Chemistry
Matter
Periodic table
- Valence electrons determine bonding
- Molecular/molar mass
- Atomic radius: decreases across
- There’s some debate about what defines the f-block.
Bonding
- Two atoms can bond only if bonding results in a lower energy configuration.
- Thus, forming a bond releases energy, and it takes energy to break a bond.
- Bond strength = how energetically favorable the bond is.
- Shorter bonds are stronger due to greater nuclear attraction.
- Smaller atoms tend to form stronger bonds.
- Multiple bonds (double or triple) are stronger than single bonds due to greater electronic overlap.
- Shorter bonds are stronger due to greater nuclear attraction.
- Bond length minimizes energy–a tradeoff between nuclear repulsion and electron orbital overlap.
- An ionic bond involves complete electron transfer from the metal to the nonmetal, leading to electrostatic attraction between charged ions.
- Very strong.
- Polar solvents like water can dissolve ionic compounds like salt via ion-dipole attraction.
- Solid crystals are not conductive since the electrons are trapped in the lattice by electrostatic forces.
- In covalent bonds, atoms share electrons via orbital overlap. Polar covalent bonds have more ionic character. Nonpolar bonds are weaker.
- Metallic bonds involve a sea of delocallized electrons. Conductive.
- Determines hardness, malleability.
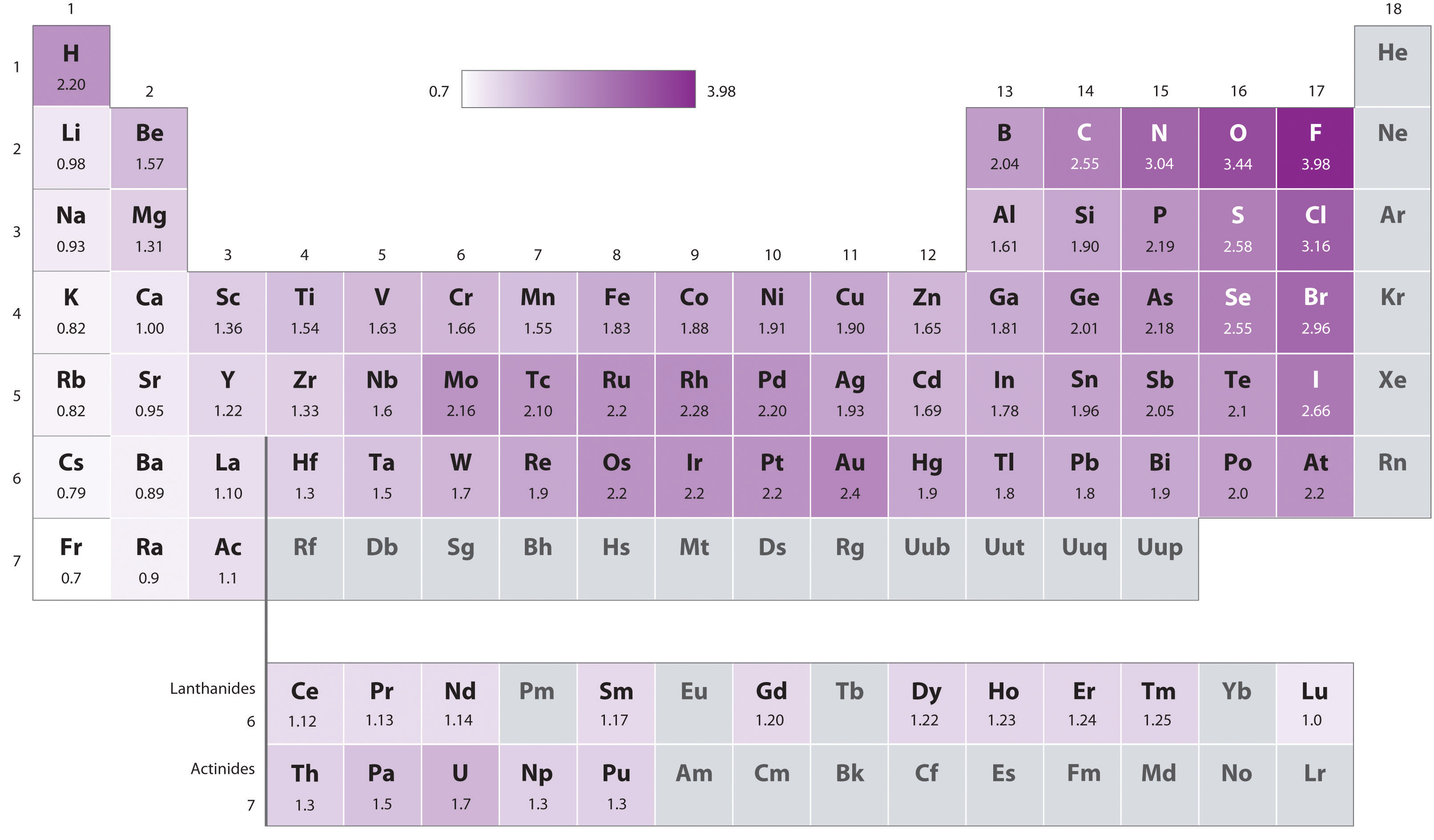
Electronegativity (EN) is how strongly an atom attracts electrons. F is the highest at 4.
- Decreases down due to shielding.
- Pauling EN is the most common. A heteronuclear AB bond energy is higher than the average homonuclear bonds AA and BB due to a higher electronegativity difference between them: \(E_d(AB) = \frac{E_d(AA)+E_d(BB)}2 + (\chi_A-\chi_B)^2 eV\).
- Ionization energy (IE) is the energy required to remove one electron.
- 1 eV * Avogadro’s number = 100 kJ
- Hydrogen: 1312.0 kJ/mol
- Lithium: 513.3 kJ/mol
- Electron affinity (EA) is the energy released when an electron is added.
- Reduction potential E° is the volt change from gaining an electron. Relative to the SHE.
- A positive reduction indicates that gaining electrons is favorable.
- Convert potential to molar energy: ΔG° = nFΔE° = -E_I
- charge number n and Faraday constant F = 96,485 C/mol.
- Taken at a 1 M electrolyte concentration. Also standard temperature and pressure (STP, 25 °C, 1 atm)
- Often battery potentials are relative to Lithium, which is more reducing, with a standard electrode potential of -3.04 V. Empirically, a -1.4 V offset is more accurate (choice of electrolyte, electrode material, surface states).
- Reduction is defined differently for 2H+ + 2e- -> H2 vs. F2 + 2e- -> 2F-
- lumen, wiki, Macmillan
- Mulliken EN = (Ionization Energy + Electron Affinity) / 2
- Allen EN = average energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom
- Allred-Rochow EN = effective nuclear charge and the covalent radius.
- Sanderson EN = average ionization energy and electron affinity.
- Reduction potential correlates inversely with electronegativity.
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic-chart-elements/ionization-energy.htm
Representations
- Molecular formula: composition
- Structural formula: connectivity
- Ball-and-stick: 3d positions
- Spacelectronfilling: overall shape
Lewis structures describe bonding using electron dots
- electron pair or Lewis pair are two electrons that occupy the same molecular orbital with opposite spins.
- Octet rule
- Shared = Needed - Available
- HONC rule: HONC atoms need 1234 electrons respectively.
- Exceptions:
- empty orbital (B, Be, Xe, Al)
- expanded octet due to d orbitals (P, S, I)
- free radicals
- Formal charge: stable when minimized or on EN elms
- Resonance: delocalized electrons, fractional bond order
- Hybrid more stable than any resonance form b/c it minimizes charge diffs
Most bonds are polar covalent
- Atoms differ in EN and electron density, creating an electric dipole
- Polar molecules have asymmetric polar bonds or lone pairs
- Molecular geometry minimizes VSEPR, based on steric number
- Bond angles explain why only certain cyclic molecules exist
Orbitals describe electron location
- Electronic configuration
- Hybrid orbitals form when the orbitals of an atom are mixed
- Have large front lobes and small back lobes
- sp hybrid linear, sp^2 trigonal, sp^3 trigonal planar
- Filled hybridized orbitals create lone pairs
- Nonhybridized bonds create pi bonds
Ideal gas law: PV = nRT
- Avg v = sqrt(3RT/m)
- nonideal for high IMF, large molecules, high P, or low T
- van der Waals eqn adds correction coeffs
- Dalton’s law (1803). In a mixture of ideal gases, the total pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of each gas.
- Raoult’s law. The vapor pressure above a mixture of liquids is the sum of the pure vapor pressures, weighted by their mole fraction.
Liquids
- Equilibrium, partial/vapor pressure
- High for high v/T, weak bonds, not affected by other gases
- bp is the T at which vp = 1 atm
Intermolecular forces
- I-D and D-D stronger than ID-ID
- H-bonds are most polar = strongest D-D
- Donor: H bonded to FON (Cl is too large = low e density)
- Acceptor: EN atom, may or may not be bonded to H
Solutions
- Solubility based on polar vs nonpolar due to IMF strength
- Electrolyte: dissociates, conductive
- Acid: creates excess hydrogen
- At high T, water pH < 7 but is still neutral
- Concentration measured in molarity or pH
- Adding a solute increases the boiling point and decreases the freezing point of the solvent.
Solids
- Polymers
- Branching = less dense, weaker bonds
- Coils = stretchy
- Charged = ionic bonding = absorbent
- Layers = soft/brittle
- Interstitial subsitutions increase hardness
Reactions
Reactions are collisions that exchange electrons/ions/atoms
- Precipitation and acid-base reactions swap ions
- Oxidation loses electrons (or gains H+), and gains energy. Reduction gains electrons or a full H. OIL RIG. Redox reactions balance oxidation states.
- Net Ionic Equations omit spectator ions, can be “no reaction”.
- Limiting reagent determines yield.
Rates are determined by concentration or pressure for the rate-limiting step.
- Instantaneous rate =
k [products]/[reactants] - k depends on T and activation energy
Reversible reactions are equilibria
- Equilibrium constant
K = [products]/[reactants]measures extent - Don’t include liquids or solids
- Strength of acid measures ability to dissociate
- High Ka for strong, polar bonds and stable/resonance conjugate base
- Ka * Kb = Kw = 10electron14: Weak acids have stronger conjugate bases
Le Chatelier’s principle: equilibria shift to reduce stress
- Color of an indicator depends on HA or A-
- Color of a transition metal cation depends on the preferred ligand
- Endothermic reactions are faster at higher T
Acid-Base Titration
- ICE table
- Special case: Henderson-Hasselbach:
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]).` - Halfway to equiv: pH = pKa
- Buffers resist changes in pH
- Equivalence point is where moles acid = moles base
- Solutions with same pH can have different eq. pt
- pH at equiv depends on whether acid or base is stronger
- Endpoint is where indicator changes color, which should be close
Solubility is the equilibrium concentration
- Reaction quotient
Q = [A (aq)], compare toKs = [A (aq)(eq)] - Under/super-saturated solutions are not at equilibrium, exothermic!
- Henry’s Law: `[dissolved gas]`` increases with partial pressure, S = KH * P
- Trends: High KH for high IMFs, low T
- Amphiphilic molecules can form micelles, liposomes, bilayers
- Supercooling due to lack of nucleation sites for ice crystal formation.
Solubility product Ksp
- Common Ion Effect decreases solubility
Separating Mixtures
- A (solute 1) ↔︎ A (solute 2), so
K_partition = [A (solute 1)] / [A (solute 2)]- E.g. octanol vs. water (polarity and solubility)
- Column chromatography: separate based on interaction
- Anion-exchange: tether cation, elute with anion, in order of charge, size
- Acidity: Elute with base
- Electrophoresis
- Vapor pressure
- Anion-exchange: tether cation, elute with anion, in order of charge, size
Energy
Exchange of energy between system and surroundings
- Most stable state has lowest potential energy
- Δq = mcΔT
- Phase transition: heat transferred without change in T
Energy is released when forming bonds
- E.g. C=O bonds during combustion
- Ionic bond energy is Ionic Attraction + Electron Affinity - Ionization Potential
- PE(r) for bonds
- 0 at infinity
- Decreases as atoms are brought close since each nucleus attracts electron of other atom
- Bond strength is maximum energy released, bond length is where this occurs
- Increases when atoms are brought very close as nuclear repulsion dominates
- Activation energy: energy needed to break reactant bonds
Heat of formation
- ΔHf° is at 1 atm
- ΔHf° for elements is 0
- ΔH of rxn = bonds broken (products) - bonds formed (reactants)
- not too accurate since bond energies affected by other atoms in molecule
- ΔH of rxn = enthalpy products - reactants
- Hess’ law: enthalpy is a state variable
Entropy
- 2nd law: total entropy of the universe always increases
- 3rd law: entropy is an absolute state variable
- entropy of ordered system at 0K is 0
- defined as S = K_B ln Ω, number of microstates at the same energy
- Change in entropy at constant T: ΔS = Δq/T
- Entropy of rxn = entropy products - reactants
- heat transfers from hot objects to cold objects
- Carnot efficiency of heat engine: 1 - Tl/Th
Gibbs Free Energy is the maximum work done by a reaction
- ΔG° = -RT ln K = ΔH° - TΔS°
- standard conditions, so 1 M and 1 atm of products/reagents
- some reactions favored/spontaneous at all T, others at high/low T
- ΔG = ΔG° + RT ln Q = -RT ln K/Q accounts for different concentration
Galvanic cell
- E.g. Zn/Zn²⁺//Ag⁺/Ag = Zn(s) + 2Ag⁺ → Zn²⁺ + 2Ag(s)
- RED CAT and AN OX: ANode OXidized (left), REDuced CAThode (right)
- Solid pieces connected by wire
- electron flows from anode to cathode (left to right)
- Salt bridge contains ions e.g. KNO3 to balance charge
- NO3- flows to the left
- Subtract reduction potential
- Reduction potential of a Standard Hydrogen Electrode defined to be 0
- ΔG° = nFΔE°
- Concentration cell: electron flows toward concentrated sol’n
- Nernst equation: ΔE = ΔE° - RT/nF lnQ
Light
Light is a particle and wave that transmits energy
- Wavelength λ * frequency ν = c
- Energy = hν (h = Planck’s constant)
- May also be viewed as photons of specific energy
- More packets = higher intensity
- Matter can absorb, reflect, or transmit light
- Color is the portion of the visible spectrum not absorbed
- Blackbody radiation: model emission spectrum of a material that absorbs all light
- Continuous spectrum determined only by T
Photoelectric effect: atoms eject photoelectrons when they absorb light
- Phototube: photons hit cathode => emit electron => detect V
- XPS: hemispherical magnet measures KE of electron and thus ionization energy
- Photoelectron spectrum: number electron emitted for each IE
- IE: need minimum ν, not minimum # to emit
- KE = E of photon - IE
- Subshell model: photoelectron specturm shows subshell energies
- stable subshells have higher IE, outer subshells have lower IE
- 1s for LiO2 has higher binding E since the 2s electron is lost
- #electron emitted determined by #electron in the subshell
- Electronic configuration and noble gas shorthand
- stable subshells have higher IE, outer subshells have lower IE
Spectroscopy: measure absorbance at different λ using monochromator
- Line spectra: electron transitions absorb or emit a discrete amount of energy
- energies that do not match a transition are ignored
- Absorption spectroscopy
- Beer’s Law: A(λ) = abC (molar absorptivity, path length, concentration)
- Absorbance A = -log Transmittance (% not absorbed)
- IR absorption can identify samples based on bonds
- C-H stretch more energy/lower λ than C-H bend
- Beer’s Law: A(λ) = abC (molar absorptivity, path length, concentration)
- Emission spectroscopy: thermal excitation of electron (flame or plasma, atoms)
- Line spectra determine concentration of metal ion solution
- Rydberg formula predicts spectral lines for H and ions with one electron
- 1/λ = RZ² (1/n_f² - 1/n_i²)
- Z is atomic number, R = 1.097e7/m
- Secondary ion mass spectrometry: analyze ejected secondary ions with mass spec to determine surface composition.
Wave equations describe electron orbitals
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: can’t know position & momentum precisely
- Square of wave amplitude gives probability of finding an electron at a position
- Increasing energies lead to more nodes (plane/sphere where Ψ=0)
- Pauli exclusion principle: Four quantum numbers uniquely describe an electron
- 1st quantum number n: shell, average radius
- 2nd quantum number l: orbital shape/number of planar nodes (spdf..n-1)
- s spherical, p dumbbell-shaped, d has four lobes.
- 3rd quantum number m_l: orbital orientation (-l..l)
- 4th quantum number m_s: magnetic spin (±½)
- n-1 nodes, l planar nodes, rest are radial nodes
- Aufbau principle: lowest energy orbitals fill first
- Hund’s rule: electrons fill unoccupied orbitals before pairing
Density functional theory
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Electronic_structure_methods
Molecular orbital theory - Valence orbitals overlap in two ways
- Bonding orbital: in-phase, lower energy, higher internuclear density
- Antibonding orbital*: destructive interference, internuclear node
- Bond order is (electron in bonding - antibonding)/2
- Positive order: releases energy, bond will form
- Paramagnetic if there are unpaired electron, otherwise diamagnetic
- Overlap is best between orbitals of similar size and energy
- highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)
- Koopmans’ theorem: first ionization energy is the negative of the HOMO energy

Sigma bond (σ bond): orbitals aligned along internuclear axis
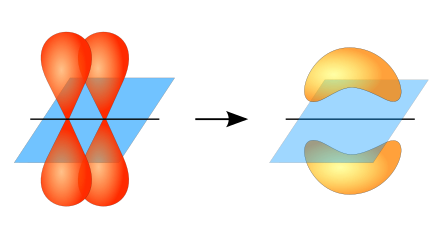
pi bond (π bond): lateral overlap, responsible for double and triple bonds.
Surface science
- Heterogeneous catalysis
- Hydrogenation on nickel, palladium or platinum.
- Haber process for producing ammonia: N2 + 3 H2 ⇌ 2 NH3
- Langmuir adsorption model
- Low-energy electron diffraction determines surface structure of single-crystalline materials. A collimated beam of low-energy electrons at 100 eV hit the surface and form a diffraction pattern of spots on a fluorescent screen.
- Electrical double layer: adsorption of ions onto a charged surface.
History
- Gas laws
- 1662. Boyle’s law: gas pressure is inversely proportional to volume.
- 1780. Charles’ law: gas volume is proportional to temperature.
- 1774. Antoine Lavoisier demonstrates that chemical reactions conserve mass using sealed glass vessels.
- 1809. Gay-Lussac discovers that gases react at integer ratios.
- 1812. Avogadro’s law: equal volumes of gas contain equal numbers of molecules.
- 1659. Johann Rudolf Glauber produces potassium permanganate by fusing pyrolusite (MnO2) and K2CO3.
- 1761. Joseph Black discovers the latent heat, specific heat, and carbon dioxide.
- 1766. Henry Cavendish discovers hydrogen.
- 1775. Joseph Priestley discovers oxygen.
- 1805. Alexander von Humboldt and Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac discover that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume.
- 1808. Boron discovered by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis Jacques Thenard.
- 1811. Iodine discovered by Bernard Courtois.
- 1822. Critical point discovered by Charles Cagniard de la Tour.
1855. Fick’s laws of diffusion: flux proportional to concentration gradient. ∂φ/∂t = DΔφ.
1884. Svante Arrhenius proposes the theory of ionic dissociation and a hydrogen theory of acids, winning the Nobel Prize in 1903. He also develops the Arrhenius equation: rate constant k = A exp(-E / RT) for molar gas constant R and activation energy E.
Chemical kinetics: 1986 Nobel Prize.
- infrared chemiluminescence by John Polanyi.
- crossed molecular beam experiments by Herschbach and Lee.
- 1935. Eyring equation: k = κ k_B T/h exp(-ΔG / RT) for Gibbs energy of activation ΔG, transmission coefficient κ, Boltzmann constant k_B.
1892. Chloralkali process: 2NaCl + 2H2O → Cl2 + H2 + 2NaOH.
1907. Bertram Boltwood pioneers uranium-lead dating, showing the first evidence that the earth is over 2 billion years old.
Ostwald’s rule: the less polymorph tends to crystallize first.
- Disappearing polymorphs may be caused by widespread tiny seed crystals.
1968. George Andrew Olah studies carbocations and stabilizes protonated methane in Magic Acid. 1994 Nobel Prize.
1980. Asymmetric chirally catalysed oxidation reactions like (Sharpless epoxidation, Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation, Sharpless oxyamination) by Karl Sharpless. Half of the 2001 Nobel Prize.
1977. Asymmetric hydrogenation by William Knowles and Ryoji Noyori. Half of the 2001 Nobel Prize.

2002. Click chemistry uses stereoselective, high yield, wide scope reactions. Copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Karl Sharpless and Morten Meldal, 2/3 of the 2022 Nobel Prize.
2003. Bioorthogonal chemistry uses small reactants and biological conditions. Carolyn Bertozzi, 1/3 of the 2022 Nobel Prize.
- Propargyl group: R-C-C≡C
An azeotrope is a mixture which has the same composition when distilled. For example, aqueous ethanol can only be distilled to 95.63% concentration. It is usually the mixture with the minimum boiling point.
A fractionating column allows mixed vapors to cool, condense, and vaporize in repeated cycles which improve separation. A Vigreux column is a glass tube with internal downward-facing cups that act as theoretical plates where vapor condenses and drips down.
Reflux distillation increases separation: condensate flows down from the top of the fractionating column and cools and condenses upflowing vapors.
Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center
Chemical engineering
- 500 BC. Ammonia for washing, fixing dyes, removing rust, and removing hair from hides. Produced via fermentation of urine.
- 500 BC. Sulfur is available in native form, such as 石硫黄. In 200, China extracts sulfur from pyrite FeS2. Elemental sulphur burns to SO2 gas.
- Limestone is calcium carbonate CaCO3.
- Potash (potassium carbonate K2CO3) created by leaching plant ashes in a pot, mainly used as a fertilizer.
- Soda ash (sodium carbonate) created by leaching plant ashes from sodium-rich soils.
- Quicklime (calcium oxide CaO) produced by thermal decomposition of CaCO3 at 1000 °C.
- Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) produced by hydrating CaO with water. pH 12. Used as lime mortar and lime plaster.
- Caustic potash (KOH): Ca(OH)2 + K2CO3 → 2 KOH + CaCO3 (insoluble).
- 1300. Lye or caustic soda (NaOH) by leaching a mix of sodium carbonate and calcium oxide. By Arabic and European soap makers.
- 1300. Sulfuric acid (“oil of vitriol”), nitric acid HNO3, and aqua regia by medieval alchemists like pseudo-Geber.
- Sulfuric was made by heating vitriol (hydrated metal sulfate) in a retort (a container with a downward-pointing condenser), or by heating sulfur with saltpeter (potassium nitrate).
- Alchemical symbol
- 1600. Hydrochloric acid HCl produced by heating vitriol and salt.
- 1625. Johann Glauber discovers sodium sulfate, a relatively safe laxative.
- 1735. Georg Brandt discovers cobalt.
- 1749. Sulfuric acid bleaches cloth in four months (versus 18 months for sour milk). Lead chamber process by John Roebuck scales production by using lead lining instead of glass vessels.
- 1799. Charles Tennant produces 10,000 tons of bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite) by reacting chlorine with dry slaked lime.
- 1818. Hydrogen peroxide H2O2 discovered by Louis Jacques Thenard, oxidizing HCl with BaO2. Now made via the anthraquinone process.
- Barium sulfate BaSO4 occurs as barite.
- Barium sulfide BaS (1600) produced by heating BaSO4 and carbon.
- Barium carbonate BaCO3 occurs as witherite. BaS + H2O + CO2 → BaCO3 + H2S.
- Barium oxide BaO: BaCO3 → BaO + CO2.
- Barium peroxide BaO2: 2 BaO + O2 ⇌ 2 BaO2 at 500 °C.
- 1822. Bonnington Chemical Works distills coal tar to separate naphtha for waterproof fabrics. It soon makes pitch oil or creosote, pitch, lampblack, and sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride).
- 1839. Vulcanized rubber from heating with sulfur by Charles Goodyear.
- 1850. Leblanc process. 100,000 tons of sodium carbonate produced in Britain. Used in glass, textile, soap, and paper. Major source of air pollution. Solvay process in 1861 is cheaper.
- 1856. William Henry Perkin invents mauveine, the first synthetic dye, from aniline derived from coal tar.
- 1867. Dynamite by Alfred Nobel.
- 1870. John Wesley Hyatt commercializes celluloid, the first plastic, made from nitrocellulose and camphor. It was a substitute ivory for billiard balls, false teeth, and piano keys.
- 1874. Sulfite process for wood pulp of pure cellulose.
- 1884. Smokeless powder.
- Flash powder: usually potassium perchlorate oxidizer and aluminium powder.
- 1892. Chloralkali process produces sodium hydroxide or other bases from electrolysis of brine.
- 1912. Cellophane is regenerated cellulose. Water resistant and semipermeable.
- 1930. kraft process for wood pulp makes stronger paperboard.
- 1913. Haber-Bosch process produces ammonia fertilizer. Now produced at 100 million tons a year. Plus 40 million tons a year of phosphate fertilizer, applied at 32 kg per hectare, for 8 tons of grain. Haber 1918 Nobel Prize. Bosch half of the 1931 Nobel Prize.
- 1913. Bergius process for hydrogenating high-volatile bituminous coal into liquid fuel at 400°C and 20 MPa. Half of the 1931 Nobel Prize.
- Processes: dissolution, mixing, distillation, crystallization
- Continuous stirred-tank bioreactor assumes perfect mixing.
- Plug flow reactor assumes no boundary effect or mixing.
- Laminar flow reactor is a long tube.
- Oscillatory baffled reactor achieves plug flow, mixing each section using baffles.
- A packed bed increases contact between phases.
- Raschig ring is a short ceramic, glass, or metal tube.
- Structured packing uses corrugated metal or PTFE plates to maximize fluid spreading.
- Activated sludge uses bacteria and protozoa to oxidize wastewater. The floc (sludge) then settles and is removed.
- Sequencing batch reactors (SBR): fill, react (mix and aerate), settle, decant
- Moving bed biofilm reactor mixes high surface area HDPE carriers in the tank.
- Membrane bioreactor for filtration.
1831. Contact process. Oxidize SO2 with V2O5 catalyst to SO3, which forms sulfuric acid in water.
burn hydrogen sulfide
selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitrogen oxides (NOx) with ammonia (NH3)
honeycomb DeNoxing catalyst
Batteries
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_battery
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daniell_cell
1899 First alkaline battery
1957 Modern alkaline battery: 1.5 V cell with zinc anode (negative) and MnO2 cathode. Potassium hydroxide electrolyte. Fully discharged when voltage drops to 0.9 V.
- anode oxidation: Zn + 2OH- → ZnO + H2O + 2e-
- prevent hydrogen gas from Zn + 2 H2O -> ZnO + H2.
- cathode reducation: 2MnO2 + 2H2O + 2e- →2MnO + 2OH-
- A rechargable battery cathode adds barium sulfate to prevent the formation of insoluble manganese compounds, and catalyst to recombine hydrogen gas. Also a stronger barrier to prevent penetration by zinc crystals.
1989 Nickel-metal hydride battery (NiMH). 1.2 V cell.
- H2O + M + e− ⇌ OH− + MH.
- Ni(OH)2 + OH− ⇌ NiO(OH) + H2O + e−.
Batteries are neutral at 50% charge and 25 C (78 F). Battery degrades when Li is plated/deposited on the anode as Solid Electrolyte Interface (SEI), and cannot intercalate (reversible inclusion without affecting the layered anode structure). Too cold/increased impedance or fast charging -> low anode potential -> plating. Too hot -> Mn dissolution + SEI.
Li batteries have an energy density of 150-300 Wh/kg and power density over 300 W/kg. (278 Wh = 1 MJ) Gasoline is 12,700 Wh/kg.
Lithium-ion battery produces voltage when Li+ move from anode (-) to cathode (+). There is a separator between the two that allows Li+ but not e-. The sheet is rolled up in a cylindrical battery. Portable devices use lithium cobalt oxide (cathode) and graphite (anode). Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP, 3.2 V) 2170 cells are cheaper. Tesla used Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) cathodes in the 2170 and 4680 sizes. Size is diameter and length in mm.
CATL produces Tesla’s lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which can charge to 100 percent and has no nickel or cobalt. They are in prismatic (rectangular) cells.
- 18650 battery: 18 mm diameter, 65 mm length.
Flow batteries have a density up to 35 Wh/kg and cycle efficiency up to 80%.
Battery sizes.
- Single-cell: AAAA, AAA, AA, C, button cell.
- 9V battery.
Chemicals
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Petroleum_industry
Oxygen tanks deliver 2 L/min to 10 L/min, at 150 atm. With a conserver, tanks last around 6 hours.
Oxygen concentrators use pressure swing adsorption to remove nitrogen. Zeolites are molecular sieves that selectively bind to nitrogen at high pressure.
Zeolites are also used to soften water in laundry detergent. They capture calcium and magnesium ions that would otherwise precipitate and interfere with the detergent.
Laundry detergent contains fluorescent optical brighteners.
Oxygen is generated by electrolysis of water or by burning lithium perchlorate
https://www.nasa.gov/johnson/HWHAP/advanced-oxygen-generation
https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-markets/market-snapshots/2018/market-snapshot-how-does-refinery-turn-crude-oil-into-products-like-gasoline-diesel.html
Coal
- Forms from peat, partially decayed vegetation often made of peat moss.
- Lignite is compressed peat. 15 MJ/kg and 25% carbon. Substantial water.
- Subbituminous coal: 20 MJ/kg, 35% carbon.
- Bituminous coal contains bitumen. 30 MJ/kg, >35% carbon. Most common.
- Anthracite has >90% carbon content. Energy dense, hard, lustrous.
- Coke is produced by heating coal or oil without oxygen at 1,000 °C.
- Coal tar is a creosote formed from pyrolysis of coal, which helps treat head lice and psoriasis.
- Syngas is carbon monoxide and hydrogen, usually made from methane: CH4 + H2O → CO + 3 H2.
- Producer gas or water gas was made by blowing steam over coke. 10% as efficient as modern syngas method.
- Coal gasification generates electricity and produces coal gas.
Bitumen, pitch, or asphalt is near solid. Used to bind aggregate particles. Occurs naturally as tar sands and oil sands. Also used in asphalt shingles, roofing felt, or tar paper for waterproofing.
Wax contains higher alkanes and lipids that are solid near room temperature.
Crude oil
- Contains benzene, a known carcinogen with a sweet smell.
- A 42 gallon barrel typically produces 20 gal gasoline, 12 gal diesel, 4 gal jet fuel.
- Heavy crude oil is dense and viscous with higher molecular weights. Higher refining cost and often high sulfur content.
- Cracking splits hydrocarbons at high heat.
- Coker cracks residual oil to petroleum coke.
- Green coke produced below 900 K.
- Calcination at 1300 °C removes volatile matter and sulfur. Anode baking produces anode coke for the metal industry.
- Crude oil assay
- API: American Petroleum Institute gravity is inverse of specific gravity, with water at 10 gravity.
- Sweet oil has less than 0.5% sulfur and is more valuable than sour oil.
- Saturate, Aromatic, Resin and Asphaltene (SARA) in increasing polarity. Saturated hydrocarbons. Resin is soluble in heptane and asphaltene is only soluble in toluene.
- Light crude oil has around 40 API.
- West Texas Intermediate (WTI) traded on the NY Mercantile Exchange.
- Brent Crude from the North Sea.
Diesel fuel boils between 200 and 350 °C. 9-25 carbon atoms. Burns at 750 °C.
- Diesel exhaust includes beryllium compounds, a known carcinogen. Also mercury and chromium, possible carcinogens.
Kerosene is C9-16. Boils between 150 and 275 °C, 0.8 g/cm3, 45 MJ/kg.
- Coal oil is kerosene-like shale oil once used for lighting.
- Jet fuel is C8-C16. Jet B is used in Alaska: C5-15 which freezes at −60 °C.
Gasoline or petrol is C4-C12.
- Engine knocking is premature detonation under pressure without a spark. A lower autoignition temperature reduces knocking.
- Octane rating is the percent of octane in an octane-heptane mixture with equivalent knocking.
- Avgas is 100 octane with 2 g tetraethyl lead per gallon to reduce knocking. Dyed blue. Lead-free 91 octane avgas can be used in piston aircraft.
- Catalytic converter contains platinum.
- Two-way: 2CO + O2 → 2CO2 and hydrocarbons + O2 -> CO2 + water.
- Three-way: also reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) to nitrogen.
- C + 2NO2 -> CO2 + 2NO
- 2CO + 2NO -> 2CO2 + N2
- Used motor oil contains petroleum base stock with benzene, arsenic, cadmium, chromium.
Heavy naphtha is C6-C10. Boils between 90 °C and 200 °C.
Light naphtha is C5-C6. Liquid, boils between 30 °C and 90 °C.
- Natural gasoline is C5-C6 condensed from natural gas. Emits 5 lb CO2/L. 80 API. Low octane rating.
Liquified petroleum gas (LPG) is C3-C4, propane and butane.
Natural gas processing removes CO2, hydrogen sulfide, mercury, and condensate to achieve pipeline quality.
- Natural gas is C1-C2, methane and ethane.
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG) condenses gas at −162 °C, reducing volume to 1/600.
- Natural gas contains up to 1% helium and is the main source of helium.
- Natural gas condensate is liquid. 3-6 carbon atoms with specific gravity between 0.5 to 0.8.
- Fischer-Tropsch process produces liquid hydrocarbons from syngas at 150 °C with metal catalyst.

Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) reduces NOx to nitrogen using ammonia and catalyst.
Catalytic reforming creates aromatics, commonly known as BTX (benzene, toluene and xylene). It takes hydrocarbons with boiling points between 60 and 200 °C, and heat them at 500°C and 10 atm with hydrogen gas and platinum chloride or rhenium chloride catalyst. Aromatics are extracted with diethylene glycol or sulfolane solvent. Benzene can be separated by distillation.
p-xylene is used create terephthalic acid, a PET precursor.
Topics
Lab equipment
- 1855. Bunsen burner. Air flow and temperature can be increased via an adjustable collar at the base. Low temperatures produce a dirty luminous flame due to soot particles heated to incandescence.
- Beaker
Corrosion is oxidation of metal.
- Rust (iron oxide) formed via Fe → Fe2+ + 2e−. Oxygen electron acceptor.
- Anaerobic corrosion
- Abiotic: Fe + 2 H2O -> Fe(OH)2 + H2
- Sulfate-reducing microorganism uses sulfate as an electron acceptor.
- SO4(2-) + 10 H+ + 8e- -> H2S + 4H2O.
- Ferroxyl indicator solution detects Fe2+ ions and hydroxyl ions as blue and pink patches
Oxygen has two unpaired electrons, each with spin 1⁄2.
- Triplet oxygen is the ground state of oxygen. The electrons are unpaired, resulting in total spin S = 1, forming a diradical (two unpaired electrons).
- Singlet oxygen is when the electrons are paired, resulting in total spin S = 0. More reactive.
4 gas monitor: oxygen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
- Chlorine, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen cyanide, amines, nitrites, ozone, phosphine, and sulfur dioxide are also hazardous.
- Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) uses a catalytic bead with platinum wire. Oxidation increases temperature causing a voltage imbalance detected in a bridge circuit.
- Sensor poisons like silicone, lead, sulfur compounds, and lubricants can encapsulate the bead. Hydrocarbon infrared sensors are immune.