1965 Northeast blackout affects 30M people. A small fluctuation from the Robert Moses hydroelectric plant in New York trips a misprogrammed protective relay, and power from Beck Station hydroelectric plant overloads the rest of Ontario and New England.
- 1977 NYC blackout results in looting and arson.
- 2003 Northeast blackout affects 55M people.
- Western Interconnection (265 GW) by the Western Electricity Coordinating Council WECC. The California ISO.
- 2000 California electricity crisis. In 1996, Enron lobbies Governor Pete Wilson to partially deregulate electricity producers while capping retail electricity prices. Enron creates shortages to drive up prices, causing PG&E to go bankrupt.
- Texas Interconnection (78 GW) managed by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) and the Texas Reliability Entity.
- Quebec Interconnection (42 GW).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Power_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_energy_storage_power_plants
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Electricity_delivery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_energy_system_databases
Radio
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radio-frequency_engineering
Modulation
- Analog modulation
- Carrier wave at constant frequency.
- Narrowband assumption: modulations are low frequency compared to the carrier.
- Amplitude modulation (AM)
- Frequency modulation (FM)
- Phase modulation (PM)
- Digital modulation (analog carrier) transmits one sample per time slot.
- Constellation diagram shows the signal as a scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants. Angle represents phase shift and radius represents amplitude.
- Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) including on-off keying (OOK)
- Frequency-shift keying (FSK)
- Phase-shift keying (PSK) modulates the phase of the carrier.
- Coherent PSK must extract the reference signal to compare the phase.
- Differential PSK encodes phase shift with respect to the phase of the previous symbol sent, which has more demodulation errors.
- Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signal adds together two carriers with the same frequency and orthogonal, 90°, or quadrature phase.
- Digital carrier (analog data)
- Pulse width modulation (PWM)
- Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM)
- Pulse position modulation (PPM)
- Digital data: Pulse coding modulation (PCM)
- Spread spectrum
- Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
- direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS)
- time-hopping spread spectrum (THSS)
- chirp spread spectrum (CSS)
- Multipath interference and shadow fading
- multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) uses multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver.
- Antenna array computes the direction of arrival (DOA) to track the target.
- MUSIC: multiple signal classification
- ESPRIT: estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariant techniques
- Antenna array computes the direction of arrival (DOA) to track the target.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Channel_access_method
- Space-division multiple access (SDMA) uses phased array antennas.
- CDMA: Code-division multiple access. Qualcomm makes 80% of revenue from CDMA, $30 per mobile device.
- OFDM: orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
- Multi-carrier CDMA (MC-CDMA)
- Single-carrier frequency-division multiple access (SC-FDMA) involves frequency-domain equalization (FDE).
3G includes LTE: long-term evolution.
- System Architecture Evolution (SAE)
Transmission line is needed when line length exceeds the wavelength, especially at radio frequency above 30 kHz.
- A transmission line is modeled as a resistance R and inductance L in series with capacitance C and conductance G in parallel. At high frequency, the conductance of dielectric material causes dielectric loss from dielectric heating from the alternating electric field.
- A stub is a line connected at one end only.
- Characteristic impedance Z0 = V(x) / I(x) for current phasor I(x) and voltage difference V(x) between two lines.
- Telegraph equations show that Z0^2 = (R + jωL) / (G + jωC)
- propagation delay τp is around 5 ns/m.
- Also important to minimize high-frequency loss and crosstalk. Crosstalk increases with decreasing separation between signals.
- Heaviside condition G/C = R/L ensures zero dispersion.
- Equalization reverses distortion, ensuring that the frequency response is flat.
- Adaptive equalization changes over time.
In the near field, field lines remain electrically attached to the antenna, so absorption of radiation in the near field by adjacent conducting objects detectably affects transmitter load. The far field is the radiative zone.
Omnidirectional antenna has a broad beam.
- dipole antenna is balanced with opposite voltages at its two terminals, with a twin-lead balanced feedline. It has its antenna null in the direction of the conductor.
- folded dipole or double rod
- monopole antenna is unbalanced, where the ground or ground plane acts as the second conductor.
- loop antenna
- slot antenna
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Antennas
Directional antenna, beam antenna, or high-gain antenna makes a focused beam.
antenna gain (pi * d / lambda)^2 for diameter d and wavelength lambda.
antenna boresight is the axis of maximum gain.
Parabolic reflector
Horn antenna
Yagi-Uda antenna array combines multiple dipole antennas. It has one driven or active element and many parasitic elements, which can be directors or reflector.
an antenna array contains multiple antennas in a specific phase relationship. Can be broadside or end-fire.
endfire log-periodic antenna for rooftop television can receive a wide range.
Cell sites use sector antenna with vertical collinear dipoles and a coaxial cable feedline.
A phased array can be electrically steered with beamforming.
a reconfigurable antenna is a single element with a programmable frequency, polarization, and radiation pattern.
A reflective array antenna is backed by a large reflector, such as a screen of parallel wires.
A curtain array is a reflective array suspended between steel towers up to 300 ft tall. Skywave propagation bounces shortwave radio off the ionosphere for transcontinental broadcasting.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voltage-controlled_oscillator
A frequency mixer multiplies two signals f1 and f2, outputting the heterodyne signals f1+f2 and f1-f2.
- An unbalanced mixer allows both input signals to pass through to the output.
- A single balanced mixer suppresses one of its input signals.
- A double balanced mixer suppresses both of its input signals and requires higher drive levels.
- Diode ring: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_modulation
- A Gilbert cell is a four-quadrant multiplier.
A phase detector outputs the difference in phase.
- Small angle approximation: α − β ≈ sin(α − β)
- Can implement with two multipliers: sin(α − β) = sin α cos β − sin β cos α
- Usually implemented with one multiplier: 2 sin α cos β = sin(α − β) + sin(α + β), where the higher frequency can be filtered out.
A phase-locked loop (PLL) generates an output with the same phase as the input.
- Can provide filter, stabilize, or denoise the signal.
- Can be used as a frequency divider or frequency synthesizer.
Spark-gap transmitter: electric spark drives electric oscillations in a antenna or resonant RC circuit at RF, producing transient damped waves. Induction coil transforms battery voltage to 10 kV. A resonant transformer couples the primary winding to a less damped secondary winding, concentrating energy in a narrower bandwidth.
- 1904. Alexanderson alternator produces high power RF output as a pure carrier wave, causing supersonic dots and dashes.
- A synchronous detector demodulates by mixing the signal with a replica of the unmodulated carrier, which can be generated with a phase-locked loop.
- 1901. Direct-conversion receiver is a synchronous detector using a local oscillator at the same frequency. Impractical due to oscillator instability. By Reginald Fessenden.
- 1905. Heterodyne system uses two Alexanderson alternators separated by an audible frequency like 3 kHz. The receiver filters for the audible beat frequency.
1913 regenerative receiver uses triode amplifier tubes with feedback above unity
Radio receiver
- A heterodyne frequency is created
- 1919. Superheterodyne receiver
- RF filter
- Distributed-element filters or lumped element filters for VHF.
- Waveguide filter for microwave.
- Surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters provide precise, narrow passbands below 2 GHz.
- Thin-film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) filters above 1 GHz.
- RF amplifier
- A tuned amplifier includes bandpass filtering. Usually capacitor-coupled.
- A double-tuned amplifier is transformer-coupled. The primary and secondary coils are tuned separately, leading to a wider bandwidth.
- Frequency mixer uses a local oscillator to convert signal to a lower intermediate frequency (IF).
- https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=40834349
- https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/news/teardown-tuesday-hb100-doppler-radar-module/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_dividers_and_directional_couplers
A RF cavity is a metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields. The resonant frequencies reinforce to form standing waves. Particle accelerators use RF cavities to store energy, with a superconductor coating to maximize quality factor Q to 1e10.
Magnetron is a resonant microwave cavity.
Klystron
Gunn diode generates microwaves
IMPATT diode generates microwaves at high power over 3 kW
HackRF One SDR can spoof GPS CDMA at 1 GHz
Flipper Zero
FM radio 88-108 MHz, AM radio 535-1705 kHz. Amateur radio at 3.5-4 MHz. TV broadcasting 54-88 MHz and 555-763 MHz.
Citizens Band 27 MHz
Multi-Use Radio Service 151 MHz
Family Radio Service and General Mobile Radio Service 462 MHz
A nonlinear junction detector (NLJD) floods high-frequency RF energy to detect unshielded electronics, which return a high second-to-third harmonic ratio.
- An isolator is a 3-port circulator where the return port is terminated with a resistor to absorb RF energy. A circulator is non-reciprocal.
- The SRT-107, Scanlock Mark VB
- Spectrum analyzer: FSH-3
- https://www.cryptomuseum.com/covert/bugs/masking/
synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to increase spatial resolution over stationary beam-scanning radar.
Side looking airborne radar (SLAR)
Telecom
Public switched telephone network (PSTN)
- Circuit switching creates an electrical circuit.
- The telephone exchange or central office contains the main distribution frame (MDF), which interconnects subscriber lines with telephone switches.
- A private branch exchange (PBX) serves a private organization. Each device is an extension.
- Core network connects exchanges over trunk lines. Access network or outside plant connects customers.
- The demarcation point or main point of entry (MPOE) connects on-premises wiring with the PSTN.
- The local loop was a wire to the local telephone exchange. A party line is a local loop shared by multiple subscribers. Sometimes used existing barbed wire fences as telephone lines.
- Restricted to narrow voice frequency (VF) of 300-3,300 Hz.
- Call progress tones: dial tone and ring tone.
- 1892. Automatic switchboard uses the Strowger stepping switch, panel switch, or crossbar switch. Rotary telephones use pulse dialing which sends pulse trains at 10 pulses per second.
- 1963. Touch tone dialing via dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) replaces rotary dials.
- 1970. Signaling System No. 5 (SS5)is a multi-frequency in-band signaling system for International Direct Distance Dialing (IDDD), leading to phreaking.
- Blue box generates in-band signaling tones. A toy whistle in Cap’n Crunch cereal emitted the 2600 Hz AT&T single frequency control tone.
- Billing distinguished -48 V on-hook and -10 V off-hook. A black box allowed incoming calls to be received for free by increasing the off-hook voltage using a resistor.
- Pay phones represented coins with tones. A red box simulated the tones to allow free calls.
- 1982. Breakup of the Bell System creates local exchange carriers (LEC) and long-distance interexchange carriers (LXC) in 1984.
- 1984. No. 4 Electronic Switching System (4ESS) uses Signaling System No. 7. (SS7). Digital out-of-band common-channel signaling.
- 1986. 2G GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
- SMS (Short Message Service) texting.
- quick codes or Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) communicates with the MNO. Starts with a star and ends with a pound sign.
- 1995. cdmaOne or IS-95.
- 1988. Telocator Alphanumeric Protocol (TAP) for sending short messages via a landline modem.
- 1996. Digital subscriber line (DSL) transmits digital data over telephone lines between a digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) and a DSL modem. Replaces ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network).
- 1997. DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) allows data over RF coaxial cable television lines.
- 1998. Session Description Protocol (SDP) is used to negotiate media types for voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing. Does not deliver media streams.
- 2000. 2.5G General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) adds packet switching to NSS.
- Mobile phone network includes the base station subsystem.
- 2000. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions.
- 2001. 3G: American CDMA2000 and UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) in Europe and Asia.
- 2007. LTE System Architecture Evolution (SAE). all-IP Network.
- 2002. Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS)
- 2010. 4G.
Cell network
- Physical channel from user equipment (UE)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Access_Stratum (link layer)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-access_stratum (network layer)
- GPRS core network mobile switching center (MSC) server
- Home location register (HLR)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Backhaul_(telecommunications) from cell tower to core network
- IP, TCP, HTTP
- CDMA2000 IS-41 and GSM Mobile Application Part (MAP): network-side standard mobility services.
- Identity
- Universal integrated circuit card (UICC) holds 100 KB of data.
- SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module) stores an international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) and key.
- IMSI usually starts with the PLMN code.
- mobile identification number, mobile station ID, or short IMSI is the last 10 digits.
- SIM lock: phone manufacturer only accepts SIM cards from some operators.
- MSISDN maps telephone number to ISMI.
- IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) used to blocklist stolen phones.
- Mobile equipment identifier (MEID) is 14 hex digits.
- A cell tower has many radios and modems. Aka base transceiver station (BTS), base station, 3G node B, LTE eNB, 5G GNodeB.
- Network switching subsystem (NSS). GPRS Core Network uses IP-based GPRS Tunnelling Protocol to carry subscriber data from the current serving GPRS support node (SGSN) to the Gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) that is handling the session.
- Part of the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN).
- Mobility management
- Public land mobile network (PLMN): Mobile Country Code (MCC) + Mobile Network Code (MNC)
- Mobile network operator (MNO) owns network infra and radio spectrum license
- Mobile virtual network operator (MVNO)
- location area identity (LAI): PLMN + Location Area Code (LAC)
- hundreds of base stations share a single GSM base station controller or UMTS Radio Network Controller (RNC).
- Routing area: part of a location area in a packet-switched network.
- LTE Tracking area
- Cell Global Identity (CGI): LAI + Cell Identification (CI)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E.214
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Call_management
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telecommunications_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Telecommunications
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:CDMA
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Cellular_network_standards
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_QoS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Call_forwarding
Displays
Seven-segment display.
1939. The Radio Corporation of America (RCA) introduces black-and-white television at the New York World’s Fair.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analog_television#Synchronization
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Set-top_box
- Back porch is the beginning of a scan line
- Colorburst at the back porch keeps the chrominance subcarrier synchronized.
- NTSC analog color
- PAL analog color
Cathode ray tube (CRT): electron-stimulated luminescence of a fluorescent phosphor surface.
- Aquadag is a conductive water-based colloidal graphite coating, serving as a high-voltage anode to accelerate the electron beam.
Liquid-crystal display (LCD) uses elongated molecules that rotate in an electric field. The backlight polarizer emits polarized light, which passes through the liquid crystals, and then is filtered in the analyzer polarizing filter in the display.
- In active matrix panels, each pixel has a thin-film transistor (TFT) to control its voltage, leading to faster response times and sharper images. Passive matrix addressing uses m row or select signals that apply n column or video signals to the bistable pixels.
- Twisted nematic field effect. An electric field rotates the crystals, changing the polarization and modulating the output amplitude.
- IPS (in-plane switching) screens use molecules that rotate in the plane of the display surface leading to wider viewing angles and better color reproduction.
- Vertical alignment (VA) uses crystals that tilt from vertical to block light, leading to higher contrast but narrower viewing angle than IPS.
Metamaterials
- Quantum dots have optoelectronic properties tunable with size. Color ranges from red (6 nm diameter) to blue (2 nm).
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems)
- wet etching with KOH, TMAH
- reactive-ion etching (RIE) or dry etching
- electrical discharge machining (EDM)
Wiring
Telegraph used single-wire earth return (SWER).
Coaxial cable
Twisted pair cable reduces radiation and cancels out electromagnetic interference (EMI). It can be shielded or unshielded. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1881.
Differential signaling uses two wires carrying the same signal with opposite polarity, giving 6 dB more signal.
Telephone wiring uses a single twisted pair per voice line. RJ11, RJ14, and RJ25 (registered jack) are 6-position modular connectors for telephone connections, with positions colored red/green, yellow/black, and white/blue. RJ11 usually uses 4-contact 6P4C connectors, where the outer contacts are unused.
Category 5e cable supports 100 MHz. It uses 4 twisted pairs terminated with 8P8C modular connectors.
A pull-up resistor connects the shared line to high voltage, giving a high signal by default. Any connection to ground results in 0 V shared. Wired-and uses an open drain MOSFET or open collector BJT ⎐, where logic high leaves the shared open or unconnected and logic low pulls the shared to ground.
A pull-down resistor gives 0 V by default. Any connection to high voltage results in high voltage shared. Wired-or uses an open source or open emitter ⎏.
A return-to-zero line code uses three line states. The line drops to 0 V between each pulse, so it is self-clocking, but requires twice the bandwidth. A non-return-to-zero (NRZ) code only uses two line states.
A serial bus transmits one bit at a time, while a parallel bus transmits multiple bits.
- RS-232 is a serial protocol between a computer (data terminal equipment) and a modem (data circuit-terminating equipment). It can also connect two computers via a “null modem” which simply connects each transmit (pin 2) to receive (pin 3) and a common ground. Each device must be configured with the same baud rate, word length, parity, and number of stop bits. Handshaking lines were optional.
- A COM port or tty is a IBM PC serial port.
- Dial-up internet used the public switched telephone network to connect to an Internet service provider. The modem opened the phone line, listened for a dial tone, autodialed the target number, and handled modulation to audio data. Modems would detect special AT commands, such as ATD to open a connection. A baud was about 1 bit per second.
A parallel bus is more complex and with more crosstalk.
- The printer port was a parallel port.
Vehicles use the CAN bus (controller area network), a message-based protocol using an NRZ code over serial differential wired-AND connection. High-speed CAN reaches 1 Mbps, where the dominant (0) state drives CAN high 3.5 V and CAN low 1.5 V, and resistors at each end pull the wires to the recessive (1) state with 0 nominal differential voltage. Each frame consists of an ID, up to eight data bytes, a CRC, and an ack slot. On-board diagnostics (OBD) can use CAN or other protocols.
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a low-level serial communication bus using just two bidirectional lines: serial data line (SDA) and serial clock line (SCL). Both lines use an open-drain MOSFET bus, where a logic 1 is output by letting the line float, requiring a pull-up resistor to the 5 V source.
Ethernet physical layer
ACPI: Advanced Configuration and Power Interface for power management.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a power and communication standard. USB 4 supports 5 GB/s (two lanes at 2.5 GB/s). It uses a packeted tiered star topology where the host controller has a root hub and connects to downstream devices or hubs. A USB device can contain multiple endpoints, each with one pipe or logical channel. USB power delivery supports up to 48 V at 5 A. USB-C is the latest connector.
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect express) is a serial expansion bus. v5 is 4 GB/s per lane, so x16 is 64 GB/s. It uses a point-to-point topology allowing full duplex communication.
- Compute Express Link (CXL) is a higher-level standard for I/O and cache-coherent memory connections.
HDMI includes a Display Data Channel I2C bus for E-DID, transition-minimized differential signaling (TMDS), and optionally a Consumer Electronics Control and Audio Return Channel. TMDS interleaves video, audio, and control data packet types.
Data storage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_storage
Analog Digital Converter (ADC) and Digital Analog Converter (DAC).
Floppy disk. 3.5", 300 rpm. Floppy drive interface uses active low logic signals, so only the falling edge is relevant. Open collector with a pull-up resistor to 5 V.
- Output: read falls low whenever the magnetic field changes orientation. Index falls low once per revolution (200 ms). Track 0 sensor held low when the read head is at the outmost track.
- Input: Side 1 select for which side to read. Direction and step pulses to change tracks.
compact disk (CD)
- Q subcode channel: current location.
- 75 frames per second. 588 samples per channel.
- ToC in the lead-in area: each track index 0 points to a 2 s pregap of silence to allow imprecise seeks. Players play the track 1 from index 1.
Hard disk drive (HDD) has the lowest cost per bit but lower IO rates (spindles). A spindle holds around two double-sided platters or disks coated in 10 nm of magnetic cobalt alloy. The disk spins at 7,200 rpm and read-and-write heads at a 5 nm flying height modify magnetic grains 200 nm wide radially and 25 nm deep in the circumference direction. Grain size is limited by superparamagnetism, where small grains can thermally flip over the Néel relaxation time. The core of the platter is aluminum, glass, or ceramic, and a protective overcoat of diamond-like carbon for protection is deposited using sputtering or chemical vapor deposition.
- Seagate (20B) and Western Digital (25B).
- SCSI: Small Computer System Interface for hard disk I/O. Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) replaced parallel SCSI (SPI).
- Fibre Channel (FC) transfers raw block data over optical fiber in data center storage area networks. A switched fabric where nodes interconnect using multiple crossbar switches, which is higher throughput than a broadcast network.
Perpendicular recording uses a “monopole” write head and soft underlayer to allow more magnetic flux to penetrate a stiffer (higher coercivity) data storage layer. It magnetizes in the up/down direction and triples storage density over longitudinal recording.
A flip-flop is an edge-triggered bistable circuit, while a latch is level-triggered. A set-reset (SR) latch can use two NOR gates where the output of one is fanned into the input of the other. One gate is designated as the set gate to store a 1, and its output is the stored bit; the other is the reset gate to store a 0. A flip-flop is gated on a rising-edge detector, which can be implemented using two relays. Since transistors can only drive a limited amount of charge, master-slave latches help to reduce the fan-out and capacitance of the clock signal.
Volatile random-access memory (RAM).
- Static RAM (SRAM) for registers and cache lines uses flip-flops. 4x area per bit vs. DRAM.
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM) uses one transistor and a capacitor per bit. DRAM is higher density but slower, and needs a memory refresh every 64 ms, causing high power draw. The latest is DDR5, Double Data Rate 5.
Nonvolatile memory. A floating-gate MOSFET stores charge in an electrically isolated gate. Secondary control gates are deposited above the floating gate and can modify it capacitatively via Fowler–Nordheim tunneling cold field electron emission.
- NAND flash memory include SD cards, flash drives, and solid-state drives (SSD). This is the highest revenue memory format. SSDs have higher bandwidth and faster flash controllers.
- NOR flash is uncommon. It can read single bits, but has lower density and slower write/erase speeds.
- EPROM (erasable programmable ROM) are programmed with a device that supplies higher voltages than normally used. It has a transparent window to allow erasing via UV light, causing ionization and charge dissipation. EEPROM is electrically erasable.
- ECC: Error correction code memory corrects bit flips.
- NVMe (Non-volatile memory express) is an interface specification for non-volatile storage media. It replaces the legacy Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI).
- The smaller M.2 form factor replaces mSATA which used PCIe mini card.
Semiconductors
A diode allows current only in one direction. There is a threshold voltage (0.5-1 V) before any current can flow. Semiconductor diodes replace vacuum tubes, which used an electron-emitting cathode.
Electrons in a single atom have a discrete set of possible energy states corresponding to molecular orbitals. In a material, these aggregate into bands of allowed electron energies. The valence band is the highest range of electron energies where electrons are normally present and is below the conduction band, the lowest vacant energy states.
The Fermi level is the energy needed to add one electron and is measured with a voltmeter. Electron or fermion energy states follow Fermi–Dirac statistics. The energy state at the Fermi level has a 50% chance of being occupied, and states far from the Fermi level are unlikely to change.
In a conductor, the Fermi level is inside a band. In a metal, electrons are delocalized, and energy fills the band from bottom to top. In an insulator, the Fermi level is in a very wide bandgap, so electron flow is impossible. In a pure semiconductor, some electrons are excited in the conduction band (n), leaving behind an equal number of holes in the valence band (p). The excitations allow a small amount of current flow.
- Silicon 1.1 eV bandgap.
An extrinsic semiconductor has been doped.
- n-type semiconductors are doped with group V electron donors like phosphorus or arsenic. They release mobile electrons and can easily jump into the conduction band.
- p-type semiconductors are doped with group III electron acceptors like boron, creating electron holes.
At a p-n junction, electrons flow from n to p causing + charge at the n-type, - charge at the p-type, an electric field until the energy level equalizes between donors and acceptors. In the depletion region, there are no electrons in the conduction band and no holes in the valence band, so current can only flow from n to p. p-n junction isolation surrounds transistors in an integrated circuit with reverse biased p–n junctions.
Solar cells or PV cells use a photodiode based on the photovoltaic effect. Upon absorbing a photon, an electron in the valence band jumps into the conduction band and becomes free, moving to the cathode and producing a photocurrent.
- Conventional cells are made from 160 to 190 μm solar wafers and are 26% efficient. The maximum theoretical efficiency is 33%.
- Thin-film solar cells use amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), or gallium arsenide (GaAs). These are cheaper, less durable, lighter, and more flexible.
- Third-generation solar cells might use perovskite, dye-sensitized Grätzel cells, quantum dots.
- Multi-junction solar cells absorb more wavelengths but are costlier and only used in aerospace. The maximum efficiency is 40% with a theoretical efficiency of 86%.
LEDs
- An LED diode requires a crystal with under 1,000 dislocations per cm^2, high electron mobility, and few scattering events. Metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD) helps grow uniform crystals. Layers are under 1,000 atoms.
- Shuji Nakamura invented the blue LED using GaN. This needs to grow on sapphire substrate, which has a 16% lattice mismatch, resulting in low efficiency.
- Two-flow MOVCD uses a second nozzle to develop a GaN buffer layer on the substrate. Also an AlN buffer layer.
- Hydrogen from ammonia gas (the nitrogen source) plugs electron holes and passivates p-type GaN. Thermal oxidation above 400 C allows hydrogen to diffuse out.
- The bare p-n junction is known as a homojunction, which has a carrier diffusion length of 1 micron and is inefficient. A double heterostructure LED uses an active layer of InGaN to reduce the band gap, which confines carriers inside the active layer, increases their density, and improves the probability of radiative emission. The inefficiencies come from the Shockley-Read-Hall (SRH) process and Auger recombination, which dissipate heat. It needs an electron wall to avoid leakage current.
- LED size is roughly 200 microns, and the smallest are 5 microns. UV LEDs use AlGaN to increase the band gap.
- Organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) are deposited as thin films, making them cost effective for large displays. They can display true blacks. They are more heat sensitive and require expensive encapsulation to minimize burn-in.
- multiple-quantum well (MQW)
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is used for amplification or switching. It can be PNP or NPN type. A current from base to emitter controls connectivity from collector to emitter. It is a minority-carrier device (electrons in NPNs, holes in PNPs). Invented by William Shockley at Bell Labs in 1948. In 1957, the traitorous eight leave to found Fairchild Semiconductor.
- Silicon surface states have dangling bonds that act as charge traps which reduce electron mobility.
A field-effect transistor (FET) uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. Gate-to-source voltage alters conductivity between source and sink. A depletion region is an insulating region that forms when mobile charge carriers have been removed. It is invented in 1959.
- 1957. Silicon surface passivation by growing a layer of silicon dioxide over the silicon wafer. By Carl Frosch and Lincoln Derick.
- 1959. The planar process creates chips in layers. By Jean Hoerni at Fairchild Semiconductor. Drain and source are adjacent at the surface.
- An n-channel has a large channel at positive voltage. A p-channel has a large channel at negative voltage.
- Depletion mode uses voltage to expand a depletion region which narrows and eventually pinches off the channel. Enhancement mode uses voltage to attract enough carriers to the gate to counter the threshold voltage from dopant ions.
- High-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) like gallium nitride (GaN) uses a heterojunction as the channel. Also used as a low-noise amplifier (LNA).
- 1959. A metal–oxide–semiconductor FET (MOSFET) uses a doped region as the channel. These were originally made with gates of metal, but are now made with a self-aligned gate in silicon.
- n-type (NMOS) passes a strong 0 but poor 1.
- p-type (PMOS) passes a strong 1 but poor 0. Made with p-type substrate for the gate with n-type channels for source and drain.
- Cameras use a charge-coupled device (CCD), an array of PMOS capacitors. Photons are converted into electric charges, and charge coupling applies a voltage at the gate to dump the charges into a charge amplifier, which outputs the voltage.
CMOS (Complementary MOS) is used for 99% of chips. It pairs an n-type and a c-type transitor. It has low static power consumption since one transistor is always off and only switching draws power, and the balanced voltages give high noise immunity. With single transistors, a small direct current must flow through a logic gate when the gate is on, leading to power drain.
- Capacitive sensing: reactive near field created when body capacitance deflects energy back to the antenna within 1/6 of a wavelength.
- A transmission gate is a CMOS-based relay.
1960. The integrated circuit (IC) or chip is a circuit manufactured as a single piece of silicon. By Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments and Robert Noyce (cofounder of Fairchild Semiconductor) using BJT and soon superseded by MOS ICs in 1964.
- front p-silicon wafer and buried SiO2 insulator layers
- CPU chip has around 10 billion transistors with 50 nm gate size.
- (p-well and n-Si or n-well and p-Si) walled off by undoped silicon glass (USG) STI. Paired with polysilicon gate, cobalt disilicide walled off by SiN barrier layer
- Up to 15 layers of copper wiring
- phosphor-silicate glass (PSG) used as insulator
- SiC seal layer and etch stop layer
- spin-on dielectric (SOD)
- SiN and SiN seal layer
Silicon
- 80% of silicon is produced as ferrosilicon alloy, where the silicon acts as an oxygen sink, controlling the steel carbon content and preventing the formation of cementite. This silicon is relatively impure.
- Metallurgical grade (MG) silicon is 95-99% pure. 55% is used for aluminum alloy, mainly in the car industry. Silumin is the eutectic mixture with 12% silicon that minimizes thermal contraction and stress fractures. About 15% is refined to nine-9 semiconductor purity.
- Silicon is purified into polycrystalline silicon by removing transition metal and dopant impurities. The Siemens process converts to SiHCl3 and then silicon in a reactor. A fluidized bed reactor is an emerging alternative.
- 1915. Czochralski method. Recrystallization produces monocrystalline silicon in cylindrical boules, which are sliced into wafers.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Crystallization
- This requires ultra high purity quartz crucibles sourced from the Spruce Pine Gem Mine in North Carolina or Caldoveiro Peak in Spain.
Fabrication
- Cleaning with piranha solution (sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide) or toxic chlorine trifluoride
- RCA clean uses hydrogen peroxie and hydrochloric acid to remove organic and ionic contaminants.
- Layering adds atoms to the surface. Epitaxy forms new crystalline film.
- chemical vapor deposition (CVD) at high temperature. Can be plasma-enhanced.
- physical vapor deposition (PVD)
- electron beam PVD (EBPVD) or electron beam evaporation (EBE): charged tungsten filament -> electron beam -> target anode -> atom gas -> coating
- anode reaches 100 W/cm2 and 3000 C.
- electron beam PVD (EBPVD) or electron beam evaporation (EBE): charged tungsten filament -> electron beam -> target anode -> atom gas -> coating
- sputtering: bombard solid source with plasma ions causing atoms to deposit on the wafer surface
- conductive: indium tin oxide (ITO)
- Thermal oxidation creates SiO2
- Sidewall spacer: deposit a thin layer of insulator like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or a polymer and use anisotropic etching to only keep sidewall material on the vertical edges of features, thus increasing their width.
- Patterning done with photolithography.
- Align wafer within 0.25 nm and surface temperature uniform to 2 mK.
- The reticle or mask with the chip pattern is a multilayer reflector that uses interference.
- Mechanical master. Laminate opaque rubylith masking film on mylar or polyester, then use a coordinatograph to cut off rubylith on a light table. Photo reduced to 1/100 onto film. Red color is light-safe for orthochromatic film.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photoplotter
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contact_lithography
- Chromium replaced silver halide for better UV opacity
- Zeiss optical column uses multilayer mirrors to shrink the reticle pattern by 4x.
- Exposes photosensitive resist. Positive photoresist like PMMA becomes soluble. Negative resist like SU-8 crosslinks.
- Stepper or scanner moves the mask over the wafer for each chip.
- Wash resist, develop or bake, etch away undesired areas, and strip resist. Wet etching uses hydrofluoric acid, dry etching such as reactive-ion etching (RIE) uses fluorine plasma.
- inductively coupled plasma RIE (ICP-RIE)
- Doping via ion implantation
- Heating or thermal annealing at 1,000 degrees repairs crystal structure and removes water.
- Chemical mechanical polishing or planarization (CMP) smooths the surface.
- 300 mm wafers are transported in FOUPs (front opening unified pod) on ceiling rails. 200 mm wafers are transported in SMIFs (standard mechanical interface).
- Suppliers
- Applied Materials makes tools for epitaxy, ion implant, deposition, and selective materials removal.
- Tokyo Electron makes deposition, etching, and cleaning equipment.
- KLA makes inspection microsopy and metrology tools.
- Lam Research
- A leading-edge fab costs $20B and produces 50k wafers/month.
- Class 100 cleanroom has <100 0.5 micron particles per cubic foot over 1M square feet. Air is changed 100 times per hour. Workers wear bunny suits.
- Pipes and equipment are teflon-coated electropolished stainless steel. Pipes joined using orbital welding. Material delivered in double-wrapped plastic bags.
- Minimize vibrations to VC-D, below 250 microinches/s RMS velocity for frequencies above 10 Hz. Floor is a two ft thick waffle slab, potentially with structural isolation break and actively damped tool pedestals.
- Sub-fab has vacuum pumps, ducts, piping, wiring, chemical storage, etc.
- Air separation plants
- Ultrafiltration
- clarifier: iron sulfate, cationic polymer, line
- acid and scale inhibitor
- Reverse osmosis
- vacuum degasification
- UV irradiation: TOC reduction, bacterial inactivation
- Ion exchange mixed beds
- Intel Copy EXACTLY!
Light source.
- Deep UV (DUV) uses 100 to 300 nm light from an excimer laser. Electric discharge creates an excimer containing excited atoms, which emits UV light as it transitions back to ground state. Cymer makes these lasers. It was founded in 1986 and acquired by ASML in 2013. The US gave ASML access to advanced Department of Energy research in the 1990s. These lasers are also used for microfluidics and LASIK cornea ablation.
- 248 nm KrF has 80 nm resolution.
- 193 nm ArF has 30 nm resolution.
- i193 is the most common. It uses a liquid immersion medium between the lens and the wafer, allowing a higher numerical aperture (NA). It has 7 nm resolution = 100 MTr/mm^2. The reticle limit is 858 mm².
- Extreme UV (EUV) uses a CO2 laser that fires two laser pulses at a fast-moving drop of tin at 50 kHz. ASML has a monopoly on this, with 80% are sold to TSMC, Intel, and Samsung.
- Low NA (0.33) systems can print 3 nm nodes with a critical dimension (CD) resolution of 13 nm, 26 nm metal pitch and tip-to-tip interconnect space pitch using single exposure patterning at 13.5 nm. They can print 2 nm with double exposure, which takes longer. They cost $200 million each. TWINSCAN NXE:3300 (2013) was the first production EUV system, and TSMC began high-volume EUV production in 2019.
- High-NA systems have a numerical aperture of 0.55, resolution of 8 nm, and reticle limit of 429 mm². Allows 1 nm resolution = 1,000 MTr/mm^2 density. Needs higher source power which increases wear. TWINSCAN EXE:5000 costs $400 million and weighs 330,000 pounds, and only Intel is prototyping these.
Packaging
- Sawing: cut water into chips or dies.
- Bonding: attach the die to its packaging substrate. Wire bonding uses tiny wires to connect chip pads to package leads. Flip-chip Ball Grid Array (FCBGA) bonding directly connects solder bumps on the chip to packaging substrate pads.
- Wafer Level Chip Scale Package (WLCSP) applies solder balls directly on the chip, without packaging substrate.
- Molding encapsulates the chip in an insulating plastic or epoxy resin.
- Trend toward disintegrating logic and SRAM into chiplets and reintegrating them using advanced 3D packaging. CMOS 2.0 uses finer-grained disintegration and stacking more dies.
- Backside power delivery (Intel PowerVia).
- Intel is also developing RibbonFET gate-all-around transitors.
SRAM is 4x the area per bit of DRAM
Moore’s law: transistor count doubles every two years. By Intel CEO Gordon Moore.
1971. Intel 4004 is the first microprocessor, manufactured via single-chip large-scale integration (LSI). Fourth generation of computer.
1975. 10k gates/chip.
1986. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) puts 1M Tr/chip.
500 nm (1992) was the gate length. 300k gates/chip. 250 mm2/chip. 200 mm wafer. 3 levels of interconnect.
- 1993. Pentium 80501, 60 MHz, 5 V, 3M transistors, 800 nm. 80502 120 MHz at 3.3 V, 600 nm.
350 nm (1995). 40,000 wafer/mo. - 1995. Pentium Pro introduces micro-ops and out-of-order execution.
250 nm (1997)
180 nm (1998)
130 nm (2001)
90 nm (2003). 20M gates/chip. 7 layers of interconnect. 400 mm wafer.
65 nm (2006). Intel Core. 1M Tr/chip.
45 nm (2007). Gate length 35 nm. 160 nm gate pitch. 9 interconnect layers. First generation Core.
32 nm (2010) half pitch. uses immersion lithography. 7M Tr/mm2. Intel Sandy Bridge, second generation Core.
Intel 22 nm (2012) half pitch uses FinFET. 16 MTr/mm2. Ivy Bridge, Third generation Core. Haswell fourth gen.
Intel 14 nm (2014). 40 MYr/mm2. iPhone 6 with A9 chip. Intel Broadwell 5th gen. Skylake 6th gen, Kaby Lake 7th gen,
TSMC N7 (2018) = Intel 10 nm = Intel 7. 100 MTr/mm2. Quantum tunneling through oxide layers. iPhone XR and A12 chip. Cannon Lake, Sunny Cove 10th gen. Raptor Cove microarchitecturw and Raptor Lake processor.
TSMC 5 nm (2020). 140 MTr/mm2. iPhone 12 with A14 chip. Intel 4 Meteor Lake.
TSMC 3 nm (2023). iPhone 15 with A17 chip.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smart_card
Electronic design automation (EDA)
- Design flow
- High-level synthesis to Register-transfer level (RTL)
- Verilog or VHDL hardware description language
- Logic synthesis into netlist (connectivity graph)
- Circuit design
- Physical design: partitioning, floorplanning, placement, clock tree synthesis, signal routing, timing closure
- SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis)
- Process Design Kit with standard cells and PCell or parameterized cell
- Design rule checking: minimum width, spacing, enclosure
- Layout Versus Schematic
- Parasitic extraction: model parasitic capacitance, inductance, resistance of interconnects
- Check for antenna effect, collection of charge which causes plasma induced gate oxide damage.
- Electrical Rule Check: proper contacts and spacings, signal transition times (slew), capacitive loads and fanouts.
- GDSII (Graphic Design System) layout or OASIS (Open Artwork System Interchange Standard)
- Mask data preparation (MDP)
https://exclusivearchitecture.com/03-technical-articles-IC-00-table-of-contents.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lean_manufacturing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toyota_Production_System
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consumer_Electronics_Hall_of_Fame
- TDP: Thermal Design Power is the maximum power draw.
- northbridge is the CPU, RAM, and PCI-E. southbridge or Intel I/O Controller Hub (ICH) connects to peripherals. CPU connects to northbridge via front-side bus (FSB) and cache via back-side bus. FSB bandwidth was a bottleneck.
- Intel Hub Architecture starts from Intel 810 (1999). memory controller hub (MCH) connects to ICH via a 266 MB/s bus.
- Direct Media Interface links northbridge and southbridge starting 2004.
- Platform Controller Hub starts from Intel 5 Series (2008) and uses a single chip.
- von Neumann architecture: shared memory for exectuable instructions and data. Harvard architecture: separate memory.
- x86: Intel, AMD
- Intel 8086 uses 20-bit address bus, giving 1 MB of addressable memory.
- Real mode: real memory like the 8086.
- protected mode
- Intel Core
- Intel Atom is an ultra-low-voltage processor.
- AMD Geode processor: 500 MHz at 2 W.
- ARM
- Cortex
- big.LITTLE uses heterogeneous processor cores.
- DynamIQ replaces big.LITTLE from Cortex-A55 (E core) and Cortex-A75 (P core).
- MediaTek has 30% smartphone chipset market share. Dimensity is its flagship chip.
- Apple M-series
- Snapdragon X Elite
- Cortex
- Memory management unit (MMU) translates virtual memory addresses into physical addresses.
- memory is stored in pages (blocks).
- translation lookaside buffer (TLB) caches virtual to physical addresses.
- Virtualization
- A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) runs virtual machines.
- Type 1 is native or bare metal, while Type 2 is hosted inside an OS.
- Hardware-assisted virtualization: trap-and-emulate for privileged instructions.
- x86 virtualization
- Intel virtualization (VT-x) adds Virtual Machine Extensions (VMX) instructions.
- Extended Page Tables (EPT) for Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) or nested paging.
- virtual machine control structure (VMCS) shadowing for nested virtualization.
- AMD-V
- A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) runs virtual machines.
- Intel Centrino Wi-Fi adapter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Semiconductor_packages
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uninterruptible_power_supply
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One_Watt_Initiative
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AC_adapter