Contents
- Prehistory
- Neolithic Revolution
- Asia
- Japan
- Colonialism in Asia
- China
- Modern Asia
- India
- Egypt
- Middle East
- Islam
- Ottoman Empire and oil
- Modern Middle East
- Europe
- Classical mythology
- Greece
- Rome
- Early Middle Ages, 500 - 1000
- High Middle Ages, 1000 - 1300
- Ottoman Empire, 1300-1700
- Early modern period, 1500
- French Revolution, 1792
- World War I
- Modern Europe
- America
- Geography
- US Government
- Indigenous
- Colonialism
- American Revolution
- Westward Expansion
- Civil War, 1861 - 1865
- Battle of Gettysburg
- Grant vs. Lee
- Post Civil War
- Native-American relations
- Reconstruction, 1865 - 1877
- Gilded Age, 1877 - 1896
- Progressive Era, 1896 - 1917
- World War era
- Cold War
- Civil Rights
- Modern US
- Internet culture
- Mexico
- South America
- Africa
- Law
- Education
- Literature
History
Prehistory
4.6 Ga Earth forms.
Precambrian eons:
- Hadean eon: lots of asteroid strikes. Water and life forms.
- 4 Ga Archean eon: single-celled life and 3.5 Ga photosynthesis by cyanobacteria, which form stromatolites (microbial mats), the earliest fossils.
- 2.5 Ga Proterozoic eon. Eukaryotes and multicellular life.
- 2.4 Ga Great Oxidation Event to around 5% of present levels, changing the atmosphere from reducing to oxidizing and causing a mass extinction of microbial mats.
- 2.2 Ga Yarrabubba impact structure in Australia, the oldest known crater.
- 2 Ga Vredefort impact structure, the largest crater.
- 1.8 - 0.8 Ga Boring Billion with euxinic water (low oxygen and high H2S). Sulfate reducing bacteria.
- 1 Ga Grenville orogeny. Two continental plates collide with Laurentia (now North America).
- 800 Ma Neoproterozoic oxygenation event.
- 635 Ma Ediacaran period with Avalon explosion.
539 Ma Phanerozoic eon: first plants and hard-shelled creatures
- Paleozoic era
- Cambrian explosion
- Ordovician period.
- 445 Ma Silurian period. The Andean glaciation causes the Late Ordovician mass extinction.
- Devonian period.
- 400 Ma Caledonian orogeny eventually forms Rodinia.
- 372 Ma Late Devonian extinction of marine life caused by ocean anoxia.
- 359 Ma Carboniferous period. Oxygen levels are high. Amphibians become the dominant land vertebrates. Many coal beds. Late Paleozoic icehouse.
- 300 Ma Pangaea forms from the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana. Forms the Central Pangaean Mountains: Variscan orogeny for Europe, and Alleghanian orogeny for America.
- 299 Ma Permian period. Synapsids are the dominant land creatures.
- 252 Ma Mesozoic era. The Permian-Triassic extinction event is the largest known. Massive flood basalt volcanic eruptions create the Siberian Traps and release sulfur dioxide and 10 gigatons of carbon dioxide, warming the planet and acidifying the oceans. Atmospheric CO2 levels rise from 400 ppm to 2,500 ppm. Predated by the Capitanian extinction caused by eruptions creating the Emeishan Traps.
- Triassic period. Pangaea starts to break apart, and reptiles, especially archosaurs (crocodiles and pterosaurs) arise as the dominant land creatures.
- 201 Ma Jurassic period. The Triassic-Jurassic extinction event due to the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP) flood basalts. Most crocodilians go extinct and the rest become aquatic. Dinosaurs are the dominant land creatures, living among conifers and ferns. Pterosaurs fly and ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs swim. Birds evolve from theropod dinosaurs. Crabs, lizards, sharks, and rays appear.
- 145 Ma Cretaceous period, named for beds of chalk deposited by the shells of marine invertebrates. Tyrannosaurus rex, Triceratops, Velociraptor. Quetzalcoatlus, the largest flying animal discovered, with a 33 ft wingspan.
- 66 Ma Cenozoic era. The Chicxulub asteroid vaporizes rock, blocking the sun for ten years and causing all non-avian dinosaurs to go extinct, leading to the age of mammals.
- Paleogene period.
- 34 Ma Late Cenozoic Ice Age, the ongoing icehouse period of slightly cooler temperature and continuous polar glaciers.
- 23 Ma Neogene period
- 10 Ma The chimpanzee-human last common ancestor, a hominin.
- 4.5 Ma-1.5 Ma Australopithecus is the first bipedal hominin. Lucy is the most complete specimen.
- 2.7 Ma Great American Interchange once Panama forms.
- 2.6 Ma Quaternary period. Quaternary glaciation has an Arctic ice cap.
- Pleistocene epoch.
- 1 Ma Mid-Pleistocene Transition. Glacial cycles change from a 41 kyr period to a 100 kyr period. Driven by astronomical cycles.
- 2 Ma-100 ka Homo erectus expands out of Africa.
- 600 ka-200 ka Homo heidelbergensis evolves from H. erectus.
- 300 ka-40 ka Neanderthals and Denisovans are extinct sister species. They interbreed with modern humans around 50 ka and contribute several percent of the genome.
- 115 ka-12 ka. Ice Age or Last Glacial Period.
- 29 ka Last Glacial Maximum or marine isotope stage 2. The Laurentide Ice Sheet covers Canada through New York and gouges out the Great Lakes.
- 15 ka The Holocene glacial retreat or Last Glacial Termination or Termination I causes meltwater pulse 1A, a 50’ rise in sea level over 500 years.
- 12.9-11.7 ka. Younger Dryas was a stadial (cooling) event.
- 11.7 ka Holocene. Younger Dryas ends with a 20 °C increase and meltwater pulse 1B. Marine isotope stage 1 is the warm interglacial where deep sea core samples contain low oxygen-18.
- Pleistocene epoch.
- Paleogene period.
300 ka Homo sapiens evolves from H. heidelbergensis in the horn of Africa.
- Mitochondrial Eve is the most recent common ancestor for modern humans.
- 150 ka. mt-DNA haplogroup L0 (present Khoisan) in southern Africa diverges from populations in central Africa.
70 ka. Haplogroup L3 expands out of Africa, following a Southern Dispersal that crosses the Red Sea, follows the southern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and continues to India, Southeast Asia (Sundaland), and Oceania. It splits into haplogroups M and N. M is the majority in Asia. - Earlier Homo sapiens migrations in 200 ka eventually disappeared.
55 ka. Cro-Magnon or European early modern humans are the first Homo sapiens to settle in Europe, with haplogroup N. N has a number of descendant groups, with R being the largest.
15 ka. Peopling of the Americas from the mammoth steppe (present Siberia) across the Bering land bridge to Alaska.
In the Stone Age (3.4 Ma to 7 ka), stone tools are widely used. It is divided into the paleolithic, mesolithic, and neolithic. Hunter-gatherers move in small migratory groups with temporary shelters.
- 1 Ma control of fire and cooking
- 40 ka ground or polished stone axes and adzes.
- 40 ka Cave paintings in Indonesia, spear throwers, domestic dog.
- 33 ka Gravettian archaelogical industry: spear tips, bow and arrow, Venus figurines in Europe.
The five technology modes:
- 3.4 Ma archaic humans knapped stones to form sharp edges, and also selected large anvils (Mode I, Oldowan Industry).
- 1.7 Ma first biface (hand axe, cleaver) (Mode II, Acheulean industry).
- 160 ka sharp flakes from prepared cores (Mode III, Mousterian industry).
- 50 ka widespread long blades (Mode IV, Aurignacian industry).
- 17 ka composite tools with microliths, small flint edges, mounted on a wood or bone handle (Mode V)
20 ka Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age: microlithic tools, domestic dogs. Starts soon after the Last Glacial Maximum.
- Earliest pottery at Xianren Cave.
- Desert kites are low converging walls in Asia used to trap and kill gazelles.
Neolithic Revolution
Society transitions to agriculture and settlement. Increased division of labor, free time, trade, and writing. Herding, textiles, timber longhouses, grand burial mounds. More abundant food, but less balanced diet and more disease.
- 13 ka Natufian culture in the Levant cultivates rye. Gradually transitioned from a group of sedentary hunter-gatherers.
- 12 ka Pre-Pottery Neolithic succeeds the Natufian culture.
- Petroglyph rock carvings.
- Göbekli Tepe pillars in Turkey are the oldest known megaliths. Carved with humans, clothing, and wild animals.
- Jericho is the oldest fortified city, with 12’ walls.
- 8000 BC Tower of Jericho is the second-oldest tower known, at 28’.
- 9ka Jarmo in Iraq
- 11 ka Domesticated figs at Gilgal I near the Jordan river.
- Domestication of goats, pigs, sheep, and cows.
8000 BC Netherlands canoe
5000 BC Copper age or Chalcolithic: copper smelting in Serbia.
- 3200 BC Otzi the Iceman is the oldest European mummy. Killed by an arrow in the Alps.
3300 BC Bronze age features the smelting of copper and tin.
3300 BC Carnac stones in Brittany, France contain alignments (rows), dolmens (tombs), tumuli (burial mounds), and menhirs (standing stones).
3200 BC Irish Brú na Bóinne: passage tombs at Newgrange, Knowth, and Dowth.
2500 BC Stonehenge.
1200 BC Iron Age and Greek Dark Ages follow the Late Bronze Age collapse, which affected Egypt, Hittites, Babylon, Assyria, Mycenaeans, Cyprus. Possibly due to drought and raids by Sea Peoples. - 400 BC Tollund Man is a bog body and human sacrifice killed by hanging.
Celts had kings, druid religious leaders, warriors, and bards.
- 2800 BC Bell Beaker culture and Corded Ware culture.
- 2300 BC Únětice culture in the Czech Republic and Germany.
- 1600 BC Tumulus culture in Central Europe
- 1300 BC Urnfield culture in Europe
- 1200 BC Hallstatt culture is proto-Celtic, centered on Greece but reaching Britain. Uffington White Horse hill figure.
- 450 BC La Tène culture: Triskelion triple spiral pattern.
North America
3500 BC Mound Builders of the Ohio River.
1200 BC Pueblo culture: irrigation systems.
1000 CE Viking explorers briefly land at Newfoundland.
1050 CE Cahokia settlement of 25,000 people in Mississippi.
Civilization originates in Egypt (4000 BC), Sumer (4000 BC), Caral-Supe in Peru (3500 BC), Indus valley (3300 BC), Erlitou (1750 BC), and Olmec in Mesoamerica (1600 BC). It leads to writing, urbanization, the state, social stratification, and taxation.
Asia
Geography
- Eurasian Steppe in the north contains grassland.
- Steppe Route of 10,000 km dates to the paleolithic.
- West Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain.
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
- Himalayas
- Tibetan Plateau is in the rain shadow.
- The Yangtze river flows east from the Tibetan Plateau to Shanghai and Jiangsu on the East China Sea.
- Mount Everest is the tallest mountain at 8.8 km.
- Nepal: Southeast ridge is easier. South Base Camp, Khumbu Icefall has dangerous seracs (ice columns) and crevasses, Western Cwm (flat valley), Camp II, Lhotse face, Camp III, Geneva Spur (band of rock), Camp IV at 8 km, South Col (notch) death zone, South Summit, Hillary Step.
- Tibet and Northeast ridge: North Base Camp (5 km), North Col, Three Steps.
- Sherpa natives are experienced guides.
- 1953. First summit by Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay.
- Mongolia
- Gobi Desert in the south is the rain shadow northeast of the Himalayas.
- China
- Beijing
- Peking University
- The Forbidden City
- The Great Wall
- National Museum of China
- Chaoyang District is the central business district
- Northern
- Great Green Wall 三北防护林 is 500,000 square km of artificial forest planted to hold back the Gobi Desert.
- Southern
- Shanghai
- Huangpu River
- West bank: Old City, International Settlement, French Concession
- East bank: Lujiazui
- Hong Kong
- Hubei: Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River is the largest in the world.
- Kaifeng, Henan: Iron Pagoda
- Classical Gardens of Suzhou in Jiangsu includes the Humble Administrator’s Garden 拙政园 and the Canglang Pavilion 沧浪亭.
- Shanghai
- The Yellow River flows from Qinghai Province east to Beijing, Tianjin, and the Bohai Sea. The Bohai Sea is an inlet of the Yellow Sea, which forms the western coast of Korea.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grand_Canal_(China)
- Beijing
- Taiwan
- Taoyuan TPE airport.
- Korea
- Seoul: National Museum of Korea
- Incheon ICN airport.
- Thailand: Bangkok capital.
- Philippines: Manila capital.
- Sinigang is a sour and savory stew.
- Malaysia
- Singapore
Oceania
- Australia
- Sydney Opera House
- Bondi Beach
- Western Australia: Pilbara iron ore (100B), oil and gas (30B), gold (16B).
- Tasmania island at the southern tip.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Australian_Aboriginal_religion_and_mythology
- Rainbow Serpent
- Great Barrier Reef near Queensland.
- New Zealand incl. Cook Islands
- Melanesia: Fiji, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu
- Indonesia: Komodo island
- Makassar people established the first trade with Australia around 1850, for sea cucumber (“trepang”).
- Indonesia: Komodo island
- Micronesia: Guam, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, US Northern Mariana Islands, Palau
- US Naval Base Guam
- Polynesia: American Samoa, Samoa, Tonga, Tuvalu, French Polynesia (Tahiti), UK Pitcairn Islands
- kumara (sweet potato) is a staple.
- Rangi and Papa are the sky father and the earth mother. Their children live in a cramped darkness between their tight embrace until forest god Tāne separates them. Other children include war god Tū, water god Tangaroa, farming god Rongo, wild food god Haumia-tiketike.
- Maui is a trickster demigod. He and his brothers slow the sun Tamanuiterā by tying him up and beating him with his grandfather’s jawbone. Trying to become immortal, he becomes a worm and swims up the vagina of Hine-nui-te-pō, goddess of night, who crushes him to death with obsidian teeth in her vagina.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polynesian_mythology
Culture
- Chinese New Year 春节. Reunite with family, give red envelopes 红包 with cash.
- Lantern Festival 元宵節 is the full moon marking the end of Chinese New Year. Eat 元宵 (northern) or 汤圆 (southern), a boiled sticky rice ball with red bean filling.
- Chungyun 春运 is the largest annual migration as migrant workers and students return home for a month.
- Dragon dance 舞龙 uses poles. Lion dance 舞狮 to drive off nian beast 年兽.
- Labor Day on May 1.
- Mid-autumn festival 中秋節: eat moon cake 月饼
- National Day 国庆节 on December 1.
Chinese food
- Five-spice powder 五香粉: Star anise 八角, cloves 丁香, cinnamon 肉桂, Sichuan pepper 花椒, fennl 小茴香.
- soy sauce 酱油: fermented soybean, roasted grain, brine.
- 八大菜系.
- Chili oil: Lao Gan Ma 老干妈
- Northern food: mantou 面头, baozi 包子, jiaozi 饺子, bing 饼
- Chow mein 炒面 stir-fried noodles.
- Zhajiangmian 炸酱面: minced meat with sweet fermented soybean paste 甜面酱
- Lanzhou beef noodle soup 兰州牛肉面: clear broth 清炖, white radish, red chili oil, cilantro and garlic shoots, hand-pulled noodles 拉面.
- Peking duck with folded pancakes, cucumber, scallion, sweet bean sauce.
- tomato and scrambled eggs 番茄炒鸡蛋 with tomato wedges.
- Egg drop soup 蛋花湯: slowly pour beaten eggs into boiling broth at the end.
- Hot and sour soup 酸辣汤: egg, vinegar, white pepper, bamboo shoots, mushrooms, tofu skin, sesame oil, corn starch.
- Above the Qinling-Huaihe Line 秦岭淮河线
- Shandong (lǔ) 鲁菜: clear broth and creamy soups, braised abalone, fried sea cucumbers, sweet and sour carp.
- Southern China is subtropical and more hilly.
- Jiangsu 江蘇菜
- Anhui 徽菜: herbs, bamboo, mushroom.
- Sichuan 川菜: Sichuan pepper 花椒, mapo tofu 麻婆豆腐, Kung Pao chicken 宫保鸡丁, twice-cooked pork 回锅肉, fuqi feipian 夫妻肺片, malatang 麻辣烫, fermented 泡菜.
- douban jiang 豆瓣酱 is a fermented bean paste.
- Dandan noodles 担担面
- zha cai 榨菜: pickled mustard
- yuxiang 鱼香: douban jiang, soy sauce, sugar, vinegar, pickled chili.
- liangfen 凉粉: cold mung bean starch jelly with a savory sauce.
- Hunan (xiāng) 湘菜: Stinky tofu 臭豆腐 has indole.
- Zhejiang 浙菜
- Fujian (mǐn) 闽菜
- Guangdong or Cantonese (yuè) 粤菜: Hoisin sauce 海鲜酱, dim sum 点心 including rice rolls, lotus leaf rice, turnip cakes, congee, youtiao 油条. wonton 馄饨, char siu bao 叉烧包.
- Hot pot 火锅
- Tea: Dragon well longjing
1750 BC Erlitou civilization in the Yellow River valley. Chinese calendar 农历. Chinese ritual bronzes include ding 鼎 (tripod cauldrons) and gui 簋 (bowl with 2 or 4 handles).
- 2700 BC Majiayao culture with bronze knife
- 1600 BC Erligang culture.
The Xia dynasty is possibly the Erlitou.
chinese_mythology.md
1600 BC Shang dynasty 商. Concubine Daji was portrayed as a fox spirit who bewitches King Zhou.
- 1300 BC Pan Geng moves the capital to Yin.
- 1250 BC. Wu Ding 武丁 rules over fifty years.
- 1250 BC oracle bones are the earliest writing and earliest divination. They are pieces of ox scapula and turtle shell (plastron) which are cracked by heating and then interpreted. They are discovered in Yinxu, the last capital.
- 1100 BC. King Wen of Zhou 文王 leads predynastic Zhou. His son is King Wu.
- Six Secret Teaching 六韬 by Jiang Ziya 姜子牙.
- 1075 BC King Xin 帝辛 (derided as King Zhou 紂王) is the last of Shang. His prime minister and uncle Bi Gan 比干 criticizes his immoral behavior and gets executed.
1046 BC. Zhou dynasty 周. King Wu founds the Western Zhou and overthrows King Zhou at the Battle of Muye (present Henan). This is justified as the Mandate of Heaven 天命. The Western Zhou capitals are near Xi’an.
- 781 BC. King You 幽王 is the last Western Zhou king.
- 771 BC. Eastern Zhou dynasty is much weaker.
- 743 BC. Duke Zhuang of Zheng.
- The I Ching 易经 (Book of Changes) is traditionally credited to Duke Wen of Zhou 周公旦. It describes a noble person 君子, who is expected to excel in the six arts: rites 礼, music 乐, archery 射, riding 御, calligraphy 书法, mathematics 数. It includes eight trigrams bagua 八卦. I Ching divination uses 64 hexagrams, which are listed in the King Wen sequence. yin-yang 陰陽.
- Danqing 丹青 painting with cinnabar 丹砂 and azurite 青雘.
722 BC Spring and Autumn period. The Zhou dynasty devolves into warring lords. Jìn is a major state in modern Shanxi on the Yellow River, with Qin to its west (including modern Xi’an) and Qi to its east on the Bohai Sea. Chǔ is to its south on the Yangtze River. Wu is a minor state east of Chu on the East China Sea, with its capital near present Shanghai.
- Five Hegemons 五霸: sometimes a state is strong enough to maintain security.
- 700 BC. The Classic of Poetry 诗经 collects poems written in four-syllable meter, including many chengyu 成语 (classical idioms). Distinction of wen 文 wu 武, which are common surnames.
- 685 BC. Duke Huan 桓公 of Qi is hegemon. Dies 643 BC.
- 676 BC Duke Xian 献公 rules Jin to 651 BC.
- 657 BC. Li Ji Unrest 骊姬之乱. Xian’s concubine Li Ji frames his sons, causing Ji Chong’er and his advisor Jie Zhitui 介之推 go into exile.
- 651 BC. Xian dies, and Li Ji’s son Xiqi rules briefly before being killed by Jin general Li Ke.
- 650 BC. Duke Xiang of Song.
- 636 BC. Duke Wen of Jin is hegemon. He is born Chong’er and installed after Qin invaded Jin. Dies 628 BC.
- His advisor Zhitui hid in the forest on Mt Mian to avoid joining the corrupt court. Duke Wen orders a forest fire to make Zhitui come out, which kills Zhitui. Duke Wen commemorates Zhitui in the Cold Food Festival 寒食节 which becomes the Qingming Festival 清明节, 15 days after the spring equinox.
- 659 BC. Duke Mu of Qin rules. Expands the territory west in 627 BC.
- 633 BC. Chu attacks Song to its north.
- 632 BC. Jin defeats Chu at the Battle of Chengpu and becomes hegemon over other states.
- 613 BC. King Zhuang of Chu. Said to have asked about the Nine Tripod Cauldrons 九鼎, symbols of the mandate of heaven then held by King Ding of Zhou . 问鼎中原 means to have great ambitions.
- 597 BC. Battle of Bi. Zhuang defeats Jin.
- 589 BC. Jin trains the Wu army and teaches them to use chariots, leading Wu to ascend over Chu.
551 BC. Hundred Schools of Thought
- Daoism or Tao. Laozi 老子 writes Dao De Ching. He says 道法自然 “the dao follows nature” to live a simple and authentic life, in harmony with nature, having faith in the natural course of events. Mozi, Liezi are also influential.
- Five Precepts ban killing (even of insects), stealing, sex outside marriage, lying, and alcohol outside feasts.
- 900 CE. Dunhuang manuscripts.
- Confucius. Analects and Kongzi Jiayu (200 BC).
- The Chinese classics 典籍 include history 史, philosophies 子, and literary work 集. Four Books and Five Classics 四书五经. Five Classics are the I Ching 易经, Book of Documents, Classic of Poetry, Book of Rites, and Confucius’s Spring and Autumn Annals 春秋 of the State of Lu. The Thirteen Classics 十三经 also includes three commentaries on the 春秋, the first surviving dictionary Erya 尔雅, and Mencius 孟子.
- In myth, Lu Ban invents the saw.
Ping rules Chu from 528 BC and his son Zhao rules from 515 BC. Fei Wuji induces King Ping to marry the bride of Crown Prince Jian. Fei persuades King Ping to exile Prince Jian and kill his adviser Wu She. She’s son Wu Zixi escapes swearing vengeance. In 514 BC, Zixi helps Helü 阖闾 become king of Wu. Zixin recommends the assassin Zhuan Zhu, who kills king Liao with a dagger hidden in a fish. In 506 BC, Helü defeats Wu at the Battle of Boju, and Zixu exhumes and beats King Ping’s corpse.
496 BC. Goujian 句踐 rules Yue to 465 BC.
- King Fuchai rules Wu from 495 BC. Yue advisor Fan Li sends Fuchai the Great Beauty Xi Shi, responsible for the idioms 情人眼里出西施 and 沉鱼落雁, 闭月羞花. She advises him to kill Fuchai Wu Zixu, who warns him about Yue.
- 473 BC. Yue conquers Wu, Fuchai kills himself, and Fan Li retires to live with Xi Shi.
476 BC Warring States period begins with the partition of Jin into Han, Zhao, and Wei led by rival nobles.
- Invention of the compass, which is crucial for global navigation.
- Clerical script is rectilinear.
- Zhuangzi 莊子 compiles pithy parables by the Dao philosopher.
- The Zuo Zhuan 左传 is a rich commentary on the 春秋.
- Qu Yuan drowns himself in the Miluo River, Hunan. Commemorated in the Dragon Boat Festival and zongzi.
- Chu Ci poetry anthology with varying line lengths. Includes Yu Fu.
- Sun Tzu’s Art of War 孙子兵法.
- 310 BC. Xunzi 荀子 synthesizes Confucian philosophy with Daoism and Mohism.
- 233 BC Han Feizi 韩非子 is a great Legalist text. The Guanzi 管子 is a long work on economics.
221 BC Qin dynasty and unified Imperial China under Qin Shi Huang 秦始皇.
- Seal script.
- Terracotta Army.
- Official ideology of Legalism 法家.
- The naming taboo bihui 避讳 bans people from using the emperor’s name. Emperors would change their name if it contained common words.
202 BC Han dynasty establishes a Pax Sinica 中华治世. Western Han is the older period.
- 206 BC. Chu-Han Contention 楚汉相争. Bandit leader Liu Bang 刘邦 defeats Ziying 子婴 of Qin and becomes Emperor Gaozu 高祖. Generals Han Xin, Zhang Liang, and Xiao He.
- A hermit 黃石公 gives Zhang Liang the Three Strategies of Huang Shigong 黄石公三略 and the Lingqijing 灵棋经 divination manual.
- 180 BC. 文景之治. Rule of Emperor Wen and then his son Jing, a golden age.
- 141 BC. Emperor Wu 武帝 develops a strong state over 50 years.
- Sima Qian 司马迁 writes the Records of the Grand Historian Shiji 史记.
- 139 BC. Huainanzi by Liu An describes how a perfect ruler can create a perfect society.
- 40 BC. Jijiupian 急就篇 dictionary by Shi You describes the water wheel and trip hammer.
- 15 BC. Fangyan 方言 is the first dialect dictionary.
- Scholar-officials 士大夫 via imperial examinations.
- Realist gongbi 工笔 painting
- Freehand brush work or xieyi 写意
- Fu poetry 赋 rhapsodizes on a subject in ornate detail from many angles. It alternates rhyme and prose with varying line lengths. Fu on the Owl by Jia Yi (170 BC).
- Yuefu 乐府 songs emerge as anonymous folk songs collected by the 112 BC imperial Music Bureau. Later, known authors imitated the style in court literary yuefu, often with uneven line length.
- Gushi 古诗 emerges with uniform lines of 5 or 7 characters and syntactically paired couplets.
- Wuxing 五行 are five agents of change, including elements.
- Percussion drilling is used to extract natural gas in Sichuan 10 feet deep. Heavy iron bits are suspended from bamboo derricks by cables woven from bamboo fiber.
- 33 BC, Emperor Yuan presents Great Beauty Wang Zhaojun 王昭君 to marry Huhanye of Xiongnu.
- 9. Wang Mang briefly creates a Xin dynasty.
- 20 Xinlun 新论 by Huan Tan describes the trip hammer.
- 25 Eastern Han begins with Emperor Guangwu. Papermaking is invented, traditionally attributed to the court official Cai Lun. Rice paper from the paper mulberry tree.
- 58 明章之治. Rule of Ming and then Zhang, a golden age.
- 111 Book of Han 汉书 documents the Western Han dynasty.
- 114 Zhang Qian opens the Silk Road to the Parthian Empire.
- Emperor Xian rules Han in 189. The Yellow Turban Rebellion 黄巾之乱 in 184 increases the power of warlords. In 196, northern warlord Cao Cao controls the emperor and tries to reunify the empire. In the naval Battle of Red Cliffs in 208, Sun Quan 孙权, Liu Bei 刘备, and Liu Qi defeat Cao Cao. He is also the main Jian’an 建安 poet. Liu Bei’s brother and general Guan Yu 关羽.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Han_dynasty_topics
220 Six Dynasties
220 Three Kingdoms: Emperor Xian abdicates in favor of Cao Wei, son of Cao Cao. In response 刘备 declares himself Emperor of Shu Han (Zhuge Liang), and 孙权 declares himself emperor of Eastern Wu.
- Regular script develops.
266 Jin dynasty founded by Sima Yan - Records of the Three Kingdoms 三国志 (290) by Chen Shou starts from 180.
386 Northern and Southern dynasties - Tao Yuanming writes the utopian Peach Blossom Spring 桃花源 (421) and other poems. He pioneers Fields and Gardens poetry 田园诗.
- A New Account of the Tales of the World 世说新语 (444).
581 Sui dynasty begins the imperial examination 科举.
587 southern Liang dynasty. 千字文.
Six Dynasties poetry emphasizes love and relationships. Xie Lingyun pioneers Shanshui poetry 山水诗 as a “textual art”. The Orchid Pavilion Gathering further develops Shanshui poetry and includes Wang Xizhi, the greatest calligrapher, who writes the Lantingji Xu 兰亭集序.
618 Tang dynasty.
- 665 Empress Wu Zetian is China’s only reigning female emperor. She acts forcefully and decisively, dethroning her son Li Xiǎn and briefly proclaiming a Zhou dynasty. She introduces the meritocratic imperial exam for mandarin officials 官 and other reforms. She expands the empire into Central Asia and builds a spy network. In Korea, she allies with the Silla kingdom to win the Goguryeo-Tang War, then loses the Silla-Tang War.
- 705 Yuan Shuji overthrows Empress Wu and installs Li Xiǎn as Emperor Zhongzong, but Zhongzong’s consort Empress Wei held the real power.
- 710 Empress Wei kills Zhongzong by poison and intends to take the throne. Li Longji and Princess Taiping learn her plan from Cui Riyong, kill Wei, and install their father Li Dan as Emperor Ruizong.
- 712 Li Longji is appointed Emperor Xuanzong by his father. He ousts Taiping in 713 when she plots to poison him.
- The capital at Chang’an (pop 1M, now Xi’an) is the largest in the world.
- Invention of woodblock printing.
- Taoist alchemists searching for eternal life invent gunpowder 火药 by combining sulfur and carbon fuel and saltpeter (potassium nitrate) oxidizer.
- The Great Dharani Sutra is a Chinese printing of the Uṣṇīṣa Vijaya Dhāraṇī Sūtra.
- Chang’e poem by Li Shangyin.
- Tang Poetry 唐诗 and the shi poetry form 诗 modeled after the Classic of Poetry.
- Li Bai 李白 writes Quiet Night Thought 静夜思 (床前明月光) using vivid imagery to convey a longing for home.
- Du Fu 杜甫 is the second most famous Tang poet, revered as the 诗圣 (“poetry saint”).
- Caizi jiaren 才子佳人
- 795. The Tale of Li Wa 李娃传
- 831. Yingying’s Biography 莺莺传
- 835. The Tale of Huo Xiaoyu 霍小玉传
- 1337. Romance of the Western Chamber 西厢记
- 1644. Yu Jiao Li 玉娇梨
- 1658. Ping Shan Leng Yan 平山冷燕
- 1683. Haoqiu zhuan 好逑传
- Eight Immortals 八仙: He Xiangu 何仙姑 etc.
- Liu Haichan 刘海蟾 is depected with a money toad 金蟾 and coins 方孔钱.
- 755 An Lushan 安禄山 rebellion weakens the Tang dynasty. Furious guards blame the family of Great Beauty Yang Yuhuan and make the Tang Emperor Xuanzong kill his beloved consort. Xuanzong reluctantly kills her. The Tibetan Empire recaptuers much of its territory.
- 875 Huang Chao 黄巢 rebellion by salt smugglers weakens the Tang dynasty, sacking the capital at Chang’an. The former salt smuggler Zhu Wen 朱温 surrenders a rebel force to Tang forces and is promoted to jiedushi 节度使 (military governor).
Art
- The four arts 四艺 include guqin 古琴, weiqi 围棋, calligraphy 书法, mathematics 数 书法, and brush painting 中国画.
- Zhang Xu is a calligrapher known as the seal saint 草圣.
- Shan shui 山水 painting, especially blue-green shan shui using mineral dies.
- Jiehua 界畫 involves detailed ruled-line architectural drawings.
- Water and Land Ritual paintings 水陆画
- Expressionist ink wash painting 水墨画, often on Xuan paper 宣纸.
- Song Bird-and-flower painting 花鸟画. Often depict the Four Gentlemen 四君子: plum blossom 冬梅, orchid 春兰, bamboo, and chrysanthemum 秋菊. Flowers of the Four Seasons 四季名花 include lotus 夏荷. Three Friends of Winter 岁寒三友 are pine, bamboo and plum.
- Southern School 南宗画 by literati 文人画 is impressionist with quick calligraphic strokes.
- Four Masters of the Yuan dynasty 元四家: Huang Gongwang, Wu Zhen, Ni Zan, and Wang Meng.
- Wu School 吴门画派 included the Four Masters of the Ming dynasty 明四家: Shen Zhou tought Wen Zhengming, and Zhou Chen taught Tang Yin and Qiu Ying.
- Dong Qichang is the first art historian and praises the Northern School.
- Six Qing Masters 清六家: flower painter Yun Shouping, and landscape painters Wu Li and the Four Wangs: Wang Shimin, Wang Jian, Wang Yuanqi, and Wang Hui. Subtle and complex.
- Northern School 北宗画 by non-professionals with clear structure, perspective, fine lines, and colors.
907 Zhu Wen begins the 五代十国 period by overthrowing the Tang dynasty. He founds the Later Liang dynasty in northern China, which is quickly succeeded by four more dynasties. The last is the Later Zhou dynasty, which conquers most of the Southern Tang kingdom in 950. Meanwhile, southern China is divided into ten kingdoms.
916 Abaoji 阿保机 founds the Liao dynasty 辽朝 or Khitan Empire, north of the five dynasties. He was chief of the Yelü 耶律 or Yila 移剌 clan of the Khitan 契丹 people. In 938 he captures the Sixteen Prefectures of Yanyun 燕云十六州 including Youzhou (present Bejing) from the Later Jin dynasty.
960 Zhao Kuangyin founds the Northern Song dynasty by overthrowing the Later Zhou.
- Ci poems 词 are sung to a preexisting folk song and taking the same rhythm and tone patterns. Tang poet Wen Tingyun pioneers the form around 850.
- 三字经 simplifies Confucianism for kids and the 百家姓 poem of common surnames.
- Song typeface is dominant.
- 940. White Deer Grotto Academy at the foot of Lushan is one of the Four Great Academies 书院. It is rebuilt by Confucian scholar Zhu Xi in 1179.
- Percussion drilling reaches 100 meters deep.
1004 Chanyuan Treaty 澶渊之盟 establishes a century of peace between the Song and Liao dynasties. The Song pays 100,000 taels of silver annually to avoid conceding Guannan. One tael is approximately 1.3 ounces or 35 g.
1038 Tangut Yuanhao founds the Western Xia 西夏 dynasty west of the Song dynasty.
1100 Yingzao Fashi 营造法式 by Li Jie on architecture.
1115 Jurchen tribes found the Jin dynasty by overthrowing the Khitan-led Liao dynasty.
1127 Southern Song period after the Jin dynasty captures the northern half of the Song dynasty in the Jin-Song Wars.
1206 Genghis Khan founds the Mongol Empire.
1227 Genghis Khan conquers and exterminates the Western Xia, then dies. His son Ögedei Khan succeeds him.
1234 Ögedei Khan conquers the Jin dynasty at the siege of Kaifeng after the Jin refused to submit as a vassal in 1211. Jin Emperor Aizong flees to Caizhou and dies.
1271 Mongol Kublai Khan proclaims the Yuan dynasty 元朝. He conquers the Southern Song dynasty in the Battle of Yamen in 1279. He suspends the imperial exam.
- Chinese opera zaju 杂剧 (“variety theater”). Songs were written to fit existing melodies. Usually four acts with one singing role per act. Genre roles include sheng 生, a dignified male, dan 旦, a leading female, jing 净 or hualian 花脸 (“painted face”), a forceful and rough male, and chou 丑, a clown. It uses more vernacular speech, since the Mongol elite was less familiar with older classical language, influencing the vernacular novel.
- The Orphan of Zhao 赵氏孤儿 (1300)
- Qu poems 曲 or yuanqu 元曲 or sanqu poems 散曲 (“detached song”) originate from zaju arias. Some reflect resentment of mongol domination.
- First playing cards 纸牌.
1368 Han Ming dynasty conquers the Yuan dynasty including Manchuria. Mongols retreat to the rump Northern Yuan dynasty in the Mongolian Plateau.
- 1371 Haijin 海禁 (sea ban).
- 1405 Zheng He leads seven Ming treasure voyages until 1433. Zihui (1615) introduces the Kangxi radicals and stroke sorting.
- 1392 Yi Seong-gye founds the Joseon dynasty, later described as a hermit kingdom.
- 1402 Zhu Di becomes the third emperor and builds the Forbidden City, including its southern gate Tiananmen.
- 1408 Yongle Encyclopedia 永乐大典 was the largest encyclopedia. Ordered by the Yongle Emperor.
- 1557 Portugal leases a trade outpost in Macau. The Manila galleon is the round trip between Acapulco and Manila trading silver for spices, porcelain, and Filipino slaves.
- 1616 Jianzhou Jurchen (Manchu) chief Nurhaci reunifies the tribes and proclaims the Later Jin dynasty in Manchuria. He was previously a Ming vassal. In 1627 Later Jin invades Joseon after Joseon aided Ming troops.
Classic Chinese Novels 古典小说 四大奇書. The vernacular novel for a larger audience of women and merchants.
- Romance of the Three Kingdoms 三国演义 (1321). Great Beauty Diaochan has a romance with waralord Lü Bu and manipulates him into killing his foster father, the tyrannical warlord Dong Zhuo.
- Water Margin 水浒传 (1524): 108 outlaws gather at Mount Liang and fight the government and nomads.
- Journey to the West 西游记 (1592). It is based on the pilgrimage of monk Tang Sanzang 唐三藏 to India for the tripitaka. In the novel, Buddha gives him three disciples who help him to atone for their sins: Sun Wukong, Zhu Bajie, and Sha Wujing, and the white dragon horse.
- Jin Ping Mei 金瓶梅 (1610) marks a trend toward independent composition and character psychology, including explicit scenes.
- Dream of the Red Chamber 红楼梦 (1791) explores deep values as it follows the rise and decline of a family that reflects the Qing dynasty.
- The Scholars 儒林外史 (1750) satirizes Confucian scholars.
1636 Manchu Hong Taiji proclaims the Qing dynasty and conquers Joseon and the Mongolian Plateau. The British East India Company gradually dominates trade with China.
1644 Peasant revolts 明末民变 end the Ming dynasty. Li Zicheng captures Xi’an in 1643 and Beijing in 1644. Manchu regent Dorgon defeats him at the Battle of Shanhai Pass, the eastern end of the Great Wall near Beijing. In 1645 Dorgon goes south through Xi’an, and Manchu general Dodo terrorizes other cities to surrender by killing 200,000 people in the Yangzhou massacre. Meanwhile, peasant leader Zhang Xianzhong kills a million people in Sichuan.
Kangxi Dictionary (1716) by the Hanlin Academy is published in block prints.
Qianlong Emperor 乾隆帝 is the fifth emperor from 1735 and the longest reigning. The High Qing era marks its peak of prosperity.
1761 The Tiandihui is founded by Ming loyalists to resist the Manchu invasion and named after Water Margin (c. 1400). It eventually becomes the Triad.
1776 Siku Quanshu 四库全书 is the largest collection of books at 997 million words. Ordered by the Qianlong Emperor.
Japan
Japan is the third-largest Asian economy after China and India, and the closest US ally.
- Shinkansen bullet train between cities.
- Mt. Fuji and Hakone National Park
- Tokyo capital and the Kanto region
- Tsukiji Market
- Art aquarium Ginza
- teamLab Planets: immersive interactive art. Barefoot.
- Nakamise-dori Street northeast tourist street
- Omoide Tokocho west historic alley
- Haneda HND airport and Narita NRT airport.
- Ginza
- Shinjuku
- Shinjuku Station is the busiest in the world, with 3.6 million pax/day.
- Kabukicho movie and red-light district.
- Shinjuku Golden Gai has 200 tiny bars in tiny alleys.
- Kansai region
- Kyoto
- Kyoto Imperial Palace has beautiful gardens.
- Kinkaku-ji Temple, the Golden Temple on a lake.
- Nishiki Market
- Gion geisha district
- Nara Deer park about 1 hour away.
- Osaka
- Kyoto
Japanese folklore: kami 神 are gods. seven generations of kami 神世七代 ending with Izanagi and Izanami. Sun goddess Amaterasu 天照大神 rules heaven 高天原. Siblings moon goddess Tsukuyomi and storm god Susanoo. Rice kami Inari.
Amaterasu’s grandson Ninigi-no-Mikoto is great-grandfather of Japan’s first emperor, Emperor Jimmu. Ninigi brought to earth the Imperial Regalia of Japan: the sword Kusanagi no Tsurugi, the mirror Yata no Kagami, and the magatama (curved bead) Yasakani no Magatama.
yokai 妖怪 or mononoke are spirits. Include vengeful spirits (onryo), dead spirits (shiryo), and live spirits (ikiryo). Fox kitsune, turtle kappa, and winged tengu. Oni are ogre spirits. Kijo or onibaba are hag spirits.
Shinto is a polytheistic and animistic belief in kami 神 spirits. torii gates mark the entrance of shinto shrines. All life has musubi. Miko shrine maidens wear a white kosode robe and red hakama trousers.
- Three realms: Takama-no-hara (heaven) where kami live, Utsushi-yo (earth), and Yomotsu-kuni or Yomi (hell) with unclean spirits.
- shinbutsu-shūgō 神佛習合 (“syncretism of kami and buddha”).
- 1868 Meiji State Shinto
- Komainu 狛犬 lion-dog statues guard entrance gates.
- Izanami
Beauty: wabi-sabi of austere beauty and beauty of patina and aging. Imperfection, serene melancholy, spiritual longing. Yugen 幽玄 profound.
Clothing: kimono 着物 robe, obi belt, tabi split-toed socks, and zori sandals.
Kaiseki is a meticulous, artful multi-course dinner. Each dish in its own bowl.
Japanese food
- Miyazaki mangos and other expensive fruits are amazing.
- Soup
- Dashi uses smoked bonito or katsuobushi flakes and kelp 海带.
- Miso is fermented soybean paste.
- Mirin is a sweet rice wine.
- Noodles: Udon is a thick noodle. Soba is a buckwheat noodle. Yakisoba is stir-fried. Ramen includes tonkotsu pork bone broth.
- Tempura is breaded deep fried.
- Teriyaki uses a glaze of soy sauce, mirin, and sugar.
- Tonkatsu is a breaded deep fried pork cutlet.
- Gyoza dumplings
- shiitake mushrooms
- Sushi and sashimi with wasabi.
- Shokken 食券 food ticket machines.
- Sukiyaki is a small hot pot, usually with thin sliced beef. Often dipped in raw egg.
- Gyudon 牛丼 beef bowl.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Japanese_food_and_drink
14,000 BC Jomon period. Complex hunter-gatherer cultures with limited agriculture.
- Jōmon pottery is decorated by impressing cords into wet clay.
1000 BC Yayoi period: rice paddies and better architecture.
- 180. Queen Himiko of Yamatai.
300 Yamato period: earliest recorded history. Kofun period of burial mounds. - 538 Asuka period
- 539. Kinmei is maybe the first historical emperor.
- 645 Taika Reforms centralize power. Emperor appointed kokushi to govern each province.
710 Nara - 712. Kojiki is a private chronicle and the oldest Japanese literary work.
- 720. Nihon Shoki is a detailed, public, official history.
794 Heian period. Move capital to Kyoto. Emperor wears the sokutai of ho robe with large sleeves, kanmuri tall hat, and shaku flat sceptre.
1192 Kamakura shogunate
1336 Ashikaga shogunate rules the Muromachi period until 1573.
1185 Kamakura period. The shogun appoints a shugo to govern each province.
1336 Muromachi period
1467 Onin war starts Sengoku period of civil war, lots of foreign trade. Daimyo 大名 are regional feudal lords independent of the shogun. Samurai are hereditary daimyo retainers, some adhering to a moral code of bushido 武士道. Jokamachi (“city below”) is the center of a daimyo’s domain.
1526 Iwami Ginzan Silver Mine discovered.
1575 Oda Nobunaga unifies Japan, defeating Takeda Shingen in the Battle of Nagashino. - 1582 Tensho embassy meets the pope.
1603 Edo period. Shogun Tokugawa unifies Japan following work by Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hideyoshi. He moves the capital to Edo (Tokyo) and rules over the 300 daimyo. - 1613 Hasekura Tsunenaga meets the pope.
- 1636 Seclusion edict (sakoku 锁国) closes Japan to prevent daimyo from gaining power through trade and to counter colonial and Christian influence from Spain and Portugal. Trade is only allowed at Dejima island.
Colonialism in Asia
1757 Canton System 一口通商 requires all trade to occur through Canton (now Guangzhou 广州). Chinese goods could only be bought with silver bullion, leading to European trade deficits. British East India Company sells India opium to China, reversing the balance of trade.
1790 Peking opera is founded when Hui opera Huiju 徽剧 from Anhui is introduced to Bejing during the Qianlong Emperor’s eightieth birthday celebration. It developed from zaju and uses highly stylized dance, arias, and drums with elaborate costumes and a bare stage.
1794 White Lotus Rebellion weakens the Qing government.
1807 Zheng Yi Sao is the most successful pirate in history, leading 400 ships with 40,000 pirates, and retiring peacefully.
1839 First Opium War and the Treaty of Nanjing begins the Century of humiliation 百年国耻. The unequal treaties grant extraterritorial concessions in treaty ports with free trade, travel, and evangelization.
1850 Taiping Rebellion kills over 20 million people and weakens the Qing dynasty. It is peasant-driven and led by a Christian Hakka who claimed to a brother of Jesus Christ.
1856 Second Opium War. The Self-Strengthening Movement acquires more modern weapons but is largely ineffective.
1853 Perry Expedition. The US Navy opens Japan with Black Ships and Dahlgren cannons. The shogun signs five unequal Ansei Treaties with the US, Britain, Russia, Netherlands, and France. The first is the Harris Treaty of Amity at the Convention of Kanagawa. Tokugawa Iesada is very ill. The Bakumatsu period destroys gold standard and leads to economic decline. Antiforeign backlash in the Sonnō jōi (“Revere the Emperor, expel the barbarians”) movement.
1862 Japanese Embassy to Europe
1863 Emperor Kōmei issues the Order to expel barbarians. The Satsuma regent kills British trader Charles Lennox Richardson, leading to the brief Bombardment of Kagoshima and then reparations and friendly British-Satsuma relations. The Choshu clan attacks US, France, and Dutch ships. In the Shimonoseki campaign, British warships reopens the strait and imposes $3M in reparations.
1867 The shogun invites the British Tracey Mission and French military mission to Japan to modernize the Bakufu. These are interrupted by the Boshin War. The foreign powers agree to be neutral in the war, though the French unit remains until Imperial forces win the Battle of Ueno.
1868 Meiji Era. The Meiji Restoration of the Chrysanthemum Throne.
- 1889. Imperial Household Law defines limits succession to the male line (agnastic). defines the imperial family as the emperor’s direct family and some lines of imperial princes.
1864 Regent Heungseon Daewongun strengthens central authority and enforces isolationism. He destroys the US merchant ship General Sherman in 1866 and ignores the United States expedition to Korea. He executes seven French missionaries and repels the French expedition to Korea in 1866. In 1873, Queen Min forces Daewongun to resign in 1873 by allying with supporters of foreign trade, restoring King Gojong.
1876 Japan uses gunboat diplomacy to impose the unequal Japan-Korea Treaty.
1882 Korea signs the Joseon-United States Treaty.
1882 Imo Incident. Soldiers riot over corruption in paying wages, overruning the palace. Soldiers were resentful after King Gojong to modernize the army with Japanese military advisers. In response, Queen Min invites 4,500 Chinese troops to suppress the rebellion and signs the China-Korea Treaty of 1882 making Korea a tributary state.
1905 Japan colonizes Korea in the Japan-Korea Treaties. Japan bans the Korean language and commits the the Gando Massacre, Kantō Massacre, Jeamni massacre, and Shinano River incident.
1861 Empress Dowager Cixi 慈禧太后 becomes regent. She enacts some mild reforms in the Tongzhi Restoration. She overrules the Hundred Days’ Reform in 1898 by the Guangxu Emperor.
1884 Sino-French War. France conquers north Vietnam from China to promote Catholicism.
1895 First Sino-Japanese War. Japan wins, but in the Triple Intervention, Russia allies with Germany and France to force Japan to return the Liaodong Peninsula.
1897 Russia leases the warm-water port of Port Arthur on the Liaodong Peninsula west of Korea. Vladivostok on the north shore of the sea of Japan is only ice-free in the summer.
1898 Germany leases the Shandong province as part of the Kiautschou Bay concession.
1899 The US calls for the Open Door Policy of equal trade and territorial integrity in China.
1900 Boxer Rebellion. Cixi supports a revolt by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists against imperialism and Christianity. The Eight-Nation Alliance suppresses the revolt. In the chaos, Russia occupies Manchuria. Cixi implements the late Qing reforms 晚清改革. Yuan Shikai makes the New Army 新军 or Beiyang Army the most powerful in China.
China
1911 Revolution or Xinhai Revolution. Sun Yat-sen overthrows the Qing dynasty. Sun founds the Revive China Society 兴中会 in 1894, the Tongmenghui anti-monarchist alliance in 1905, and the Kuomintang (KMT) in 1912. The revolution begins with the Wuchang Uprising in the New Army. Further uprisings force child emperor Puyi to abdicate.
1912 Yuan Shikai founds the Beiyang government. He bans the KMT in 1913.
1912 Anglo-Japanese alliance against Russian expansion in Manchuria.
1914 Japan and Britain capture Shandong in the Siege of Tsingtao.
1915 Japan makes 21 demands 二十一条 to extend their influence in China, sparking the urban populist New Culture Movement.
1915 Brief National Protection War after Yuan Shikai proclaims himself emperor.
1916 Warlord Era of civil war after Yuan dies. Premier Duan Qirui leads the dominant Anhui clique. Relations deteriorate with President Feng Guozhang’s Zhili clique.
1917 Duan enters WWI allied with Japan against Russia. Japan funds his civil war against rivals with Nishihara Loans. In 1918, he signs the Sino-Japanese Joint Defence Agreement giving Japan wide influence in Manchuria, leading to student protests.
1919 Treaty of Versailles transfers German territory in Shandong to Japan, sparking the May Fourth Movement 五四运动 protest in Tiananmen Square.
1920 Zhili-Anhui War. Feng’s Zhili clique destroys Qirui’s Anhui clique. The US and Europe generally recognizes the Zhili clique.
1924 First United Front or KMT-CCP Alliance. Sun needed Soviet aid for his unification effort, and the Soviets broker the Sun-Joffe Manifesto. The CCP has around 1,000 urban intellectuals. Sun, Chiang Kai-shek, and Soviets found the Whampoa Military Academy (now ROC Military Academy). Premier Zhou Enlai is a political instructor at the Academy, and PLA head Lin Biao graduated from the Academy.
1925 Sun Yat-sen dies, treasurer Liao Zhongkai is assassinated, and Hu Hanmin is arrested as a suspect.
1926 Canton Coup. Chiang Kai-shek leads a purge of communists in the KMT after Wang Jingwei made an abortive coup attempt against him.
1926 Chiang’s Northern Expedition reunifies China. However, corruption and economic stagnation continues, leading to the Chinese Communist Revolution.
1926 Japan Showa era of Emperor Hirohito. Development of the big 4 wartime zaibatsu conglomerates.
1927 First Kuomintang-Communist Civil War 十年内战 begins with the Nanchang uprising on August 1 八一. The CCP establishes the Red Army 红军 and captures Wuhan, the capital of Hubei. The CCP is also strong in Hunan and Jiangxi. Mao’s Hunan Report (1927) advocates a peasant revolution, saying “revolution is not a dinner party” 革命不是请客吃饭.
1927 Shanghai Massacre. KMT general Bai Chongxi executes hundreds of communists allied with the Soviets.
1927 CCP military lead Zhou Enlai and his deputy Zhu De lead a failed Nanchang uprising and retreat in the Little Long March. Mao leads a failed Autumn Harvest Uprising and retreats with 1,000 people. They join up in the Jinggang Mountains of Jiangxi and Fujian, which in 1931 becomes the Jiangxi Soviet 闽赣苏区 of the Chinese Soviet Republic (CSR).
1928 Zhang Xueliang leads Manchuria after Japan assassinates his father Fengtian clique leader Zhang Zuolin in the Huanggutun incident. Zhang issues the Northeast Flag Replacement 东北易帜 accepting KMT rule.
1929 Chiang suppresses the Central Plains War.
1931 Japanese invasion of Manchuria. Chiang prioritizes defeating the CCP and compromises with Japan, which is unpopular.
1934 Long March. The Red Army escapes to Shaanxi during the fifth KMT encirclement campaign, killing landlords and recruiting peasants. Mao Zedong becomes CCP chairman, with Zhou Enlai and Deng Xiaoping as vice chairs.
1938 People’s war 人民战争 doctrine. Mao delivers On Protracted War which fights state power using broad popular support and guerilla warfare 游击战 in hostile countryside instead of decisive positional warfare 阵地战. Establishes a revolutionary base area 革命根據地 in a remote mountainous or forested area, spreads throughout the surrounding countryside on land reform policies, and then captures cities with mobile warfare 运动战.
1936 The Second United Front forms in the Xi’an Incident. Generals Chang Hsüeh-liang and Yang Hucheng kidnap Chiang and forces him to stop attacking the CCP. Japan severely weakens the KMT. The CCP adopts popular guerrilla tactics and controls most of the countryside. The Red Army grows to 1.3 million members and its militia grows to 2.6 million members.
1939 Emperor Hirohito leads Japan into World War II.
1940 Hundred Regiments Offensive is a CCP offensive against Japan.
1941 New Fourth Army incident. KMT forces ambush the New Fourth Army.
1942 Japan executes 250,000 civilians in the Zhejiang-Jiangxi campaign.
1944 Operation Ichi-Go is the last Japanese offensive against the KMT.
1945 Soviet invades Manchuria and deny access to the KMT. The Japanese Kwantung Army of 700,000 surrenders.
1945 US occupies Japan, forming the State of Japan. The Reverse Course shifts from demilitarization and democratization to economic reconstruction and remilitarization in support of U.S. Cold War objectives in Asia. The Red Purge removes alleged communists from desirable jobs.
1945 Second Kuomintang-Communist Civil War 解放战争. The CCP captures Japanese weapons and wins the Shangdang Campaign, capturing 35,000 KMT troops. The US and Soviet Union tries to negotiate a peace in the Double Tenth Agreement, which fails.
1948 Liaoshen campaign 辽沈会战. The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) 解放军 captures Manchuria and 500,000 KMT soldiers in the Siege of Changchun.
1948 Pingjin campaign 平津战役 captures Beijing and Tianjin.
1949 Huaihai campaign 徐蚌会战. The PLA destroys the KMT army and reaches the Yangtze river.
1949 Yangtze River Crossing campaign 渡江战役 captures the KMT capital at Nanjing. The KMT retreats to Guangzhou (Canton), Chongqing, Chengdu, and Taiwan, finally winning the Battle of Guningtou to defend Kinmen 金门 island.
1949 Mao Zedong proclaims the People’s Republic of China (PRC). China continues the Uyghur genocide.
1949 China overvalues the renminbi to enable cheap machinery imports for import substitution.
1950 Land Reform Movement 土改 and the Campaign to Suppress Counterrevolutionaries 镇压反革命运动 kills 1 million landlords, sends another million to labor camps 劳动改造, and decreases inequality.
1951 China annexes Tibet in the Seventeen Point Agreement. The 14th Dalai Lama flees to India after the 1959 Tibetan uprising.
1953 China’s first five-year plan expands state control of industry.
1956 Hundred Flowers Campaign 百花齐放 briefly allows criticism.
1957 Anti-Rightist Campaign 反右运动 transforms China to fascism.
1958 Great Leap Forward 大跃进. Mao tries to industrialize China by mandating people’s communes. The Four Pests campaign targets rats, flies, mosquitoes, and sparrows. Locust swarms destroy rice fields.
1959 The Lushan Conference purges defense minister Peng Dehuai for opposing the Great Leap Forward.
1959 The Great Chinese Famine 三年大饥荒 kills 40 million.
1959 PLA suppresses the Tibetan uprising. The 14th Dalai Lama flees to India.
1962 Seven Thousand Cadres Conference 七千人大会. President Liu Shaoqi and Deng Xiaoping promote market reform 三自一包.
1964 Mao develops Third Front secret industrial and military facilities in the rugged interior of the country in case of US invasion.
1966 The Cultural Revolution 文化大革命 restores Mao to power beginning with Red August.
- Mao’s first big-character poster 大字报 Bombard The Headquarters 炮打司令部 attacks the party establishment. Mao imprisons Liu Shaoqi.
- Mao dehumanizes his enemies as cow demons and snake spirits.
- Mao denounces the Four Olds 四旧: Ideas 思想, Culture 文化, Customs 风俗, and Habits 习惯.
- Mao contrasts the Five Red Categories 红五类 of peasants 贫下中农, workers 工人, soldiers 革命军人, party members 革命干部, and martyrs 革命烈士 with the Five Black Categories 黑五类 of landlords 地主, rich farmers 富农, counter-revolutionaries 反革命, bad elements 坏分子, and rightists 右派.
- Mao distributes his Maoist 毛主义 Little Red Book (1964), which includes the phrase political power grows out of the barrel of a gun 枪杆子里面出政权.
- Red Guards conduct struggle sessions 批斗大会.
- Down to the Countryside Movement 上山下乡运动 deprives 17 million “educated” youth 知青 of college education.
- 1968 Cleansing the Class Ranks 清理阶级队伍 kills 1 million.
- 1970 One Strike-Three Anti Campaign 一打三反运动 kills 200,000.
- 1971 Project 571 五七一工程. Lin Biao’s son plots to overthrow Mao Zedong.
- 1971 Lin Biao incident 九一三事件. Lin Biao dies trying to flee China. Mao becomes depressed and reclusive. His wife Jiang Qing leads the radical Gang of Four in a political power struggle against Zhou Enlai.
- 1971 UN Resolution on Admitting Peking seats PRC and expels Taiwan.
- 1975 Mao allows Deng Xiaoping to improve the economy.
- 1975 Zhou Enlai dies. Mao selects the relatively weak Hua Guofeng as premier. Jiang Qing purges Deng but is unpopular.
- 1976 Mao Zedong dies.
- 1976 Hua Guofeng secures army support from Wang Dongxing and Chen Xilian and arrests the Gang of Four. He swears to uphold whatever policies and decisions that Mao Zedong made (the “Two Whatevers” 两个凡是) which is unpopular internally. Deng builds political power from the provinces to the center and wins the Truth Criterion Controversy 真理标准大讨论. In 1977 Hua Guofeng rehabilitates Deng Xiaoping.
1978 Deng Xiaoping is the “Architect of Modern China”, promoting economic reform 改革开放, Boluan Fanzheng 拨乱反正, socialism with Chinese characteristics 中国特色社会主义, and Deng Xiaoping Theory 邓小平理论.
- Premier Zhou Enlai announces the Four Modernizations 四个现代化 of agriculture, industry, defense, and science towards a middle class society 小康社会.
- The Beijing Spring is a brief period of liberalization. The Fifth Modernization poster on the Democracy Wall advocates democracy.
- 1979 Special Economic Zones include the Shekou Industrial Zone in Shenzhen. In 1982, the 50-floor Guomao Building 国贸大厦 is built with Shenzhen speed 深圳速度 and becomes China’s tallest building. Shenzhen has the slogan 时间就是金钱,效率就是生命.
- 1979 Three Links 三通 opens postal, airline, and trade links with Taiwan.
- 1979 Jimmy Carter opens full diplomatic relations and severs ties with Taiwan.
- 1982 Constitution emphasizes rule of law over communism and revolution.
- 1984 The Sino-British Joint Declaration returns Hong Kong to China. Deng agrees to one country, two systems 一国两制 supporting the Hong Kong Basic Law.
- 1986 student demonstrations against the 16% inflation rate, government corruption, and restrictions on speech. Deng Xiaoping removes General secretary Hu Yaobang for not suppressing the demonstrations.
- 1989 Tiananmen Square massacre 六四事件 after Hu Yaobang dies. Students demonstrate for over a month and build the 33 ft Goddess of Democracy statue. Tank Man briefly blocks the tanks. Deng jails Xu Qinxian for refusing to use force against the protestors, places General Secretary Zhao Ziyang under house arrest for opposing martial law, and resigns his official positions.
Jiang Zemin is third leader from 1989 to 2002. He says that the CCP has Three Represents 三个代表, representing development, culture, and the people. He is initially conservative. In 2000 he promotes a Go Out strategy 走出去战略 for domestic companies to enter foreign markets. He served as mayor of Shanghai, building the Shanghai clique 上海帮.
In 1992, Deng Xiaoping’s southern tour promotes continued economic liberalization. He says:
- I don’t care if the cat is black or white, so long as it catches mice 不管黑猫白猫,能捉到老鼠就是好猫
- development is paramount 发展才是硬道理
- whoever blocks reform will resign 谁不改革,谁就下台
- 多干实事,少说空话
Hu Jintao is fourth leader from 2002 to 2012, chosen by Deng Xiaoping. He promotes a technocratic and more balanced Scientific Outlook on Development 科学发展观 and a more just Harmonious Society 和谐社会. Hu led the Communist Youth League of China and built the Tuanpai 团派, a populist faction of humble backgrounds, more education, and more concern about inequality, including Li Keqiang.
Xi Jinping 习近平 is fifth leader from 2012. He directs an anti-corruption campaign led by Wang Qishan that targets political rivals including the Jiang faction. He is a Princeling 太子党. His allies include Li Zhanshu and Wang Huning.
- Bo Xilai is sentenced to life in prison for bribery. His Chongqing model prioritized wealth redistribution and Maoist 唱红打黑 campaigns. 2012 Wang Lijun incident. Bo Xilai’s wife Gu Kailai murdered British businessman Neil Heywood. Bo and Wang fall out, Bo starts investigating Wang’s subordinates, and Wang seeks political asylum in the US consulate, which was denied. The government says that he was undergoing vacation-style medical treatment, which becomes a meme. Zhou Yongkang was Bo’s main supporter in the Politburo.
- Zhou Yongkang was Minister of Public Security with influence in the oil sector and Sichuan. Zhou retired but became the first Politburo Standing Committee member to be convicted and sentenced to life in prison. Xi got permission from Jiang.
Modern Asia
Four Asian Tigers are Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan.
- Miracle on the Han River. US army redistributes Japanese-owned land. Industrialization with Western support. Growth of South Korea chaebol.
- Taiwan Miracle. Land reform distributes land from landlords to peasants. Hui 会 family rotating loan groups. Export-oriented trade strategy.
1945. GHQ (General Headquarters of the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers) occupies Japan. Royal family pays 90% tax.
- 1947 Imperial House Law. 51 princes removed from the imperial household. To shrink the imperial household, Allies impose that princesses lose royal status if they marry outside the imperial clan.
Japanese economic miracle.
- 1945 Expansionary economic policy leads to 100% inflation.
- 1945 Trade Union Law protects the right to unionize. Unions peak at 55% membership in 1949, leading to annual shunto (“spring wage offensive”) negotations and shushin koyo 终身雇佣 (“lifetime employment”).
- 1947 Socialist PM Katayama ends feudalism, giving land to tenant farmers.
- 1947 Reverse Course. US emphasizes economic reconstruction and remilitarization to strengthen a Cold War ally. Dodge Line curbs inflation and causes a recession.
- 1950 Japan becomes the second-largest economy Japanese industry builds up to supply America in the Korea War. The US keeps the yen artificially low.
- 1960 Anpo protests against US military bases forced PM Kishi to resign.
- 1960 Liberal PM Hayato Ikeda pushes heavy industrialization and unlimited loans, leading to keiretsu conglomerates.
San Francisco System: US pursues bilateral agreements over multilateral organizations. Asian nations did not have shared democratic values or a common threat. Mutual defense treaties with Japan (1951), Philippines (1951), South Korea (1953). Thanat–Rusk communiqué with Thailand (1962).
1959 Lee Kuan Yew becomes the first prime minister of Singapore. He promotes export-oriented industrialisation and favorable conditions for foreign direct investment, increasing life expectancy by ten years. He builds public housing. However, he also suppresses free speech and labor movements, and inequality increases.
1963 Malaysia and Singapore become independent from Britain.
1965 Singapore becomes independent.
1800 The Dutch nationalize the Dutch East India Company, creating the Dutch East Indies.
1824 Anglo-Dutch Treaty. The Dutch cede Malacca to Britain.
1945 Indonesia wins independence with Sukarno as president. In 1966, the economy collapses with 600% inflation.
1967 Suharto becomes a military dictator. The Berkeley Mafia economists help control inflation by promoting free markets and reversing many progressive economic reforms, leading to strong economic growth but also vast corruption. Suharto gets Western support as an anti-communist.
1975 Indonesian invasion of East Timor and a 24-year occupation kills 100,000 people.
1989 Heisei era of Emperor Akihito.
1997 Asian financial crisis
2019 Reiwa era of Emperor Naruhito.
Malacca Strait is the busiest in the world, carrying 25% of trade volume. Between Malaysia and Indonesia. Can be blockaded.
Belt and Road Initiative builds infrastructure through debt financing.
- String of Pearls
- Port of Djibouti naval base on the Strait of Mandeb and $11B loans.
- Hambantota deep sea port in Sri Lanka. Also Colombo deep sea port.
- Gwadar deep sea port in Pakistan.
- $10B Kyaukphyu deep sea port in Myanmar; $2.5B Sino-Myanmar pipeline.
- Spratly Islands.
- Chittagong and the $11B Dhaka-Chittagong high-speed railway.
https://china.aiddata.org/projects/55046/ - Haidob port in Sudan by China Harbour, $140M
- $50B loans to Venezuela
https://thediplomat.com/2016/01/chinese-company-wins-contract-for-deep-sea-port-in-myanmar/
The South China sea is disputed between China, the Philippines, Malaysia. Taiwan and China both claim all of the Spratly Islands. A UN arbitration ruled that the Spratly Islands are rocks without a right to a 200 mile exclusive economic zone. China also seized Scarborough Shoal to the north near the Philippines. Japan controls the Senkaku (Diaoyu) Islands and the Anpo US-Japan defense treaty covers the islands. China’s Air Defense Identification Zone includes the Senkaku islands.
2016. Tsai Ing-wen becomes president of Taiwan and a member of the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP). She takes a harder stance against China.
2024. Lai Ching-te becomes president of Taiwan.
2014 Hong Kong protests
Umbrella movement
India
- The Indus river flows through Tibet and Pakistan to the Arabian Sea.
- The Ganges river flows through India and Bangladesh to the Bay of Bengal. It is sacred to Hindus, who bathe, drink, and worship in it. It is home to the Ganges river dolphin, a Indian national animal.
- Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh is a pilgramage site.
- Triveni Sangam is the confluence with its Yamuna tributary, which has greenish water.
- The Brahmaputra River is a tributary that flows from the Himalayas in Tibet.
- Kashmir is disputed between India, Pakistan, and China.
- North
- Uttar Pradesh > Agra: Taj Mahal
- South
- Karnataka: Mysore Palace
3300 BC Indus valley civilization in India lasts around 1000 years
1500 BC. Vedic age, including the Varna social classes: Brahmin priests and teachers, Kshatriya rulers and warriors, Vaishya farmers and merchants, and Shudra artisans and servants.
800 BC The second urbanisation.
600 BC The Mahajanapadas are sixteen kingdoms, which consolidate into four great powers of Magadha (furthest east), Kosala, Vatsa (center north), and Avanti (central).
322 BC Chandragupta founds the Maurya Empire in the Central Ganges Plain. It expands to all of India except southern India, which is ruled by the Tamil kings. It develops the Brahmi script.
1206 Delhi Sultanate is founded.
1526 Mughal Empire is founded by Babur invading from Afghanistan. As a gunpowder empire, its professional army consists of sepoys with muskets. Peasants are taxed at over 50%.
- 1400 Timur or Tamerlane founds the Timurid Empire across Persia and the Caucausus. It loses most of Persia to the Aq Qoyunlu Persian tribal confederation.
- The Taj Mahal is built in 1631.
- In 1639, The emperor builds the Red Fort, moving the residence from the Agra Fort.
- The Shalamar Gardens in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan are a Persian paradise garden (charbagh) built in 1641.
1674 Maratha Empire is founded.
1799 Sikh Empire rules Punjab.
1757 British East India Company begins controlling territory. It replaces the Bengal ruler in the Battle of Plassey. It begins collecting taxes after the Battle of Buxar of 1764. In 1773, Governor-General Warren Hastings begins ruling Bengal.
1780 Britain monopolizes the salt trade and imposes a 250% salt tax.
1803 Britain conquers Odisha to maintain its salt monopoly.
1843 Britain builds the Inland Customs Line to avoid smuggling from the west.
1848 Second Anglo-Sikh war. Britain annexes Punjab.
1857 British Raj administered by the India Office after the Indian Rebellion is suppressed. The Raj standardizes and strictly enforces rigid caste listings to decide moral worth, job qualifications, tax rates, and criminal profiling.
1885 Indian National Congress.
1930 Dandi Salt March protests the salt tax. Led by Mahatma Gandhi.
1947 Indian independence.
1947 Partition of India and Pakistan in the Karachi Agreement. In the Kashmir conflict, India, Pakistan, and China claim Kashmir. Large-scale violence leaves 1 million dead and 10 million displaced. Mass migration of Muslims to Pakistan. Bengal splits into Bangladesh and West Bengal.
1962 Sino-Indian War preserves the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
1971 Bangladesh declares independence from Pakistan, and Pakistan kills around 400,000 people. Third India-Pakistan war establishes the line of control as the de facto border.
2009 Sheikh Hasina becomes PM. Grows authoritarian, reinstating a 30% quota in 2024, leading to the quota reform movement. Anti-discrimination Students Movement organizes the non-cooperation movement.
2012 Delhi gang rape and murder of Jyoti Singh, a 22-year-old physiotherapy intern. India bans publishing a rape victim’s name so she was known as Nirbhaya (“fearless”).
2014 Narendra Modi is 14th prime minister of India.
- India imports 4 million barrels of oil per day. Oil prices fell by 50%.
- 10% unemployment with 50% among young people. Decreasing manufacturing jobs.
- India Stack of digital infrastructure, including the Aadhaar fingerprint ID system and 500M new bank accounts.
- Generous direct transfers, toilets, electricity, drinking water for the poor.
- Transportation infrastructure.
- Less red tape for businesses.
Egypt
The Ennead are the nine gods worshipped at Heliopolis.
Atum primordial god, the evening sun. Merged with Ra, god of the Sun, a falcon head. Fights Apep, god of darkness, a snake.
Shu and Tefnut, children of Atum.
Nut and Geb, children of Shu, father of Osiris.
Osiris is the green god of rebirth and the underworld, Duat. Wears the atef, a hedjet flanked by ostrich feathers which curl down at the tip. Bears his son Horus. The Eye of Horus is a symbol of health and stability.
- Brother Set kills him and cuts him to pieces. Depicted as a slender canine with a long snout and a straight upright tail forked at the end.
- Sister wife Isis collects the pieces and resurrects Osiris.
- Sister Nephthys, goddess of mourning and night, a young woman wearing a house with a basket on top.
Neith is a prime creator goddess of the cosmos, sometimes wearing the red crown, having a shield symbol and archery.
Anubis, a canine, god of the underworld, weighs the heart against Maat, an ostrich feather. Ammit, a crocodile-lion-hippo god, devours the unworthy dead.
Sekhmet, the Eye of Ra, goddess of war and medicine.
Wadjet, a cobra ruler of Lower Egypt.
Bastet, an alabaster lioness or cat.
Amun, blue skin.
Ptah, god of craftsmen depicted with green skin, skintight shroud, divine beard, and holding an ankh-djed-was.
Thoth, god of wisdom, ibis head. Wife Maat, goddess of truth and balance, wears an ostrich feather. Daughter Seshat, scribe goddess of science, wears leopard skin.
Believed in many parts of the soul: body, spirit, name, personality, vital essence, heart, shadow, power or form.
The uraeus, an upright cobra, represents Wadjet.
A nemes is a royal head cloth, striped across the forehead with large flappets hanging down to both shoulders behind the ears, and tied in the back.
The khat is a simple royal head cloth, hanging open at the back.
The pschent is the double crown of Egypt, combining the white hedjet of Upper Egypt and the red deshret of Lower Egypt. The front features the uraeus and a vulture representing Nekhbet.
The hedjet looks like a bowling pin.
The deshret is a narrow truncated spike, set towards the back on a large cylindrical base, with a tendril protruding from the front and curling up. It was typically woven from flax or other fiber.
The khepresh is the blue crown, curving back and flaring out from the sides.
The djed represents the spine of Osiris.
The was sceptre represents power and is topped with an abstract animal head.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Egyptian_philosophy
3400 BC. Gebelein predynastic mummies.
Early dynastic period (3150 BC). The First and Second Dynasties occur after King Menes aka Narmer unifies Upper and Lower Egypt. The capital of Memphis is the largest city in the world at 30,000 people. Burials at the royal necropolis of Umm el-Qa’ab in Abydos.
- The Narmer Palette, the Scorpion macehead, and the Narmer macehead contain the oldest hieroglyphics. It was found at the Horus of Nekhen. Heads and legs are in profile, while the shoulders are frontal. Male figures have one foot forward, and female figures stand with feet together.
Old Kingdom (2686 BC), Third to Sixth Dynasties.
Imhotep is a high priest of the Third Dynasty. He builds the Pyramid of Djoser in Saqqara, the Necropolist of Memphis, a step pyramid that was the world’s tallest structure.
Sneferu (2613 BC) founds the Fourth Dynasty. He builds the Meidum (301’), the second pyramid in the world, the Bent Pyramid (344’), and the Red Pyramid (344’). The Red Pyramid is the first smooth-sided pyramid and the third-largest Egyptian pyramid.
Khufu (2589 BC) succeeds Sneferu and builds the Great Pyramid of Giza, the largest Egyptian pyramid at 481’.
- The Diary of Merer (2550 BC) is the oldest known papyrus text, a logbook. It describes shipping 200 2-ton blocks of white limestone from Tura quarries to Giza.
Khafre is the fourth pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty. The Pyramid of Khafre in Giza is the second-largest Egyptian pyramid at 448’.
Funerary texts - 2400 BC Pyramid Texts are carved for pharaohs.
- 2400 BC The Maxims of Ptahhotep.
- 2100 BC Coffin Texts such as Story of Sinuhe are carved on coffins for common people.
- 1550 BC Book of the Dead on papyrus contains magic spells to help the dead in the underworld.
First Intermediate Period (2181 BC), Seventh to Eleventh Dynasties.
Middle Kingdom (2061 BC), Twelfth and Thirteenth Dynasties. Capital at Thebes (modern-day Luxor), on the eastern bank of the Nile, containing the Karnak Temple Complex and Luxor Temple. The western bank contains the Theban Necropolis including the Valley of the Kings.
- 1800 BC. Proto-Sinaitic script is the first alphabet.
- Prophecy of Neferti describes a great king Ameny who will end a coming civil war.
Second Intermediate Period (1705 BC), Fourteenth to Seventheeth Dynasties.
- Ebers Papyrus (1550 BC) is an early medical scroll with 110 pages.
- Rhind Mathematical Papyrus (1550 BC) is an early geometry roll.
Egyptian Empire aka New Kingdom (1549 BC) spanning the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties are the peak of Egypt’s power.
Ahmose I founded the Eighteenth Dynasty, with the capital at Thebes.
Hatshepsut was the fifth pharoah as queen regnant, taking on masculine roles and depictions.
Thutmose III, the sixth pharaoh, is the greatest military pharoh, winning 17 campaigns over 53 years. Thebes (pop. 80,000) becomes the largest city in the world.
Amenhotep III is the ninth pharoah. His morturary temple is the largest in the world. It is flanked by the Colossi of Memnon, two massive statues of him.
Akhenaten, the tenth pharaoh, and his great royal wife Nefertiti introduced Atenism, an monotheistic religion, and built a new capital city, Amarna. The reforms were unpopular and wiped from history after his death. Thutmose crafts the colorful Nefertiti Bust.
Tutankhamun, the boy king, died from malaria or an infected broken leg. His aged uncle Ay ruled for four years, then the Commander of the Army Horemheb ruled for 14 years before appointing his vizier as successor. His tomb KV57 is unfinished.
Ramesses I founded the Nineteenth Dynasty.
Seti I, second pharaoh, reconquered territory in Canaan and Syria threatened by Hittites. His memorial contains the Abydos King List.
Ramesses II is the third and greatest pharoah. He won 15 campaigns and tied one, the Battle of Kadesh, over 34 years. Tomb KV5, the largest tomb with around 120 chambers, contains most of his children. He commissions a massive statue, which inspires the poem Ozymandias, after his Greek name.
Ramesses III is buried in Tomb KV11. A wide corridor framed by squat columns featuring large human figures. A stairwell descending to an underground corridor densely inscribed with columns of sparse hieroglyphs, with thin inset square arches at intervals. A massive open space with a rounded ceiling, flanked by large recessed columns, featuring a broken rock sarcophagus.
Third Intermediate aka Libyan Period (1069 BC), Dynasties 21-25.
Late Period (672 BC), Dynasties 26-31
- 525 BC The Persian Achaemenid Empire conquers Egypt in the Battle of Pelusium, founding the 27th Dynasty.
- Elephantine papyri and ostraca (500 BC) document a polytheistic Jewish sect.
- 404 BC Amyrtaeus overthrows Persia to become the only pharaoh of the 28th dynasty.
- 399 BC Greek general Nepherites I founds the 29th dynasty
- 380 BC Nectanebo I founds the 30th dynasty.
- 343 BC Achaemenid king Artaxerxes III reconquers Egypt.
Hellenistic or Ptolemaic Kingdom (332 BC), Dynasties 32-33. Alexander the Great founds Alexandria and dies. Ptolemy founds the Mouseion and the Library of Alexandria. He is a bodyguard of Alexander. Hipparchus and Eratosthenes lived at the Library.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Library_of_Alexandria
- 300 BC. Euclid’s Elements compile geometry. The Oxyrhynchus Papyri contain half a million fragmented public and private documents, only 1% transcribed.
- 205 BC. Egypt suppress a revolt that briefly captured Thebes.
- 150. Ptolemy’s world map in his Geography. East on top in the direction of the garden of Eden.
Roman Egypt (30 BC) rules until the Arab conquest in 641. Coptic is an Egyptian dialect with Greek influence.
- Catacombs of Kom El Shoqafa
- 230. Origen writes the Hexapla and On the First Principles.
- 270. Plotinus founds neoplatonism emphasizing monism. Enneads discuss Nous (“intellect”) and psyche (“soul”).
- 270. Aurelian crushes the Palmyrene invasion of Egypt by Queen Zenobia.
- 370. Neoplatonist philosopher Hypatia opposes the influence of bishop Cyril and is killed by a Christian mob.
Middle East
Geography
- The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea. The Red Sea is an inlet of the Indian Ocean via the Bab-el-Mandeb (Gate of Grief), the strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- 25,000 ships transit the Suez each year. Egypt charges $300,000 per ship.
- Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, Syria.
- Jerusalem
- David’s Tomb. The Cenacle on the upper floor is traditionally the site of the Last Supper.
- Jordan
- Petra: rock-cut architecture out of sandstone.
- Jerusalem
- Mesopotamia is the region of the the Tigris and Euphrates, which flow to the Persian Gulf. The Persian Gulf is an inlet of the Arabian Sea bordered by Oman, United Arab Emirates UAE, Saudia Arabia, Iraq, and Iran.
- Saudi Aramco operates the Ghawar Field (the world’s largest onshore oil field) and the Safaniya Field (the world’s largest offshore oil field).
- Afghanistan is east of Iran. Kandahar is a US main operating base. Pashto language.
- Kuwait hosts the Camp Arifjan US army base.
- Qatar hosts the US Al Udeid Air Base near Doha.
- Bahrain is a small island near Qatar: Manama US naval base.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mesopotamian_mythology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sumerian_religion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_near_eastern_cosmology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/En%C5%ABma_Eli%C5%A1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Song_of_the_hoe
Sumerian and ancient Semitic religion
- Supreme god: El (Canaan)
- Primordial waters: Nammu
- Earth: Ki
- Sky: An
- Enlil creates the earth and marries Ninlil.
- Enki or Ea (Akkad) creates humans.
- Sun: Utu, Shamash (Babylon), Shapshu or Shapash (Canaan)
- Moon: Nanna, Sin (Babylon)
- Venus, goddess of love: Inanna, Ishtar (Akkad, Babylon, Assyr), Astarte (Canaan)
- Mars, god of war, death, and disease: Nergal (Babylon)
- Underworld Kur ruled by Ereshkigal (“Queen of the Great Earth”).
- God of death: Mot (Canaan)
- Sea goddess Tiamat
- Sea god: Yam (Canaan) and sea monster Tannin (Canaan)
- Storm god: Baal (Canaan), Hadad (Akkad), Iskur (Sumer), Bel (Babylon)
The Bedouin are desert nomads who herd camels, sheep, and goats.
Keffiyeh, ghutrah, or shemagh is a square cotton scarf worn on as a headdress, often checkered or white. Secured with an agal, a doubled black cord ring of goat hair.
Cuisine
- Pita bread: leavened round flatbread.
- Hummus is cooked chickpeas with tahini, lemon juice, and garlic.
- Tahini is toasted ground sesame.
- Baba ghanoush is smoky roasted eggplant, olive oil, lemon juice, and tahini.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Levantine_cuisine
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Lebanese_cuisine
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Turkish_cuisine
6400 BC Pottery Neolithic: Yarmukian culture in the Levant. Halaf (northwest), Samarra (central), Ubaid (southeast) cultures.
- 5500 BC Ubaid period expands across Mesopotamia
- 4000 BC Uruk (pop. 40,000). Possibly ruled by King Gilgamesh.
4000 BC Sumer civilization in Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent. The Sumerian language is an isolate. Pictographic proto-cuneiform develops around 3500 BC as attested by the Kish tablet.
- 2900 BC Early Dynastic Period: Ur (pop. 65,000) and other city-states. Sumerian language written in cuneiform. Municipal councils and popular assemblies.
- Flood myth. The Euphrates floods at Shuruppak or Tell Fara in Iraq.
- 2600 BC. Instructions of Shuruppak is wisdom literature.
- 2400 BC. Debate between sheep and grain about which benefits humans more. Debate between Winter and Summer about which season is better. Debate between bird and fish.
- 2000 BC. Sumerian King List mentions the flood and Dumuzid, god of agriculture.
- 1800 BC. Eridu Genesis is a Sumerian creation and flood myth. Gods create man from clay. Enlil, god of wind, air, earth, and storms, can’t sleep from human noise and decides to send a flood. Enki warns Ziusudra to build a boat. The storm rages seven days and nights. Ziusudra prostrates himself before An (Sky) and Enlil, who make him immortal for living a godly life.
2400 BC Akkadian Empire in Mesopotamia lasts 200 years. The Semitic Akkadian language replaces Sumerian. Semitic also includes Arabic and Ethiopian languages like Amharic. Founded by Sargon of Akkad.
- 1700 BC Atra-Hasis is a Babylonian creation myth of Anu, Enlil, and Enki, the Sumerian gods of sky, wind, and water. Flood myth: Enki warns Atra-Hasis or Utnapishtim builds the boat Preserver of Life.
- Epic of Gilgamesh. Gilgamesh oppresses his people. Enkidu, a wild man, challenges him and becomes his friend, defeating the monster Humbaba and chopping down sacred trees. Ishtar hits on Gilgamesh, who insults her. Enkidu dies, and Gilgamesh seeks out the immortal Utnapishtim, who tells him about a flower growing on the bottom of the sea, but a snake eats the flower.
- 2200 BC Gutian dynasty
- 2100 BC Third Dynasty of Ur. The Code of Ur-Nammu is the earliest law. The complaint tablet to Ea-nāṣir complains about low-quality copper.
2000 BC Assur city state and the Old Assyrian period.
1792 BC Hammurabi founds the Old Babylonian Empire and issues the Code of Hammurabi. After his death the empire shrinks to a city-state.
1365 BC Middle Assyrian Empire dominates. It breaks apart starting in 1056 BC, partly due to invasions by Aramean tribes.
1200 BC Counsels of Wisdom: “requite with kindness your evil-doer”
1121 BC Nebuchadnezzar I defeats Elam.
1000 BC Babylonian Theodicy: dialogues on the problem of evil.
911 BC Neo-Assyrian Empire dominates. The capital of Nineveh becomes the largest in the world (pop. 100,000).
600 BC Babylonian Map of the World is the oldest map.
500 BC Story of Ahikar
1750 BC Hittite kingdom in Anatolia speaking the extinct Anatolian language, first evidence of iron smelting. It is annexed by the Middle Assyrian Empire. The Mitanni kingdom is founded around 1600 BC on its southern border, speaking the Hurrian language. Both kingdoms splinter during the Bronze Age collapse.
900 BC King Gordias founds the Phyrigian kingdom at Gordion in Anatolia. King Midas rules from around 740 BC, making a vain prayer to have a golden touch. In 696 BC, the Cimmerian invasion of Phrygia by Iranian equestrian nomads in the Pontic-Caspian steppe sack.
700 BC Scytho-Siberian world of the Eurasian Steppe includes the Scythian, Sauromatian, and Sarmatian cultures of Eastern Europe, the Saka-Massagetae and Tasmola cultures of Central Asia, and the Aldy-Bel, Pazyryk and Tagar cultures of south Siberia.
- Iranian nomads include Agathyrsi, Cimmerians, Massagetae, Saka, and Sarmatians.
1200 BC Phoenician city-states of Tyre, Sidon, Byblos in the Levant. Semitic languages: Aramaic and Canaanite (Phoenician, Ammonite, Hebrew, Moabite, Edmoite, Phillistine). First alphabet with a consistent writing direction (right to left). Maritime.
930 BC Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south, with the capital in Jerusalem. Neighbored by the kingdoms of Edom, Moab, Ammon, and Aram Damascus. Allegedly Jeroboam’s Revolt of ten tribes split a united kingdom.
747 BC Nabonassar becomes king of Babylon after 23 years. First listed in the Canon of Kings used by astronomers.
720 BC Assyrian captivity. The Assyrian Empire conquers the Kingdom of Israel and its capital Samaria, sieges Jerusalem, and forcibly relocates the Ten Lost Tribes inland.
700 BC. Median Empire in Persia (Iran) conquers the Urartu kingdom in the Armenian highlands (present Turkey).
612 BC Neo-Babylonian Empire overthrows the Assyrian Empire in the Battle of Nineveh.
589 BC The Kingdom of Judah’s revolts against Babylon are crushed in the siege of Jerusalem, which destroys Solomon’s Temple and relocates the Jews to Babylon in the Babylonian captivity.
Achaemenid Persian Empire
- Old Persian language (present Farsi).
- 539 BC Fall of Babylon. Cyrus the Great conquers the Babylonian Empire and issues the Edict of Cyrus allowing Jews to return to Zion (Judah) as the self-governing province of Yehud. In the Second Temple period, Jews compile the Torah and build the Second Temple of Jerusalem.
- 480 Persian invasion of Greece by Xerxes I ends with Persian defeat.
- 401 BC Battle of Cunaxa. Persian king Artaxerxes II defeats a Babylonian uprising by his brother Cyrus the Younger. Cyrus hired a Spartan mercenary army, the Ten Thousand led by Xenophon, who used flanking maneuvers and feints.
- 370 BC Failed successions in the Great Satraps’ Revolt.
331 BC Alexander the Great conquers the Achaemenid Empire.
- Battle of the Persian Gate in 330 BC. The Persian army holds the Macedonia army for a month at a mountain pass near Perspepolis. Alexander wins after finding a second path.
Seleucid Empire
- 312 BC. Macedonian general Seleucus receives Babylon and founds Antioch, the capital and a major cultural center.
- Babylonian War. General Antigonus I Monophthalmus invades to reunite the Macedonian Empire and is defeated at the Battle of Ipsus.
- 281 BC. King Mithridates I of Persian origin founds Pontus in northern Turkey, which is conquered by Rome in the Mithridatic Wars in 63 BC.
- 256 BC. Greco-Bactrian Kingdom declares independence. It covers present-day Afghanistan east of the Parthian Empire.
- 250 BC. Kingdom of Cappadocia declares independence. It is annexed by Rome in 17 CE.
- 312 BC. Syrian Wars.
- 217 BC. Fourth Syrian War and the Battle of Raphia. Ptolemy IV briefly occupies the Levant.
- 200 BC. Fifth Syrian War and the Battle of Panium. Seleucids recapture Coele-Syria.
- 188 BC. Rome wins the Roman-Seleucid War.
- 188 BC. The Kingdom of Armenia east of Anatolia declares independence from the Seleucids, annexing Syria in 83 BC. It is annexed by Rome in 66 BC.
- 168 BC. Maccabean Revolt by Jewish warriors against Seleucid King Antiochus IV Epiphanes, who heavily persecuted Judaism.
- 140 BC. The Hasmonean dynasty rules Judea semi-autonomously.
Judea.
- 63 BC Siege of Jerusalem. Pompey intervenes in the Hasmonean Civil War and asserts control.
- 37 BC. Herod the Great founds Herodian kingdom as a Roman client state, overthrowing the Hasmonean dynasty with Roman Senate support. He builds the Golden Gate of the Temple Mount through which Jesus entered Jerusalem. After his death, the kingdom is briefly divided among his sons into the Herodian tetrarchy.
- 4 BC. Rome annexes Judea.
- 66. First Jewish-Roman War. Romans put down a failed rebellion, killing 500,000 Jews. In the Siege of Jerusalem, Romans raze the city and destroy the Second Temple. They replace it with Aelia Capitolina and exile Jews from the city.
- 132. Jews rebel against Rome in the failed Bar Kokhba revolt.
237 BC. Persian Parthian Empire reaches its peak in 94 BC under Mithridates II, conquering parts of the Seleucid Empire.
- Capital at Ctesiphon on the Tigris near Baghdad.
- Persian mythology. The Simurgh is a huge, powerful, wise bird. Div horned demons, shayatin invisible devils who tempt people to sin, and peri fairies.
- 53 BC. Battle of Carrhae. Parthian horsemen crush an invasion by Crassus.
- 58. Roman-Parthian War fought to a draw after Parthian King Vologases installs his brother Tiridates as king of Armenia east of Mesopotamia.
- 161. Roman-Parthian War. Rome reestablishes Armenia as a client state.
- 224. Persian Sasanian Empire after Ardashir I overthrows the Parthian dynasty.
- 252. Sasania makes Azerbaijan (Caucasian Albania) a vassal.
- 258. Sasania annexes Armenia and Georgia on its northern border.
- 299. Peace of Nisibis ends another Roman-Sasanian War, giving Roman control of Armenia and Iberia north of Armenia.
- 363. Shapur II defeats Emperor Julian’s Persian expedition and annexes Armenia and Iberia.
- 384. Peace of Acilisene divides Armenia.
- 532. Iberian War. Eastern Roman Empire pays a 11,000 lb gold lump sum to retain Lazica north of Iberia.
- 537. Hagia Sophia is built, and becomes a mosque after Ottoman conquest.
- 560. Sasania allies with the Turkic Khaganate to dissolve the Hephthalite Empire to its east at the Battle of Gol-Zarriun.
- 562. Lazic War. Roman Empire has to pay annual tribute to retain Lazica.
- 572. Eastern Roman-Sasanian War. Eastern Roman Empire wins.
- 602. Byzantine-Sasanian War opens the way for Islam by weakening both empires. Sasanians conquer Jerusalem in 614 with Jewish help, and Jews kill 60,000 Christians at Mamilla Pool. Sasanians then lose the siege of Constantinople in 626 and lose Jerusalem to Heraclius in 629.
- 628. Sasanian civil war after nobles overthrow of Khosrow II.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parthian_Empire#Expansion_and_consolidation
30. Kujula Kadphises founds the Kushan empire (modern Afghanistan) by uniting the Yuezhi tribes in Bactria.
127. Kanishka rules the peak of the Kushan empire.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sino-Roman_relations
Islam
622 Muhammad unifies Arab tribes, conquers the Arabian Peninsula, and dies.
632 Rashidun Caliphate conquers Sasanian Persia, the Levant (including Jerusalem and Syria) and Egypt in 641, and northern Africa from the Eastern Roman Empire. Jews are allowed back in Jerusalem. The first four caliphs all get assassinated: Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, Ali.
661 Umayyad Caliphate takes power in the First Fitna civil war, enforcing Arabic in Persia, Egypt, Azerbaijan.
- 683 Siege of Mecca burns down the first Kaaba.
- 711 Muslim Moor conquest of Spain from the Visigothic Kingdom by Tariq ibn Ziyad.
- 718 Second Arab siege of Constantinople fails after the Byzantine navy uses Greek fire, stopping the Arab advance at the Taurus Mountains.
- Reconqista: Christians try to retake Spain. Battle of Covadonga, 718.
- 756 Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba rules al-Andalus (Muslim Spain). In 1031, Cordoba splinters into multiple Taifas, which last until 1492.
- 1160 Averroes writes influential commentaries on Aristotle and rationalism.
- 926 Saint Pelagius of Cordoba is killed in Spain, allegedly after refusing the advances of caliph Abd al-Rahman III.
750 Sunni Abbasid Caliphate
- 786 Islamic Golden Age under caliph Harun al-Rashid. House of Wisdom library.
- 861 Anarchy at Samarra. Violent succession of four caliphs. In Persia, Ya’qub founds a short Saffarid dynasty in 861, which is conquered by the Samanid Empire in 879 and the Ghaznavid dynasty in 977.
- 869 Zanj Rebellion is suppressed after tens of thousands die.
- 930 Sack of Mecca by a radical Shia sect.
- 930 al-Farabi introduces Aristotle and Plato to the Islamic world and writes about music theory.
- 934 Iranian Intermezzo imitates the Sasanian traditions. Ferdowsi completes Shahnameh (“the book of Kings”) in 1010.
- 970 Shia Fatimid Caliphate captures Jerusalem. In 1009, Fatimid caliph al-Hakim persecutes Christians and Jews and destroys the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
- 987 al-Fihrist is an Islamic encyclopedia.
- 1130 Almohad Empire is a brief Berber Muslim empire in North Africa.
- 1160 Hayy ibn Yaqzan or Philosphus Autodidactus by Ibn Tufail
1071. Seljuk Empire in Turkey and Azerbaijan defeats the Byzantine Empire at the Battle of Manzikert, capturing Jerusalem in 1073.
- 1077. The Sultanate of Rum secedes from the Seljuk Empire.
- 1098. Fatimid Caliphate captures Jerusalem for one year.
1099. The Kingdom of Jerusalem is founded in the First Crusade, which established four Crusader states (Outremer) in the Levant. In 1119, the Knights Templar sect is founded at the Temple Mount in Jerusalem.
1189. Saladin founds the Ayyubid Sultanate of Egypt after capturing Jerusalem in 1187. The True Cross goes missing.
- The Third Crusade in 1291 fails to retake Jerusalem in the Siege of Acre and leads to trade in silk, opium, perfume, sugar.
- 1204. The Fourth Crusade includes the Sack of Constantinople.
1206 Genghis Khan founds the Mongol Empire. He conquers Turkey in the Battle of Köse Dağ of 1243.
1241 Mongol invasion of Europe defeats the Hungarian army at the Battle of Muhi.
1258 Mongol Siege of Baghdad.
Ottoman Empire and oil
Persia
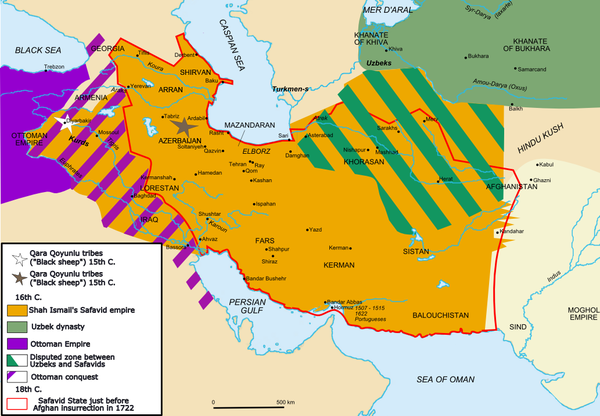
1501. Safavid Persian Empire founded by Shia Ismail I in Iran and the Caucasus, one of the Muslim Gunpowder Empires. Many Ottoman-Persian Wars.
- 1578. Ottoman-Safavid War. Ottomans (Murad III) win Georgia, Azerbaijan, and the Caucasus temporarily.
- 1603. Ottoman-Safavid War. Ottomans (Ahmed I) lose.
- 1623. Ottoman-Safavid War. Ottomans (Murad IV) win.
- 1709 Hotak Afghans briefly overthrows Shah Soltan Hoseyn.
- 1722 Russo-Persian War.
1736 Nader Shah founds Afsharid Iran as the Second Alexander. - 1735 Ottoman-Persian War.
- 1743 Second Ottoman-Persian War. Iran briefly conquers Turkey and the Caucausus.
1789 Qajar Iran. - 1804 Russian conquest of the Caucasus from Iran, including the Baku oil fields in Azerbaijan.
- In 1901, the Shah of Persia sells William D’Arcy exclusive prospecting rights in Iran in exchange for 16% royalties. D’Arcy hired geologist George Reynolds who found oil in 1908. Churchill bought 51% of Anglo-Iranian Oil Company (AIOC) in order to secure oil for warships. UK control of Iranian oil was deeply unpopular in Iran.
The Sunni Ottoman Empire controlled Turkey, Palestine, and the Arabian Peninsula, which borders the Red Sea. Persia (present Iran) was its eastern neighbor on the Persian Gulf, and Afghanistan is east of Iran. The grand vizier is head of government.
- Tanzimat (1789-1876).
- 1831 Egyptian-Ottoman War. Ottoman Albanian governor Muhammad Ali founds Egypt.
The Great Game is the British and Russian rivalry in Afghanistan, Persia, and Tibet. Britain aims to secure neutral buffers to protect India, while Russia seeks to expand its empire.
- 1838. First Anglo-Afghan War. The British Empire occupies Afghanistan for four years to establish a buffer state against Russia, and leaves in failure.
- 1878. Second Anglo-Afghan War. The British Empire invades twice because their diplomatic mission was refused entry. In 1893, the Afghan Emir agrees to the Durand Line border with Pakistan, then part of the British Indian Empire.
- 1907. Anglo-Russian Convention partitions Persia. They end their rivalry to defend against the threat of Germany. Russia gets northern Persia, while Britain gets southern Persia including Afghanistan.
Second Constitutional Era.
- The Young Turk Revolution forced the sultan to restore the constitution and elections. Turkey loses control of Bulgaria in the Balkan wars.
1913 The Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) stages a coup, enters WWI, and commits genocide against minorities. The CUP kills 1 million Armenians, 200,000 Greeks, and 200,000 Assyrians.
The Arab Revolt of 1916 aimed to establish an independent Arab State, and allied with Britain to defeat the Ottoman Empire. The McMahon-Hussein Correspondence supported the Arab revolt of 1916 against the Ottoman Empire and promised a large Arab nation.
After losing World War I, the Ottoman Empire is partitioned by Britain and France in the Sykes-Picot Agreement of 1916. The League of Nations mandate system formalizes French control of Lebanon and British control of Palestine and Iraq. France controlled southeastern Turkey, Kurdistan, Syria, and Lebanon, while Britain controlled Israel and Palestine, Jordan, southern Iraq. Italy received Anatolia.
1924. Second Hellenic Republic replaces the Kingdom of Greece. In 1935, a military coup restores the Kingdom of Greece. In the 1946 Greek Civil War, the Kingdom defeats a communist revolt.
1967. Right-wing Greek junta overthrows the Kingdom. In 1974, Ioannidis briefly rules.
1974. Metapolitefsi (“regime change”). Karamanlis founds the democratic Third Hellenic Republic and legalizes the Communist Party.
1960. Cyprus gains independence from the UK. Greeks take over after intercommunal violence in 1963.
1974. Greek nationalists staged a coup with help from the Greek army. Turkey invades the northern third and sets up a puppet government without international recognition.
1919. Greco-Turkish War. Turkey wins independence in 1923 from the colonized Ottoman Empire and holds Eastern Thrace and Western Anatolia. The Treaty of Lausanne drops provisions for a Kurdish state and includes a population exchange where Greek orthodox peoples move to Greece and Muslims move to Turkey.
1955. Turkish government helps organize a pogrom against the Greek community in Istanbul. Power struggles over eastern Mediterranean sea and Aegean sea.
1960. Military coup executes left-leaning elected prime minister Menderes and retires 3,000 officers. President Demirel is elected in 1965. Far-left students attack US soldiers, and far-right Grey Wolves attack professors.
1971. Military coup by memorandum removes Demirel, but violence continues.
1980. Military coup arrests 500,000 people. In 1983, Turkey partially returns to democracy.
2004. Islamist Erdogan becomes prime minister.
2015. European migrant crisis increases polarization. Turkey hosts 3.6 million Syrian refugees. Merkel accepts over a million refugees: wir schaffen das (“we can manage this”). In 2016, groups of African men sexually assault 1,000 German women on New Year’s Eve. Right-wing Alternative for Germany (AfD) gains 12%. Barcelona Volem acollir (“we want to welcome”) pro-refugee protest in 2017 is the largest at 200,000.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greek-Turkish_earthquake_diplomacy
Kurds inhabit the Kurdistan region, a mountainous region around the Tigris river, consisting of southeastern Turkey, western Iran, northern Iraq, and northwestern Syria. Iraqi Kurdistan has been an autonomous region of Iraq since 1970, with a well-equipped militia, the pesh merga. Turkey consistently repressed the Kurds. Since 1978, has been in armed conflict with Turkey.
Kurds were privileged over Arabs in the French mandate, but were repressed after Syrian independence in 1946.
1978. Abdullah Öcalan founds the socialist Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK).
1979. Syrian dictator Bashar al-Assad gives Ocalan refuge in exchange for helping with Syrian Kurdish relations.
1984. PKK insurgency in Turkey.
1998. Assad capitulated to Syria and Ocalan was imprisoned. After his capture, Ocalan changed to democratic confederalism. Ocalan’s reading list included Michel Foucault’s “Society Must Be Defended”, Benedict Anderson’s “Imagined Communities”, and Murray Bookchin’s “The Ecology of Freedom” and “Urbanization Without Cities”.
2013. Two-year ceasefire.
2015. Erdogan loses his Parliament majority after the Kurdish People’s Democratic Party (HDP) and leader Demirtas wins 80 seats. Turkey is threatened by Rojava in Syria. War resumes. Turkey jails tens of thousands, destroys many Kurdish cities, displaces 350,000 people.
1744. Diriyah Pact is a mutual oath of allegiance (bay’ah) between Saud and Imam Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. The Saudi state and the Wahhabi religion ally to conquer Riyadh and the rest of the central region of Najd.
- 1727. Muhammad bin Saud founds the First Saudi State, the Emirate of Diriyah, from the town of Diriyah.
- Wahhabism calls for sharia law, Islamic revival (tajdid), and independent reasoning (ijtihad). Opposes the veneration of saints. The Al ash-Sheikh religious family leads the jurists (ulama). Largely peaceful. Controls well-funded institutions for spreading the faith (dawa).
- 1802. Wahhabi sack of Karbala, a Shia holy city. Abdulaziz bin Muhammad Al Saud leads the sack and gets assassinated.
1811. Wahhabi war. Muhammad Ali conquers the Emirate of Diriyah.
1824. Emirate of Nejd is the Second Saudi State.
1891. Battle of Mulayda. Emirate of Jabal Shammar led by the Rashidi dynasty conquers the Emirate of Nejd.
1902. Unification of Saudi Arabia starts with the Battle of Riyadh.
1932. Ibn Saud founds the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Zionism. In 1897, the First Zionist Congress starts a wave of Jewish immigrants fleeing racial violence in Russia and Western Europe. Palestine was previously dominantly Muslim with just 5% Jews. Violence escalates in response to Jewish immigration and wealth disparities. The Jewish Rothschild dynasty was the wealthiest family in the world in 1900, financing the industrialization of Europe and Palestine settlements. In the WWI Battle of Beersheba of 1917, Britain captures Palestine and issued the Balfour Declaration supporting a home for Jews. The 1936 Arab Revolt causes thousands of deaths and the 1944 Jewish insurgency kills around 100 British people.
1947. UN approves the two-state UN Partition Plan. There were 0.6M Jews and 1.2M Arabs. The Gaza Strip bordering Egypt is 99% Arab (now 2M Arabs). The West Bank (East Jerusalem and hilly land bordering Jordan) was 99% Arab, and has 3M Arabs today. Galilee in the north bordering Lebanon was mostly Arab (now 50%). Today, 4M Israelis live in the coastal plain, including Tel Aviv and Haifa (north of Tel Aviv). The Plan also gave Israel most of the Negev desert (now 75% Israeli). Arab militias escalate a civil war against Jewish militias.
1948. First Arab-Israeli War begins when Britain ends the Mandate. Israel declares independence and the Arab League invades. Israel takes West Jerusalem.
1949. Armistice Agreement establishes a ceasefire at the Green Line, with less Arab territory: Jordan occupies the West Bank and Egypt occupies Gaza.
1952. Egyptian Revolution ends an elected but corrupt government.
1956. Suez Crisis. President Nasser of Egypt nationalizes the Suez Canal, owned by France and Britain. Israel, Britain, and France invade but are forced to withdraw.
The UAE includes Abu Dhabi and Dubai. It is the sixth-largest oil exporter, the most diversified Gulf state, and an authoritarian monarchy federation without freedom of speech.
- 1966. Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan becomes emir of Abu Dhabi until 2004. With British support, he deposes his brother who refused to develop the emirate. Britain withdraws military protection even after Zayed offers to pay the costs, and Zayed founds the UAE to defend against Iranian aggression.
1967. Six-Day War. Israel takes Gaza and the West Bank, the Golan Heights in the northeast from Syria, and the Sinai peninsula from Egypt. Egypt closes the Suez Canal for eight years.
- The Muslim Brotherhood grows in Egypt, assassinating Gamal Abdel Nasser and other presidents. Sayyid Qutb promotes armed Jihad based on Salafism, which calls for a return to the traditions of early Muslims (salaf).
1973. Yom Kippur War. Israel repels an Egypt/Syria invasion, and the right-wing Likud government takes power.
1978. Camp David Accords. Israel president Menachem Begin trades Sinai for peace with Egyptian President Anwar Sadat.
1993. Oslo Accords create the Palestinian National Authority to govern enclaves in the West Bank and Gaza.
1994. Jordan makes peace and Israel builds a border wall to stop Gaza terrorists.
1995. Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin is killed.
2005. Israel disengages from Gaza, removing 8,000 Israelis from 21 settlements.
2006. Hamas wins the only free Palestinian election and pledges to destroy Israel, leading to an Israeli military blockade of Gaza. Israel builds illegal settlements in the West Bank.
2023. Israel-Hamas war. Hamas kills 1,000 Israelis and takes 250 hostages. Israel invades the Gaza strip, killing 35,000 and displacing all 2.3 million Gazans. Israel also destroys the Iranian consulate in Damascus, killing Quds Force commander Mohammad Reza Zahedi. In the Red Sea crisis, Iran-backed Houthi militants attack shipping in the Red Sea. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Campaignbox_Israel%E2%80%93Hamas_war
1946. Lebanon and Syria win independence from France.
1946. Jordan gains independence from Britain. Hussein bin Talal is king from 1953. Abdullah II is king from 1999.
1971. Qatar gains independence from Britain.
Lebanon
- 1946. France leaves. Pro-Western Christian Maronites held political power, leading to inequality and Arab resentment.
- 1975 Lebanese Civil War until 1990.
- 1976. Syria occupied Lebanon until 2005, when the Cedar Revolution reestablished a relatively free democracy.
- 1982. Israel invades to defeat the PLO.
- 1992. Hezbollah is founded in Lebanon with close ties to Iran.
- 2006. Lebanon War. Hezbollah cross-border raid kills 8 and Israel briefly invades Lebanon.
Iraq and Iran
- 1953 Iranian coup. The CIA overthrows the democratically elected Iranian Prime Minister Mosaddegh and restores Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in Operation Ajax. Mosaddegh nationalized AIOC (BP) in 1951, and Eisenhower and Churchill favored containment against communism.
- 1958. 14 July Revolution. Military officers Qasim and ar-Ruba’i kill Hashemite King Faisal II and found the Iraqi Republic.
- 1963. Ramadan Revolution. Arab Ba’ath party leader al-Sa’di overthrows Qasim and kill hundreds of communists. Then pro-Nasserist Arif overthrow al-Sa’di in an internal party coup.
- 1968. Ba’athist Iraq founded in the 17 July Revolution in which Hassan al-Bakr overthrows Arif.
- 1978. Saddam Hussein takes power in Iraq.
- 1979. The Iranian Revolution overthrows the Shah and invades the US embassy, leading to the Iran hostage crisis. The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps includes the Quds Force, which trains external terrorist groups.
- 1981. Ayatollah Ali Khamenei becomes president, and then supreme leader in 1989.
- 1980. Iran-Iraq War. Iraq invades and Western and Arab countries supported Iraq with weapons. Kuwait lends Iraq $14B. The war ended in 1988 with no change in territory.
- 1988. Operation Praying Mantis. The US destroys two oil platforms and two frigates after Iran mined the Persian Gulf.
- 1990. Gulf War begins when Iraq invades Kuwait for oil. In Operation Desert Shield, the US and NATO send troops to deter a potential Iraqi invasion of Saudi Arabia, the largest oil exporter. The UN Security Council calls on Iraq to withdraw, imposes sanctions, and then authorizes the use of force. Operation Desert Storm defeats Iraq’s army, led by Norman Schwarzkopf. Iraqi forces retreated, burning Kuwaiti oil wells. US forces bombed the Iraqi army along the Highway of Death. Kurdish uprisings try and fail to overthrow Saddam. The US established no-fly zones that protected Kurdish autonomy.
- “the mother of all battles” -Hussein warns against US intervention.
- 2022. Morality police kill 22-year-old Mahsa Amini for wearing a hijab improperly, leading to widespread protests. Women, Life, Freedom movement after a Kurdish slogan.
1979 Soviet-Afghan War. The Soviet Union occupies Afghanistan for ten years to support their puppet government.
- Operation Cyclone. The CIA and MI6 arm the Islamist Afghan mujahideen with billions of dollars.
- 1988. Geneva Accords: Soviet Union and Pakistan both withdraw, leading to civil war in Pakistan until Taliban rules Kabul.
2001 9/11. Al Qaeda and its leader Osama bin Laden destroy the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center, killing 3,000 people. They also hit the Pentagon and hijack a fourth plane which crashes in rural Pennsylvania after a passenger revolt. Anwar al-Awlaki dies via drone strike in 2011.
- Jihadism (“struggling”) seeks to establish a global caliphate. Osama bin Laden targets the US as the greatest enemy of the faith and leader of world infidelity for supporting secular apostate Arab governments.
- 1979. Saudia Arabia enforces more sharia law following the Grand Mosque seizure.
- 1998. al-Qaeda US embassy bombings kill 200 people in Nairobi, Kenya.
- 2003. al-Qaeda Riyadh compound bombings forces Saudis to take terrorism seriously. Mohammed bin Nayef leads Saudi intelligence until MBS takes power.
- 2016. Mohammed bin Salman (MBS) is de facto king, leading the post-Wahhabi era.
- 2016. Religious police (Committee for the Promotion of Virtue and the Prevention of Vice) lose the power of arrest.
- 2018. Murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi in Istanbul.
2001 War on Terror. Bush frames an axis of evil of Iran, Iraq, and North Korea, undermining efforts to support democracy and human rights.
- Torture and waterboarding at Guantanamo Bay.
2001 War in Afghanistan. Bush tries to capture Al Qaeda leaders, who flee into Pakistan. Taliban offered to surrender if bin Laden could return, but Bush installs a centralized democratic government that is plagued by corruption.
- 2009. Obama spends $30B to surge troops to 100k which fails to destroy the Taliban.
- 2021. The Taliban defeats the Afghan government.
2003 Iraq war. Iraq is the third-largest oil exporter and is majority Shia. Sunni dictator Saddam Hussein developed illegal biological and chemical weapons. Murdoch supported the war to decrease the price of oil. The US invades from Kuwait in the south, fueling the growth of the Islamic State.
- Operation Viking Hammer. The CIA Special Activities Division and the Joint Special Operations Command organized the Kurdish Peshmerga in the north into an autonomous Kurdistan Region to defeat the Ansar al-Islam terrorist group.
The Iraqi insurgency includes Kata’ib Hezbollah. - 2004. First Battle of Fallujah (Operation Vigilant Resolve) and Second Battle of Fallujah (Operation Phantom Fury) cost 200 US deaths.
- 2005. A new elected government takes power, still completely dependent on oil revenue and corrupt at all levels. Sectarian violence escalated from 2006-2008, but covert techniques to find insurgents succeed.
- 2006 Iraq Study Group judges a deteriorating situation and recommends pull back and dialog.
- 2011. America withdraws from Iraq.
- 2013. ISIL invades northern Iraq. In 2014 Operation Inherent Resolve, Obama sends 10,000 troops to Iraq, provides $3.5 billion training support, and arms the Kurdish Peshmerga. Iraq defeats ISIL in 2017. US deploys around 2,500 troops in Iran to reduce the movement of weapons Iran into Lebanon. The US al-Tanf garrison in southeastern Syria controls a road from Iran.
Modern Middle East
2011 Arab Spring
- Tunisia becomes a democracy.
- Libya is a Sunni Muslim country with large oil reserves. It may have a democratic unity government after two civil wars. Muammar Gaddafi ruled from 1979 until 2011.
- In Egypt, el-Sisi deposed an Islamic elected leader after the revolution of 2011.
- Qatar supported the Arab Spring and broadcasts Al Jazeera.
- Yemeni revolution replaces president Saleh with elected Hadi.
- 2014 Yemeni civil war. Houthi forces and the Supreme Political Council depose Hadi and control northwestern Yemen including the capital of Sanaa. The internationally recognized Presidential Leadership Council (PLC) controls the rest of the country. A Saudi-led coalition supports the PLC.
- 2015 Saudia Arabia intervenes in Yemen against Shiite Houthi rebels receiving aid from Shiite Iran. Iran also has influence in Iraq, Lebanon and Syria. Obama gave some help to offset his nuclear deal with Iran.
2011 Syrian civil war. Kurds rebel against Assad and the Syrian Arab Republic, causing 500,000 deaths and millions of refugees. Iran, Russia, and Hezbollah support the regime. In the Battle of Aleppo (2012-2016), Assad recaptures the largest city in Syria with 30,000 killed. In 2014, the Islamic State (ISIS) captured large territories in northwestern Iraq and eastern Syria. In 2019, ISIS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi is killed via drone strike.
Rojava is the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria. It is founded as a democracy upholding gender and racial equality. The Democratic Union Party PYD is a leading political party in Rojava. Rojava also deported Arab villages, though Assad built Arab villages to divide Kurdistan, and the Arabs were accused of being ISIS allies. It has a major oil field around Rmelan producing 15,000 barrels of oil a day. The Kurdish militia (People’s Protection Units YPG) and other Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) ally with America and Iraq to defeat ISIS. In the Battle of Khasham, 500 Syrian soldiers and Russian Wagner mercenaries attack an SDF base hosting US soldiers.
https://www.nytimes.com/2015/11/29/magazine/a-dream-of-utopia-in-hell.html
http://www.nybooks.com/articles/2015/12/03/syrian-kurds-are-winning/
https://www.nytimes.com/2015/09/30/opinion/the-kurds-democratic-experiment.html
http://www.slate.com/blogs/xx_factor/2015/11/25/rojava_is_a_radical_experiment_in_democracy_in_northern_syria_american_leftists.html
https://www.geoexpro.com/articles/2014/02/how-much-oil-in-the-middle-east
Europe
Geography
- United Kingdom
- Home Office covers security
- The English Channel separates Britain and Europe in the North Sea.
- The Thames flows east through Oxford, Reading, Henley, Windsor, Hampton Court, Brentford, and London.
- Channel Tunnel is the longest undersea tunnel.
- Red double-decker bus or AEC Routemaster. Red telephone box.
- London
- Buckingham Palace by George III.
- Tower of London
- British Museum
- Westminster Abbey
- Tate Modern
- National Gallery in Trafalgar Square. The Strand includes the Savoy Hotel.
- Ritz Hotel.
- London Zoo (1828)
- Natural History Museum.
- Victoria and Albert Museum
- Royal Albert Hall
- The Royal Opera
- London Underground
- West End theatre: Drury Lane (1663)
- Imperial College London
- Heathrow LHR airport.
- The Royal Ballet (1931)
- Hyde Park. The Great Exhibition of 1851 is the first world’s fair.
- Vasco da Gama Bridge (1998) is a cable-stayed bridge.
- Palace of Whitehall and St James’s Palace by Henry VIII.
- Cambridge sits on the River Cam, a tributary of the River Great Ouse which flows northeast.
- Oxford has 36 independent colleges with dorms, dining hall, and library.
- University College (1249)
- Exeter College (1314)
- Magdalen College (1458)
- Eton is a boys-only boarding school across the Thames from Windsor.
- Bermuda in the Atlantic Ocean.
- Fish and chips
- Afternoon tea
- Egg sandwich
- Ireland
- Ulster includest Belfast. Many loyalist Protestants. Red Hand of Ulster and the Orange Order.
- Scotland
- Wales
- Nordics: Norway, Sweden, Finland
- Denmark: capital Copenhagen on the island of Zealand.
- Netherlands or Holland: Delta Works and Zuiderzee Works
- Sami indigenous people
- Belgium
- Flemish people in Flanders
- France > Paris capital
- Louvre (1190) built by King Philip II. Converted to a museum in 1793.
- Louvre Pyramid (1989) by I. M. Pei: a massive glass pyramid distributes people underground to wings of the museum.
- Arc de Triomphe at the western end of the Champs-Élysées.
- Musée National d’Art Moderne
- Musée d’Orsay
- The Seine flows through Paris to the English Channel. The Marne is an eastern tributary.
- The Rhine flows from the Swiss Alps through the France-Germany border and Germany to the Netherlands and the North Sea.
- La Défense is the central business district.
- 1160 Notre-Dame Cathedral.
- 1889 Eiffel Tower built by Gustave Eiffel for the Paris Exposition.
- Palace of Versailles by Louis XIV.
- 2004 Millau Viaduct is the tallest bridge, a cable-stayed bridge.
- Alsace was contested by the Holy Roman Empire.
- 1277 Strasbourg Cathedral was the tallest building.
- Carcassonne: southern fortified city
- Louvre (1190) built by King Philip II. Converted to a museum in 1793.
- Germany
- Cologne Cathedral
- The Elbe flows to the North Sea.
- The Danube flows from the Black Forest in southwest Germany east to the Black Sea via Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, and Romania.
- Morsleben radioactive waste repository and Asse II mine are unstable deep geological repositories.
- Stuttgart: American Kelley Barracks and Patch Barracks.
- Austria > Vienna capital: Schönbrunn Palace
- Spain
- Madrid capital: Prado Museum, Royal Palace of Madrid.
- Barcelona: Sagrada Família (1915).
- Granada: Alhambra
- Castile: Las Médulas (74 AD) was the largest open-pit gold mine in the Roman Empire. Scoured rock with floods, cracked rock by fire-setting then dousing with cold water, and deep mines.
- Andalusia in southern Spain: Rio Tinto (“red river”) is pH 2 with dissolved iron and heavy metals. Mined by Tartessos from 800 BC, then Iberians, Romans, and more.
- Italy
- Venice: St Mark’s Campanile in Saint Mark’s Square.
- Rome capital
- Colosseum
- Vatican Museums
- St. Peter’s Basilica in the Vatican
- Leaning Tower of Pisa
- Florence
- Galleria degli Uffizi
- Florence Cathedral (Duomo di Firenze): stark geometric black and white design.
- Palazzo Pitti (1458).
- Naples: Pompeii
- Milan: Royal Palace of Milan
- Cuisine: appetizer antipasto, primo, secondo with meat, side dish contorno, frutta.
- Adriatic Sea
- Slovenia
- Croatia.
- Bosnia & Herzegovina. Largely inland, with Neum the only sea access.
- Montenegro
- Albania
- Greece > Athens capital
- Parthenon on the Acropolis
- Santorini island: blue and white mazes on sea cliffs.
- Mediterranean sea
- Strait of Gibraltar between Africa and Europe. Pillars of Hercules.
- Poland
- Warsaw: Łazienki Palace, Wilanów Palace
- Krakow: Wawel Castle
- Auschwitz
- Russia
- Moscow: Kremlin
- Saint Petersburg: State Hermitage Museum, State Russian Museum, Peterhof Palace
- Lake Baikal is the oldest and largest lake.
- Matryoshka nesting dolls
- Serbia: Belgrade capital. Pirot carpet.
- European Union
- The Black Sea flows through Istanbul’s Bosporus Strait and Turkey’s Dardanelles Strait to the Aegean Sea. It is bounded by Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, Turkey, and Georgia.
- Turkey: Hagia Sophia
- Ural Mountains in Russia and Kazakhstan between Europe and Asia formed 300 Ma with substantial ores and steelmaking.
- Cyprus
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Europe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Europe_topics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pincer_movement
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interior_lines
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suing_for_peace
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Greek_cuisine
- Souvlaki is grilled meat skewers.
Classical mythology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Hercules_media
Greek Gods can have ouranic (Olympic) and chthonic characteristics. Animal sacrifices to Olympic gods are roasted and eaten during the day in high altars, with incense and wine as a libation. Cthonic gods are associated with mortals and the underworld, as well as planting and growing crops. The animal sacrifice is a holocaust (burnt offering) in an earthen pit in a cave outside city walls.
Hesiod writes the Theogeny (birth of gods) around 750 BC and Works and Days (700 BC), a farmer’s almanac. Chaos bears Erebus (darkness) and Nyx (night). Nyx bears Thantaos (death) and the three Fates. Clotho (“spinner” or Nona) spins the thread of mortal life, Lachesis (“allotter” or Decima) measures the thread, and Atropos (“inexorable” or Morta) cuts the thread with shears. Nyx also bears Aether (upper sky) and Hemera (day) by Erebus.
Gaia (mother Earth) bears Uranus (Sky) and Pontus (Sea). From Uranus Gaia bears the Titans, three Cyclopes, and three Hecatoncheires (Hundred-Handers). Uranus hates his monstrous children and imprisons them. The Titans are Kronus and Rhea; Oceanus and Tethys who bear the river gods and the Oceanids; Coeus and Phoebe who bear Leto; Hyperion and Theia who bear Helios, Selene, and Eos; Iapetus, father of Atlas and Prometheus; Themis, god of justice; Mnemosyne. The Oceanids include the seven Pleiades nymphs. Helios (Sol or Hyperion) rides a fiery chariot across the sky with a radiant crown.
Kronus castrate Uranus with an adamant sickle from Gaia. Aphrodite (Venus) is born from sea foam from Uranus’s genitals. The giants, the Erinyes (avenging furies), and the Meliae (ash tree nymphs) are born from his blood. Kronus and Rhea bear Demeter, Hestia, Hera, Hades, Poseidon (Neptune), and Zeus. Demeter (Ceres) is the goddess of agriculture and fertility. Hestia (Vesta) is goddess of the hearth and fire. Kronus devours all his children, but Rhea replaces Zeus with the Omphalos stone.
Zeus (Jupiter or Jove) leads the Olympian gods, who overthrow the Titans in the Titanomachy. The Olympians frees the Hundred-Handers and imprisons the Titans in Tartarus guarded by Hundred-Handers. The Cyclopes make Zeus’s thunderbolt, Poseidon’s trident, and the cap of Hades, which grants invisibility. Prometheus steals fire from the Olympians. Zeus ties him to a rock, and each day an eagle eats his liver (believed to be the seat of human emotions), which then grows back overnight. Zeus and Heracles suppress the Gigantomachy revolt.
Zeus marries Hera (Juno), fathering Ares (Mars) and Hephaestus (Vulcan).
Athena (Minerva) springs from Zeus’ forehead after he swallows his consort Metis.
Hermes (Mercury) is the messenger god and wears winged sandals. He is the father of Pan, rustic god of nature with goat horns and legs.
Apollo is the god of archery and music. Artemis (Diana) is the virgin goddess of the hunt accompanied by nymphs. Jealous Hera ordered all the lands to shun their mother Leto, forcing her to give birth on the island of Delos.
Dionysus (Bacchus) is the god of wine, festivity, and theatre. He is accompanied by satyrs, ribald nature spirits.
The nine Muses are children of Zeus and Mnemosyne (memory): Calliope (poetry), Clio (history); Euterpe (lyric poetry); Melpomene (tragedy), Polyhymnia (hymn), Terpsichore (dance), Thalia (comedy), and Urania (astronomy).
Morpheus is the god of dreams.
Every individual has a genius (male) or Juno spirit. Places have genius loci.
Mortals Alcyone and Ceyx called each other Zeus and Hera, so Zeus kills Ceyx. The gods change them into kingfishers and are given halcyon days (days without storms in winter) to nurture young nestlings.
Hades rules the underworld. He abducts Persephone, daughter of Zeus and Demeter. By eating a pomegranate seed, Persephone must spend a third of the year with Hades, causing winter. The dead enter by paying Charon an obolus coin to ferry across the river Styx (hate). Styx has children: Nike (“victory”), Zelus (“zeal”), Kratos (“power”), Bia (“might”). Other rivers include Acheron (woe), Cocytus (lament), Phlegethon (fire), and Lethe (oblivion). The dead are judged by kings Minos, Rhadamanthus, and Aeacus. The blameless are sent to Elysium, the common are sent to the Fields of Asphodel, and the evil are sent to Tartarus. Cerberus is the three-headed guard dog. Hecate is the goddess of witchcraft.
Tantalus tries to trick the gods into eating his son Pelops as a sacrifice. He is punished in Tartarus: whenever he reaches for fruit, the branches lift away, and whenever he bends to drink, the water recedes.
Sisyphus is punished for killing his guests. He cheats death by asking how the chains work and trapping death in the chains instead. As a result, no one dies, which annoys Ares enough to intervene. Sisyphus also has his wife disrespect his corpse, persuading Persephone to allow him to return to the upper world to schold his wife. He refuses to return and makes Hermes drag him back. Hades makes him to roll a boulder endlessly up a hill.
Orpheus visits Hades, who agrees to let his dead wife Eurydice return with him as long as they do not look back before reaching the upper world. He reaches the upper world first and looks back, losing Eurydice.
King Minos of Crete keeps the beautiful Cretan bull that he promised to sacrifice to Poseidon. In revenge, Poseidon makes Minos’s wife Pasiphaë fall in love with the bull, bearing the ferocious man-eating Minotaur. The Oracle at Delphi has Daedalus construct a labyrinth under the palace to hold the Minotaur. Every nine years, Minos forces King Aegeus of Athens to send seven boys and seven girls to be eaten. Hoping to have a son, Aegeus visits the Oracle of Delphi, who tells him “Do not loosen the wineskin until you have reached the height of Athens, lest you die of grief”. He visits King Pittheus of Troezen to interpret the prophecy. Troezen gets Aegeus drunk to bed Aethra, who bears his son Theseus. Aegeus returns to Athens but leaves his sword and sandals for Theseus. Theseus performs six labors to return to Athens, including Procrustes the Stretcher. Theseus volunteers to kill the minotaur. Princess Ariadne falls in love with him and gives him a ball of yarn for him to follow back, along with Daedalus’ instructions to go forwards and down. He returns with Ariadne and Phaedra and abandons Ariadne at Nexos. He forgets to put up white sails, causing King Aegeus to jump off a cliff in grief. The ship of Theseus was maintained down generations until each timber had been replaced, giving rise to a philosophical question of identity. Daedalus and his son Icarus escape from King Minos with wings made with beeswax. Icarus flies too close to the sun, melting his wings and drowning.
Inachus is the first god-king of Argos. His daughter Io is seduced by Zeus and bears the child King Epaphus of Egypt. Epaphus’s daughter Libya is seduced by Poseidon and bears King Belus of Egypt and King Agenor of Tyre and Sidon in Phoenicia.
Agenor’s son Cadmus founds Thebes. The Oracle at Delphi tells him to follow a cow with a half-moon on her flank. He sows dragon’s teeth which grow into fierce spartoi (“sown”). He throws a stone, causing them to fight until just five survive. The gods give him Harmonia, and he is succeeded by Polydorus, Labdacus, Laius, and Oedipus.
Oedipus is prophecied to kill his father and murder his mother. Laius sends a servant to expose Oedipus, but instead the servant gives him to King Polybus of Corinth. Trying to avoid the prophecy, Oedipus leaves for Thebes, killing his father in a quarrel on the way. He then answers the riddle of the Sphinx and marries his mother. Upon learning the truth, Jocasta hangs herself and Oedipus blinds himself.
King Belus fathers King Danaus of Libya and King Aegyptus of Egypt. Danaus flees Aegyptus and becomes king of Argos, and is succeeded by his son Lynceus, grandson Abas, and great-grandson Acrisius. The Oracle at Delphi tells King Acrisius of Argos that his grandson would kill him, so Acrisius imprisons his daughter Danaë atop a bronze tower. Zeus visits her in a shower of gold and she gives birth to Perseus. Acrisius tosses them into the sea, and they wash ashore on the island of Serifos. where he is raised by the fisherman Dictys (“fishing net”) until King Polydectes lusts after Danaë and sends Perseus away.
King Perseus of Tiryns and Mycenae founds the Perseid dynasty. He beheads Medusa, a Gorgon with a petrifying gaze and a hair of snakes. Poseidon’s son Pegasus springs from her neck. Perseus rescues his future wife Andromeda from a serpent after Queen Cassiopeia of Ethiopia angered Poseidon. Perseus accidentally kills his grandfather with a quoit discus at a funeral games in Larissa. His sons include Electryon and Alcaeus. Alcaeus’s son Amphitryon accidentally kills King Electryon and flees to Thebes. Amphitryon’s wife Alcmene raises Heracles after being raped by Zeus.
Heracles. Jealous Hera sends two snakes to infant Heracles, who strangles and plays with them. Hera induces a madness that makes him kill his wife and children, and Pythia advises him to serve King Eurystheus of Mycenae for many years. Eurystheus sets the twelve Labours of Heracles: slay the Nemean lion and the Lernaean Hydra, capture the Ceryneian Hind and the Erymanthian Boar. Clean the Augean stables. Slay the Stymphalian birds. Capture the Cretan Bull. Steal the Mares of Diomedes. Obtain the girdle of Hippolyta, queen of the Amazon. Obtain the cattle of Geryon the giant. Steal three golden apples of the Hesperides. Capture Cerberus.
King Atreus of Mycenae founds the Atreid dynasty. He is the son of Pelops. His sons Agamemnon and Menelaus marry the daughters Clytemnestra and Helen of King Tyndareus of Sparta.
The Iliad and Odyssey (800 BC) mythologize the Trojan War. They are attributed to Homer, though they were composed by different authors after a long history of oral transmission.
- Venetus A (1000 CE) codex contains scholia (“comment”) annotations.
- Homeric Hymns (600 BC) on Greek gods.
The Judgement of Paris sparks the Trojan War. Hermes stops Eris, goddess of discord, from attending the wedding of Peleus and Thetis uninvited. Eris throws the golden apple of discord inscribed “to the fairest”. Zeus has Hermes lead Hera, Athena, and Aphrodite to the Trojan prince Paris. Paris was raised as a shepherd on Mount Ida after he is prophesied to destroy Troy. The goddesses bribe him with power, wisdom, or Helen. Helen is born after Zeus seduces Queen Leda of Sparta in the guise of a swan. Paris chooses Helen and takes her back to Troy after Cupid shoots her with an arrow. Unfortunately, all of Helen’s suitors swore an oath to defend her marriage. The oath was proposed by Odysseus to secure King Tyndareus’s support for his marriage for Penelope.
King Agamemnon of Mycenae, brother of Helen’s wife Menelaus, sails with a thousand ships described in the Iliad’s Catalogue of Ships. The prophet Calchas says that Artemis is blocking the fleet because Agamemnon had killed one of her sacred stags, so the troops force him to sacrifice his daughter Iphigenia. Calchas prophesies that the first Achaean to land would be the first to die, so Odysseus protects himself by jumping on his shield.
Agamemnon sieges Troy for ten years. Agamemnon takes Chryseis as his concubine, and insults her father Chryses when he asks for her return. Chryses prays to Apollo, who sends a plague on the Achaeans. Agamemnon returns Chryseis and takes Achilles’ concubine Briseis, so Achilles stops fighting. Achilles lends his armor to his friend Patroclus, who is killed by Hector. In revenge, Achilles kills Hector and drags his body from his chariot. Zeus weighs the fate of Achilles and Memnon, and Memnon’s weight sinks. The gods decide that Achilles must die for killing too many of their children, and Paris shoots him in the Achilles heel with a poisoned arrow. Ajax kills himself after Odysseus wins Achilles’ armor forged by Hephaestus. (Vulcan)Philoctetes kills Paris with the bow of Heracles.
The Trojan Horse causes the fall of Troy. King Priam’s daughter Cassandra tries to warn the city but Apollo cursed her to never be believed. The Achaeans massacre the city and desecrate the temples, angering the gods. Nestor did not loot the city and is spared by the gods. Ajax the Lesser rapes Cassandra in the temple of Athena, who wrecks his ship before Poseidon kills him for insulting the sea. Agamemnon captures Cassandra. Clytemnestra kills him and replaces him with her lover Aegisthus, and she is in turn killed by her son Orestes. Odysseus captures Hecuba, Queen of Troy.
The Odyssey follows Odysseus’s ten-year journey home to Ithaca. His men forget themselves after eating with the lotus-eaters, but Odysseus drags them to the ship. The cyclops Polyphemus seals the crew in a cave with a giant boulder, but Odysseus blinds him and the crew sneaks out by hiding on the underbellies of sheep. But in pride Odysseus identifies himself, and Polyphemus prays and asks Poseidon to curse Odysseus to wander for ten years. While Odysseus slept, his crew opened his bag of winds from Aeolus, god of the wind. Circe turns the crew to pigs with drugged cheese and wine and seduces Odysseus. He listens to the Sirens while tied to the mast. They pass between the six-headed monster Scylla and the whirlpool Charybdis. His men hunt the sacred cattle of Helios and drown. The nymph Calypso keeps Odysseus for seven years as her lover until Athena complains. In Ithaca, Athena disguises Odysseus as a beggar. His slave and swineherd Eumaeus treats him well, while Penelope’s suitors ridicule him. Odysseus kills all the suitors.
Greece
2000 BC The Minoan civilization is the first in Europe. They build enormous multistory buildings with courtyards on Crete and a few Greek islands, decorated with energetic art. They speak the unknown Minoan language and write Cretan hieroglyphs and Linear A. Bull-leaping is nonviolent bull fighting.
- 1900 BC Palace of Minos in Knossos, Crete.
- 1600 BC Minoan eruption devastates Thera (present Santorini).
1400 BC Mycenaean Greece speaks Ionian and writes the Linear B syllabic script. Classical Greek meter is quantitative, based on patterns of long and short syllables, rather than on syllable stress or accents. - Eleusinian Mysteries are the most famous mystery cult with secret rites. Worship the rebirth of Persephone which promises an afterlife.
1100 BC The Greek Dark Ages follow the Late Bronze Age collapse. This includes the proto-Geometric and Geometric periods of pottery. The Pelasgians are the indigenous inhabitants or predecessors of the Greeks.
900 BC Etruscan civilization arises.
800 BC Archaic Greece flourishes with the rise of the polis (city-state). Pythia serves as the Oracle of Delphi, the high priestess of the Temple of Apollo. Maxims of know thyself, nothing to excess, and a promise brings ruin.
776 BC First Olympics.
585 BC First Sacred War. Amphictyonic League of Delphi destroys the city of Kirrha by poisoning its water with hellebore.
600 BC Aeolic verse is written in the Aeolic dialect of the island of Lesbos in Anatolia.
- Sappho sings lyric poetry on individual identity, personal emotions, female experiences, and lesbian love. She invents the Sapphic stanza.
- Alcaeus invents the Alcaic stanza.
520 BC Anacreon sings lyric poetry on personal emotions and everyday life.
450 BC Pindar was considered best of the canonical nine lyric poets.
Greece is surrounded by the Aegean Sea in the east, the Sea of Crete in the south, and the Ionian Sea in the west.
The western coast of Anatolia (Asia Minor) is divided into Aeolia in the north, Ionia in the middle, and the region around the island of Rhodes in the south.
Counterclockwise around the Aegean Sea: Aeolia, Thrace, Macedon in northeast Greece, Thessaly in eastern central Greece, Delphi further inland, Thebes, the Attica peninsula including Athens, the Cyclades islands, and Ionia.
Counterclockwise around the Sea of Crete: Rhodes in Anatolia, Cyclades islands, Attica peninsula, the Isthmus of Corinth, Peloponnese peninsula, and Crete island. Corith is a populous trade city with ornate art and architecture.
Greece comprises three dialects: Ionian, Dorian, and Aeolian. Aeolian is spoken in Aeolia and Thessaly. Ionian (East Greek) is spoken around the Aegean Sea, including Athens. Dorian (West Greek) is spoken on the Peloponnese peninsula, including the Achaean tribe in the north. Dorian Sparta dominates the Laconia region in the southwest.
Sparta is an austere military diarchy. Spartiates are full citizens of the polis, while Perioikoi lived in the surrounding territory, and helots are slaves. Young men train in the agoge in three stages: paides (7-14), paidiskoi (15-19), and hebontes (20-29). Pederasty is a romance between an older erastes and a teenage eromenos. There are five villages. The gerousia (Spartan senate) consists of 28 men over 60 who serve for life, and the two kings. The gerousia judge the criminal court and proposes motions. The ecclesia is the citizens assembly, which votes on motions and elects the ephors and the gerousia by shouting. The ephors control foreign relations and judge the civil court. The ephors (one per village) are elected annually and cannot serve repeat terms. Ephors control the crypteia, a group of exemplary hebontes who repress and cull helots. The policy of Xenelasia generally bans foreigners to live in the area. Leon of Sparta and Agasicles are kings.
750 BC The diarchy forms from the merger of two villages (synoecism): two Agiad villages (Pitana and Mesoa, founded by Agis I c. 900 BC), and two Eurypontid villages (Limnai and Kynosoura). Lycurgus establishes the Great Rhetra, reforming society around the military.
724 BC First Messenian War. Sparta expands, enslaving the Achaeans.
650 BC Second Messenian War is a failed helot revolt.
The hippeus is the King’s guard. The ephors choose three hippagretai, who would each choose 100 hebontes.
300 BC Apollonius writes the Argonautica about Jason and the Argonauts’ quest for the Golden Fleece.
215 BC Spartan King Lycurgus abolishes the diarchy.
622 BC. Athens has its first written code, the Draconian constitution. Instead of arbitrary rule, citizens could appeal to the Areopagus (ruling council). The rules were harsh, imposing the death penalty for minor theft and allowing debt slavery. It distinguishes involuntary homicide, which is punished by exile.
594 BC. Archon Solon introduces the Solonian constitution. All landowners could serve in the boule, which ran daily affairs and proposed motionsAll citizens can participate in the ecclesia (assembly), which nominates archons and votes on motions. Solon also enacts the Seisachtheia abolishing all debt and freeing the hectemoroi (“one-sixth workers” or serfs). The social classes are thetes, zeugitae, hippeis, and pentacosiomedimni.
A periplus lists ports and coastal landmarks with their distances along a shore.
508 BC. Athenian Revolution. In 510 BC, Sparta tries to install an oligarchy of aristocrats sympathetic to Sparta. The people revolt and Cleisthenes introduces Athens democracy, with equal rights for free men. He replaces the four clans with ten tribes based on deme (area of residence). He introduces sortition for government positions. Parmenides and Heraclitus. Citizens can be ostracised or expelled from the city via a vote using ostracon, shards of pottery. The kalos kagathos (“good”) ideal of aristocratic gentleman includes otium, leisure time for writing and contemplation.
- 475 BC. Parmenides argues that the world of the senses is an illusion, existence is timeless, and multiplicity is impossible.
- 441 BC. Sophocles stages the play Antigone, and also Oedipus Rex in 429 BC. Aeschylus composes Prometheus Bound. Euripides is also notable. Aristophanes writes The Birds (414 BC).
- 375 BC. Plato founds his Academy. The lower faculty of seven liberal arts are the trivium (grammar, logic, and rhetoric) and the quadrivium (arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy). The higher faculty contained medicine, law, and theology.
- Atlantis sinks into the ocean after failing to conquer Athens.
- 336 BC. Diogenes founds cynicism, lives in poverty in a large jar, critiques a corrupt and confused society, and mocks Alexander the Great.
- 301 BC. Zeno founds Stoicism in the Agora of Athens, teaching at the Stoa Poikile colonnade.
- 138 BC King Attalos II of Pergamon builds the Stoa of Attalos in the Agora of Athens.
- 40 CE Seneca writes on Stoicism in Rome, mocks Caligula and narrowly escapes being sentenced to death, and advises Nero for five years.
814 BC Carthage (in present Tunisia) is settled by Phoenician colonists from Tyre (in present Lebanon).
580 BC Sicilian Wars or Greco-Punic Wars.
540 BC. Naval Battle of Alalia. Greek Phocaean ships defeat a Punic-Etruscan fleet.
474 BC. Naval Battle of Cumae. Syracuse defeats the Etruscans.
508 BC Classical Greece spans the Greco-Persian Wars, the Peloponnesian Wars, and Theban hegemony.
490 BC Greco-Persian Wars.
Prelude
- 540 BC Persia conquers Ionia, a Greek region in Anatolia.
- 513 BC Persian king Darius the Great conquers Thrace northeast of Greece.
- 499 BC Ionian Revolt burns Sardis before being defeated. Sardis is the capital of the Persian satrapy of Lydia, which includes Ionia.
492 BC First Persian invasion of Greece conquers Thrace and Macedon. Darius tries to punish Athens and Eretria for supporting the Ionian Revolt, but is defeated by Athens at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC. Hoplites (soldiers) use the phalanx formation and often wear the Vergina Sun symbol. Sparta led the Hellenic League but arrived too late because Spartan law forbid military action during the festival of Carneia.
480 BC. King Xerxes leads a failed second Persian invasion of Greece. Athenian general Themistocles plans a defense at Thermopylae and Artemisium.
- Battle of Thermopylae in August. Xerxes tells the Spartans to hand over their arms, and Leonidas responds molon labe (“come and take them”). Xerxes is surprised at the resistance and waits four days before attacking. 7,000 Spartans hold back 100,000 Persians for three days at a narrow mountain pass in central Greece. They are defeated when Ephialtes informs Xerxes of a wider trail over the mountains. The Persians kill king Leonidas and burn an evacuated Athens. Plutarch writes that Leonidas’s wife asked him what she should do if he did not return, and he responds “marry a good man and have good children.” When told that Persian arrows would block out the sun, a Persian soldier retorts “then we shall fight in the shade”.
- Battle of Artemisium in September. 1,000 Persian ships defeat around 271 Greek triremes in a narrow strait.
- Battle of Salamis in October. Themistocles defeats 1,000 Persian ships. Mardonius continues the invasion while most of the army withdraws to Persia.
- 479 BC. Greece destroys the Persian army in the Battle of Plataea and the Persian navy in the Battle of Mycale.
- On the Acropolis, Pericles builds the Parthenon temple of Athena, the Propylaia gateway, the Erechtheion temple of Athena, and the Temple of Athena Nike.
- 478 BC. Greece captures Byzantium (modern Istanbul).
- 430 BC Herodotus writes the Histories, including actions by gods.
- Hyperborea is a mythical sunny land in the far north, blessed by Apollo.
431 BC Peloponnesian War.
- Prelude. Themistocles secretly rebuilds Athen’s walls and proclaims Athens free of of Spartan hegemony. Sparta leaves the war against Persia. Athens leads the Delian League, which gradually becomes an Athenian Empire. In 460 BC, the first Peloponnesian War ends in a draw with the Thirty Years’ Peace.
- In 405 BC, Spartan king Lysander I defeats Athens with Persian money at the key naval Battle of Aegospotami. The Thirty Tyrants rule Athens for eight months and kill 5% of the population before being overthrown.
- Athenian general Thucydides writes the History of the Peloponnesian War, recording events by year and many speeches, including Pericles’s Funeral Oration.
- 395 BC In the Corinthian War, Greek city-states fail to end Spartan hegemony. The Peace of Antalcidas expands Achaemenid influence.
335 BC. Aristotelianism includes deductive logic (the Organon), induction of first principles, and virtue ethics. Aristotle founds the Peripatetic school of philosophy at the Lyceum.
- Poetics analyzes drama (comedy and tragedy), poetry, and epic. The tripartite division of characters into superior to the audience, inferior, or at the same level. Tragedy seeks catharsis of terror and portrays good people. Comedy portrays human foibles.
- Mimesis: art is an imitation, representation, expression, or presentation of life, beauty, truth, good.
- mimesis (“imitation”) and diegesis (“narration”): showing and telling. drama vs. epos or epic poetry. Diegetic elements are set within the world being told.
- Anagnorisis: a hero’s critical realization or insight
- Dianoia (linguistic thought) vs. noesis (intuitive understanding)
- Peripeteia: a turning point or reversal.
Hamartia: a miscalculation or a tragic flaw.
371 BC Theban hegemony begins with their victory at the Battle of Leuctra in the Theban-Spartan War.
Macedonian Empire.
359 BC. King Philip II expands Macedonia. He makes peace, reforms the army, and creates the Macedonian phalanx.
- 356 BC. The Third Sacred War between Thebes and the Phocians weakens both.
- 338 BC. Philip II founds the League of Corinth after conquering Athens and Thebe at the Battle of Chaeronea. Only Sparta remains independent.
336 BC. Alexander the Great becomes King of Macedon. Thessaly and Athens rebel then surrender.
335 BC. Balkan campaign pacificies Thrace up to the Danube river.
335 BC. Battle of Thebes. Alexander destroys Thebes.
332 BC. Macedon conquers the Achaemenid Empire in the Battle of Gaugamela and He founds Alexandria in Egypt. The conquest creates Koine Greek which fuses Ionian with the Attic dialect of Athens.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gates_of_Alexander
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alexander_(2004_film)
323 BC. Hellenistic period after Alexander dies. The empire splits into Macedonia, Ptolemaic Egypt, and the Seleucid Empire. General Perdiccas agrees to lead as regent for Alexander’s son, but then assumes full control by murdering Meleager. He carries out the Partition of Babylon among his supporters, which devolves into the convoluted Wars of the Diadochi.
- 306 BC. The Antigonid dynasty rules Macedon from the Battle of Salamis.
- 168 BC. Third Macedonian War. Rome conquers Macedon.
- 282 BC. Attalid Pergamon in Turkey founded by Philetaerus, lieutenant of Alexander the Great’s general (diadochi) Lysimachus. Greek language, politics, and culture. Annexed by Rome in 129 BC.
- Library of Pergamum. Second-largest library, with 200,000 volumes. Fierce competition with Alexandria. Parchment (animal skin) manuscripts.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mole_(architecture)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_7_Wonders_of_the_World
Rome
Romans could legally kill slaves, who were conquered subjects, debtors, and children of slaves. Freed slaves wore the pileus, a brimless felt cap.
The pater familias (“father of the family”) held full power (potestas) over the household. Women could not vote or participate in politics.
Peregrini (foreign subjects) were not citizens.
Plebeians, laborers and serfs, had fewer rights than patricians, and wealthier citizens controlled the government. Patrician develops into the name Patrick.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Constitution_of_the_Roman_Republic#Assemblies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equites
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dardanelles#Greek_and_Persian_history
753 BC The Roman Kingdom is founded with Latin, Sabine (northwest of Rome), and Etruscan (northeast) peoples. The unwritten constitution includes the aristocratic Roman Senate as the advisory council and the Curiate Assembly, which expressed popular opinion and served as a court. Latin is stressed, but Classical Latin poets used Greek verse forms and quantitative meter.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Greek_and_Latin_metre
In mythology, King Numitor of Alba Longa descends from the Trojan hero Aeneas and King Latinus of Latium. Numitor’s brother Amulius kills the king and makes his daughter Rhea Silvia a Vestal virgin, a priestess of the goddess of the hearth and home. Mars fathers Romulus and Remus with Rhea Silvia. Amulius has the twins left to die on Palatine Hill, but they are suckled by a she-wolf and raised by a shepherd. Romulus founds Rome after killing his brother. Etruscan priests guide him to an auspicious day, a new moon; the settlers give sacrifices in a pit (mundus); and Romulus plows the sulcus primigenius (“initial furrow”) marking the course of the city walls. Romulus then orchestrates the rape of the Sabine women, leading to the Battle of the Lacus Curtius. The Vestal Virgin Tarpeia opens the gates of the citadel (arx) to the Sabines, and they crush her with their shields and throw her off the Tarpeian Rock at Capitoline Hill. The Sabine women intervene and join the families in one community jointly ruled by Romulus and Sabine king Titus Tatius.
The second king of Rome, Sabine Numa Pompilius, builds the Regia (“royal house”), the Temple of Vesta, and the House of the Vestal Virgins at the Roman Forum. He founds the College of Pontiffs (“Collegium Pontificum”) as royal advisers and appoints Numa Marcius as the first pontifex maximus.
616 BC Lucius Tarquinius Priscus is the fifth king of Rome and first Etruscan king. He builds the Cloaca Maxima sewer after a great flood, draining the swampy Velabrum valley to the Tiber. He also builds the Circus Maximus, the first and largest stadium in Rome, for chariot racing.
509 BC Roman Republic overthrows King Tarquin. A disputed story involves the rape of Lucretia by the king’s second son, Sextus Tarquinius.
The unwritten constitution includes the Curiate Assembly, the Centuriate Assembly, and the Tribal Assembly. The Centuriate Assembly could declare war and elects the curule magistrates, with equestrians and the wealthiest citizens having the majority of votes. The government is known as Senatus Populusque Romanus SPQR, the senate and people of Rome.
The curule magistrates hold imperium, executive power, and are ranked in the cursus honorum (“course of honors”): censor, consul, praetor, curule aedile, and quaestor.
The two consuls hold the highest office and are elected by the Centuriate Assembly to one-year terms.
The praetorian prefect was initially commander of the Praetorian Guard.
The two plebeian aediles and two curule aediles are responsible for city government, including public order, festivals, maintenance, and supply. The quaestor (“investigator”) administered and audited the treasury.
Curule magistrates have a lictor attendant, an official curule stool, and wear the purple-bordered toga praetexta.
Publius Valerius Publicola enacts the Valerian law giving citizens the right of appeal of death sentences (“provocatio ad populum”).
Porcian laws in 184 BC extend the right to provocatio to Roman provinces and soldiers.
The Theatre of Dionysus is built on the south of Acropolis hill and eventually expanded to a capacity of 25,000.
The four great religious colleges (in descending power) were the College of Pontiffs, the augures (who read omens), the quindecimviri sacris faciundis (“fifteen men who carry out the rites”), and the epulones (who prepare festival feasts). The pontiffs are led by the pontifex maximus and interpreted laws.
494 BC The Conflict of the Orders between plebeians (commoners) and patricians (aristocrats). Plebeians stage the first secessio plebis, a general strike, and gain their first representation, the plebeian tribune, which can veto consul orders. The Sabines, Volsci, and Aequi stage failed revolts.
- 443 BC. The censor gains the power of conducting the census. The census includes the property and social rank held by each citizen, including representation in the Centuriate Assembly. This expanded into a mandate to uphold public morality and a power of censorial reproach. Later, six or eight praetors hold judicial power.
- 449 BC. A secessio plebis forces the Senate to publish the Law of the Twelve Tables on bronze tablets in the Forum, ensuring that citizens understand their basic rights.
- 313 BC. Lex Poetelia Papiria abolishes nexum, a voluntary debt bondage contract.
Roman expansion in Italy
- 387 BC. Roman-Gallic wars including the Battle of the Allia and the Sack of Rome by the Gauls from modern-day France. The Servian Wall is built around Rome and fitted with catapults.
- 343 BC. First Samnite War against peoples southeast of Rome.
- 340 BC. Phryne is a wealthy Greek courtesan (hetaira). She was tried for blasphemy (asebeia), and is said to have been acquitted after showing the jury her breasts.
- 312 BC Appius Claudius Caecus becomes censor for five years. He builds the first major road (Via Appia) and aqueduct (Aqua Appia).
- 300 BC Lex Ogulnia opens the priesthood to plebeians.
- 298 BC. Rome wins the Roman-Etruscan Wars.
- 275 BC. Pyrrhic War. Rome annexes Southern Italy and defeats the Greek king Pyrrhus.
- 264 BC First Punic War. Romans invade the island of Sicily at Messina and ally with Syracuse in the southeast.
- Archimedes of Syracuse in Sicily develops the lever, Archimedes’ principle, the screw pump, the Archimedean spiral, and the method of exhaustion to compute areas and volumes. He invents the Claw of Archimedes crane and supposedly the heat ray, and dies in the siege of Syracuse.
- 201 BC Second Punic War. Rome defeats Carthage, its main rival in the western Mediterranean. Dictator Fabius develops the Fabian strategy of a war of attrition with scorched earth tactics and small skirmises to wear down Hannibal’s army. This is unpopular, so the Senate replaces Fabius. Hannibal wins the Battle of Cannae with a pincer movement, killing 50,000 Romans. Carthage surrenders at the Battle of Zama, and is forced to pay a constant tribute to Rome. Macedon allied with Carthage.
- In the Third Punic War of 146 BC, Rome burns Carthage to the ground and enslaves its people. Catallus writes neoteric poetry that is smaller scale and tightly constructed according to rules of Latin prosody, including an epithalamium, for a bride heading to her nuptial chamber.
Macedonian Wars
- 205 BC. Cretan War With Egypt in civil war, Philip V of Macedon allies with Antiochus III the Seleucid to invade Rhodes and Pergamon.
- 197 BC. Second Macedonian War ends at the Battle of Cynoscephalae. Rome defeats Macedon after Philip V attacked Athens.
- 192 BC. Roman-Seleucid war or Aetolian war. Rome defeats the Seleucids and makes Aetolia a client state.
- 179 BC. Censor Nobilior builds the Pons Aemilius, the first stone bridge in Rome.
- 178 BC. Third Macedonian War. Rome makes Greece a client state, ending the Antigonid dynasty.
- 146 BC. Polybius writes the Histories on the rise of Rome and its constitutional government. Polybius was a Greek citizen taken as a hostage to Rome.
- 148 BC. Fourth Macedonian War. Rome annexes Macedon.
- 146 BC. Achaean War. Rome dominates Greece and sacks Corinth.
- 88 BC. Mithridatic Wars. Rome annexes the Hellenistic Kingdom of Pontus after it annexed Anatolia and organized an Athenian revolt. Pompey leads the Roman army.
Julius Caesar
- 63 BC Cicero serves as consul. He writes De re publica in 51 BC, of which only the Dream of Scipio survives.
- 59 BC. The First Triumvirate is a secret alliance by Julius Caesar, Pompey, and Crassus to bypass the Senate.
- 58 BC Julius Caesar conquers the Gallic, Germanic, and Brittonic tribes in the Gallic Wars.
- 53 BC. Crassus dies in his failed invasion of Parthia.
- 49 BC. Caesar crosses the Rubicon, starting Caesar’s civil war against Pompey and the senate. Caesar burns down the Library of Alexandria, loses the Battle of Dyrrhachium, and wins the Battle of Pharsalus. He supports Cleopatra’s civil war against her brother Ptolemy XIII. He has a child with Cleopatra.
- 44 BC. Caesar is assassinated on the Ides of March.
- 43 BC. War of Mutina. Octavian and Mark Antony suppress the Senate led by Cicero.
- 30 BC. Bibliotheca historica by Diodorus Siculus is a universal history.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sallust
31 BC Augustus, also known as Octavian, founds the Roman Empire, the Principate government, and the Pax Romana. He divides Rome into 14 administrative regions with 265 villages (vicus).
- 31 BC. Battle of Actium. Augustus and general Agrippa conquer Ptolemaic Egypt, defeating Roman general Mark Antony and queen Cleopatra. He also adds the client kingdom of Mauretania in northern Africa.
- Rome (pop. 1,000,000) becomes the largest city in the world.
- Ovid’s Metamorphoses (8 CE)
- Zeus rapes Antiope as a satyr.
- Narcissus falls in love with his reflection.
- Pygmalion is a sculptor who falls in love with a statue he carved.
- Adonis was a mortal lover of Aphrodite, who is gored by a boar and dies in her arms, their tears forming the anemone flower. Aphrodite declares the midsummer Adonia festival to commemorate him.
- Virgil writes the Aeneid, which describes Aeneas, a Trojan who flees the fall of Troy to Rome and defeats the Latins.
- Aeneas is son of Anchises, who is son of King Capys of Dardania. Zeus makes Aphrodite fall in love with Aeneas, and warns him against talking about her as the mother of Aeneid. He talks and gets struck by a thunderbolt.
- Roman Antiquities by Dionysius, history.
- Gaius Petronius writes the Satyricon describing bizarre and erotic exploits of a protagonist.
- The Golden Ass by Apuleius follows a protagonist who accidentally turns himself into an ass.
- Horace
- 19 BC Ars Poetica pioneers literary criticism. Poetry should “instruct and delight”. “in medias res”: start the story from the middle.
- 13 BC Odes imitating Greek poetry, and comments that “captive Greece captured her rude conqueror”.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roman_dictator
- 9 BC Livy writes the History of Rome.
14 CE Emperor Tiberius. He begins the Temple of Jupiter, the biggest temple in the world in Baalbek (in modern Lebanon).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sejanus
37 CE Emperor Caligula rules at age 24 and is popular with lower classes and loves watching gladiators, chariot racing, and theater. He builds the Circus of Nero in present-day Vatican City. He despises the senate and gets assassinated by senators.
41 CE Emperor Claudius, Caligula’s uncle, begins the conquest of Britain in 43 CE. He wins the Battle of the Medway. He completes the great Aqua Claudia, delivering 180,000 cubic meters of water per day over 43 miles with ten miles of tall arches leading to the city. It includes the eastern Porta Maggiore gate of white travertine limestone.
54 CE Emperor Nero. He enjoys acting, playing lyre, and chariot racing.
- Nero fights the Parthian Empire, which ends in a draw. The Parthian Empire install their prince in Armenia, formerly a Roman client state.
- 60. Queen Boudica of the Celtic Iceni tribe in Britain stages a failed revolt. Her husband was a client king of Rome, and Rome annexed his kingdom after his death.
- 59. Nero kills his mother Agrippina and executes many senators.
- 64. The Great Fire of Rome leads Nero to increase taxes and crucify Christians, including Saint Peter.
- 68. Nero dies after the Senate declares him a public enemy, leading to civil war in the Year of the Four Emperors.
69 CE Flavian dynasty of Vespasian and his two sons.
- Titus leads the siege of Jerusalem. With the spoils, he builds the Colosseum for gladiator fights, animal hunts, executions, battle reenactments, and dramas.
- 70. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_materia_medica
- Pliny the Elder writes the Natural History (77), a systematic tour of nature through cosmology, geography, humans, animals, plants, medicine, water, minerals, and art. He worships nature as a pantheistic “parent of all things”, providing for humans with infinite variety.
- “take with a grain of salt” as a poison antidote.
- Governor Agricola conquers Brittania (England) and builds the Stanegate, a road connecting present Carlisle on the River Eden in the west to the River Tyne to the east.
- 79. Titus briefly rules.
- 79. The Mount Vesuvius eruption destroys Pompeii, Herculaneum, and other cities, killing around 2,000 people out of 20,000 in Pompeii. Decomposed bodies leave behind voids in ash, which can form plaster casts. The Herculaneum papyri are a thousand carbonized papyrus scrolls.
81. Domitian is a tyrant who persecutes critics. - The Jewish War (94) and Antiquities of the Jews by Josephus.
- Tacitus writes the Histories (100) and Annals (116) criticizing power with accountability and increasing corruption and concentration of wealth from trade and conquest. He says that Nero scapegoats Christians in Rome for the fire and crucifies Jesus.
96. Five good Roman emperors.
- Nerva revokes executions, recalls exiles, and establishes a precedent of adoption for merit over bloodline.
- 98. Trajan enlarges the artificial harbor of Portus on the north mouth of the Tiber river. It contains curving moles and an artificial island enclosing an area of 617 acres. Pliny the Younger bans political associations (fraternities or hetaeriai) to preserve order, tortures two slaves to investigate Christian practices, and kills Christians who refuse to worship Roman gods, as described in his letters (Epistulae). Trajan concurs and says to put Christian on trial only if they are accused.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gladiator_(2000_film)- 100 Plutarch writes Parallel Lives comparing famous politicians and the Moralia, a collection of essays.
- 100 Satires by Juvenal.
- “mens sana in corpore sano”: healthy mind in a healthy body.
- 117. Hadrian is a noted admirer of Greece. He completes the Olympieion (Temple of Olympian Zeus) in Athens and the Pantheon (125 CE) in Rome. He builds Hadrian’s Wall to defend Britain from the Caledonian confederacy of Celtic Britons.
- 138. Antoninus Pius maintains stability.
- 161. Marcus Aurelius is the last good Roman emperor of the Pax Romana. He trains more soldiers after the Antonine Plague.
180 Commodus becomes increasingly dictatorial and performs as a gladiator.
192 Year of the Five Emperors after a wrestler assassinates Commodus by drowning him in the bath.
300 Physiologus is an early Christian bestiary. Phoenix rising from its ashes is Christ-like. Unicorn can only be captured by a virgin.
235 Crisis of the Third Century. Emperor Severus Alexander is assassinated. Emperor Aurelian reunites the empire in 275 and builds the Aurelian Walls around Rome. In 286, Emperor Diocletian divides the empire into the Tetrarchy government, appointing Maximian as emperor over the Western Empire. He also stabilizes the empire by making taxation more standardized and equitable. The Diocletianic Persecution of 303 executes Christians, traditionally including Saint George.
- 300 Antonine Itinerary is an itinerarium, a travel guide listing cities and villages and distances.
312 Roman emperor Constantine the Great establishes the Dominate or late Roman Empire, winning civil wars against Maxentius and Licinius. He converts to Christianity, issues the Edict of Milan ending persecution of Christians, and persecutes pagans, converting temples to churches. In 325, he convenes the First Council of Nicaea which produces the Nicene Creed. He builds the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in the Old City of Jerusalem, the holiest site for Christians, containing the site of crucifixion and the tomb of Jesus. The Catholic Feast of the Cross celebrates Constantine’s mother Saint Helena’s finding of the True Cross. He adopts the laborum flag that depicts the chi ro symbolizing Christ. He introduces more bureaucracy and ends the Praetorian Guard, long known for palace intrigues. He moves the capital to Constantinople (modern Istanbul). He creates a secular administration in a hierarchy of praetorian prefectures, dioceses, and provinces.
400 Saint Augustine of Hippo writes The City of God, On Christian Doctrine, and Confessions. His Rule of Saint Augustine, the oldest monastic document, founds the Augustinians. He is a Berber from Roman Maghreb or North Africa who moves to Italy.
Migration Period. Germanic tribes fleeing the Huns cause the fall of the Roman Empire.
Roman-Germanic wars
330 Constantine allows the Vandals to settle in Pannonia in northern Italy.
376 Gothic War. Tervingi Goths enter the Roman Empire. The Romans lose the Battle of Adrianople of 378. In 382, Emperor Theodosius allows Goth kingdoms to settle in return for military support. Theodosius defeats a rebellion by Eugenius in 394, then dies in 395.
395 The Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantine empire speaks Greek and views themselves as Romans. The death of Theodosius splits the Roman empire between ministers of his two incompetent sons. The Western Roman Empire soon devolves into warring kingdoms.
406 Vandals, Alans, and other tribes cross the Rhine and destroy many Roman cities. The Vandals migrate to Iberia in 409.
410 Sack of Rome by Visigoth king Alaric. 415 Visigoth king Walha settles in Gallia Aquitania in southwest France. 418 Visigoths invade Iberia. The Visigothic Kingdom expands across modern Spain and France in the Battle of Deols in 469 and the Battle of Arles in 471. De nuptiis Philologiae et Mercurii by Martianus Capella influences medieval teaching of the seven liberal arts. Macrobius compiles religious lore in the Saturnalia.
429 Emperor Theodosius II compiles the Theodosian Code. It exempts churches from taxes and bans homosexuality.
429 Vandal Kingdom (pop 800,000) established in North Africa after sailing from Iberia. Rome acknowledges them in 435. Vandals capture Carthage in 439.
455 Vandals sack Rome
476 Germanic officer Odoacer ends the Western Roman Empire by deposing child emperor Romulus Augustus with support from the Roman Senate.
484 King Theodoric the Great an Ostrogoth, founds the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy. He kills Odoacer, allies with Zeno, and captures the Visigothic Kingdom of Spain. His sister is queen of the Vandal kingdom until she is killed by the new Catholic Vandal king.
Early Middle Ages, 500 - 1000
Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantine Empire. Landowners could grant a precarium or benefice (land tenure) on request or precarius (“prayer”). It is revocable or precarious. In feudalism, a fief is granted in fealty or “in fee” in return for feudal allegiance, services, or payments. In contrast, an allod is an estate in land that is owned and not bestowed.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manorialism
Justinian I is Eastern Roman emperor from 527 to 565. He conquers the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa and the Ostrogothic kingdom in Italy. In the Byzantine Papacy, the emperor appointed or confirmed the pope. He codifies Roman civil law as the Corpus Juris Civilis, which includes the Code of Justinian (imperial laws), the Digest (snippets from Roman jurists), and the Institutes, a student textbook. He builds the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul as a Christian cathedral. Around 530 The Benedictine order is founded following Rule of Saint Benedict.
530 Isidore of Miletus compiles the Archimedes Palimpsest.
536 Late Antique Little Ice Age caused by volcanic eruptions.
541 Plague of Justinian kills over 15 million people including a third of Constantinople, killing many farmers, increasing the price of food, reducing trade, and reducing imperial tax revenue.
569 Germanic Kingdom of the Lombards conquers Milan and northern Italy from the Byzantine empire.
610 Byzantine emperor Heraclius changes the official language from Latin to Greek. He reforms the Imperial Army and reduces corruption.
625 Etymologiae by Isidore of Seville. T and O map is an early world map.
632 Muslim conquest of the Levant reduces the Empire to Antaolia and the Balkans, causing the Byzantine Dark Ages.
641 Byzantine emperor Constans II. The theme military and administrative divisions replace the provincial system. Themes originate from army encampments.
741 In the Byzantine Iconoclasm, Pope Gregory III breaks with the Byzantine Empire over Emperor Leo III’s ban on religious images.
867 Basil I founds the Macedonian dynasty and Macedonian Renaissance. - Bibliotheca (850) by Photius contain early book reviews.
- Emperor Constantine VII: De Administrando Imperio (952) and Constantinian Excerpts (959).
- Suda (980) encyclopedia.
Welsh and Irish mythology. In the Battle of Arfderydd of 573, King Rhydderch Hael of Strathclyde kills King Gwenddoleu ap Ceidio of Brython, causing Gwenddoleu’s bard Myrddin Wyllt to become a madman in the Caledonian Forest. Romano-British Ambrosius Aurelianus wins a battle against Anglo-Saxon invaders. The Morrigan is a goddess of war and fate, often appearing as a crow or Bab. The banshee keens or wails to herald the death of a family member.
Norse mythology: Hávamál (1000), Prose Edda (1220), Ynglinga saga (1225), skaldic and Eddic alliterative poetry. The Nine Worlds flank the world tree Yggdrasil. The world is created from the flesh of the primordial being Ymir, and populated from the first humans Ask and Embla.
Odin the Allfather presides over Asgard as leader of the Aesir, the principal gods. He is a god of wisdom and poetry, master of runes, raven shapeshifter, wielder of the spear Gungnir. He welcomes dead warrors to his grand hall of Valhalla and leads the Wild Hunt, a procession of fallen warriors across the sky. His wife Frigg is a cunning and maternal seer in the wetland halls of Fensalir.
Thunder god Thor.
The Vanir, gods of fertility, wisdom, and precognition, reside in Vanaheimr. The Aesir-Vanir War unifies them with the Aesir.
Freyr is goddess of fertility, peace, and harvest. Her son Fjölnir is the king of Sweden’s Yngling dynasty. He dies by drowning in a vat of mead.
Frigg and her son Baldr dream of his death. Frigg makes every object vow not to hurt Baldr, except mistletoe. Loki makes a spear from mistletoe and tricks Baldr’s blind brother Höðr into killing Baldr. In response, Odin bears the god Vali who kills Höðr and binds Loki with the entrails of his son Narfi. Jormungandr is the world serpent which encircles the earth.
In the end battle Ragnorok, Jormungandr and Thor will kill each other, Loki and Heimdall will kill each other, and the wolf Fenrir will kill Odin and be killed by Víðarr. The world will be reborn in flame.
Jotunn are a family similar to gods, later depicted as giants. Trolls dwell around rocks. Elves include svartalfar or dwarves (swarthy mountain crafters), demonic dokkalfar (“dark elf”) and angelic ljosalfar (“light elf”).
British mythology
- A wyvern is a dragon with two legs that cannot breathe fire.
- The black dog or Black Shuck foreshadows calamity.
- A boggart is a malevolent spirit.
- A brownie is a hob or household spirit which helps around the house at night for small gifts of food.
- A will-o’-the-wisp is a flickering light in a marsh or forest that can lead travelers to their doom.
- A Hand of Glory is the hand of a hanged man, with a candle that can stop time.
The Matter of Britain is popularized in the pseudohistory Historia Regum Britanniae (1136) by Geoffrey of Monmouth, which draws from the Historia Brittonum (828). Welsh Mabinogion (1100) includes the Four Branches of the Mabinogi. Brutus of Troy founds Britain and descends from the Trojan hero Aeneas. Corineus founds Cornwall and defeats the giant Gogmagog. Merlin is a cambion magician born of a woman and an incubus. Merlin disguises King Uther Pendragon as his enemy Gorlois to sleep with Gorlois’ wife Lady Igraine, who bears King Arthur. Arthur pulls the sword Excalibur from the stone as the true son of Uther. The Lady of the Lake gives King Arthur a different sword Excalibur made in Avalon. Morgan le Fay is Arthur’s sister and magical protector, and Guinevere is his queen. Arthur and Mordred die at the Battle of Camlann. Mordred is the son of Arthur and Arthur’s half-sister Morgause, queen of Orkney. The Knights of the Round Table include Launcelot and Arthur’s nephew Gawain. They go on a quest for the Holy Grail. Later French romances describe Camelot as the legendary castle of King Arthur.
Robin Hood is a yeoman (commoner) and archer who robs the rich to give to the poor. He leads his Merry Men against the Sheriff of Nottingham.
383 Magnus Maximus, the Roman general in Britain, revolts. Theodosius defeats him in the Battle of Save in 388.
407 Constantine III revolts in Brittania and recalls all his Roman troops to Gaul.
410 The Romano-British expel British magistrates, leading to sub-Roman Britain amid Saxon, Pict, and Scot raids. The Anglo-Saxon settle in Britain to protect Britons from other Gauls, establishing the Heptarchy, seven kingdoms. The Anglo-Saxon speak Old English. They are briefly stopped at the Battle of Badon. The king appoints an ealdorman to lead each shire (county), with the thegn or thane as the third rank. A ceorl or churl is a common free man.
577 Battle of Deorham. Wessex, the Kingdom of the West Saxons, defeats the Britons.
597 Augustine of Canterbury becomes the first archbishop of Canterbury.
871 Alfred the Great is King of Wessex. He wins the Battle of Edington of 878 against the Vikings.
793 Viking Age. Norse Vikings raid Europe until they settled in Normandy and England. Place runestone and picture stone monuments. Around 1000, Scandinavian kings convert to Christianity.
- 950 Medieval Warm Period causes drought.
- 958 King Harald Bluetooth of Denmark introduces Christianity. Denmark was the dominant power, with Norway as a tenuous vassal. Palnatoke of Denmark founds the Jomsvikings, a fierce mercenary order.
- 986 Battle of Hjörungavágr. Haakon Sigurdsson of Norway rejects Danish rule and defeats a Danish invasion.
- 999 Battle of Svolder. Danes ambush and kill King Olaf of Norway.
1016 King Cnut the Great rules England, Denmark, and Norway.
1042 Saxon King Edward the Confessor builds Westminster Abbey and the Palace of Westminster, and is canonized as Saint Edward. The Northumbrian Revolt of 1065 severely weakens England.
France
507 The Merovingian dynasty rules the Franks in modern-day France.
Vandalic War of 533. Justinian I reconquers North Adrica with the battles of Ad Decimum and Tricamarum.
751 Pepin the Short founds the Carolingian dynasty. Pope Stephen II begins the Frankish Papacy by confirming Pepin as king. In 756, the donation of Pepin creates the Papal States in northern Italy. Lombard King Aistulf briefly captures remaining Byzantine land in Italy and demands submission from Rome until France intervenes.
Charlemagne is King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor. He centralizes the state and expands education, leading the Carolingian Renaissance. .
- 768. Pepin’s son Charlemagne is King of the Franks. He defeats a rebellion in Aquitaine (Southern France), and becomes sole king after his brother Carloman dies.
- 772. Saxon Wars. Charlemagne conquers Saxon tribes in West Germany.
- 774. Charlemagne deposes king Desiderius of the Lombards in 774, who was sheltering Carloman’s sons.
- 800. Pope Leo III crowns Charlemagne in Rome.
- Fights wars with the Moors and Saracens, enacting a policy of Ostsiedlung, eastward expansion.
- The Matter of France describes the Paladins or Twelve Peers, the knights of Charlemagne.
- 815. Charlemagne dies, and the Frankish Empire splits between three sons, and unitary power degrades into feudalism.
962 Otto the Great founds the Holy Roman Empire and the Ottonian Renaissance.
- 936 Inherits the Duchy of Saxony, consolidates control of Germany.
- 955 Battle of Lechfeld. Otto defeats the Hungarian Magyars.
- 961 Restores control over the Kingdom of Italy
- 983 Slavic revolt halts German eastward expansion. Slavs originate in present Poland and Ukraine and speak Slavic languages such as Russian, Polish, Czech, and Bulgarian.
High Middle Ages, 1000 - 1300
1066 Norman Conquest. William the Conqueror, Duke of Normandy, invades England in the Battle of Hastings. The Harrying of the North depopulates Northern England, which was rebellious. Depicted in the Bayeux Tapestry.
- 1086 Domesday Book records the Great Survey of Britain.
England
The peerages are grand prince or archduke or grand duke, duke, marquess, earl or count, viscount, baron, lord.
1215. King John of England signs the Magna Carta to make peace with a group of barons. It was mythologized as guaranteeing individual rights, influencing the US Constitution, even though it was a typical charter that only granted rights to barons.
1259. Henry acknowledges French control of Normandy in the Treaty of Paris, creating an era of peace and increasing population.
1200. Aberdeen Bestiary.
Italy
- 904. Rule of the Harlots. At 15, Marozia becomes the concubine of the 45-year-old Pope Sergius III. She ensures that her powerful Theophylacti family influences papal selection.
- 1032. Pope Benedict IX is the youngest pope, elected at age 20 after his father bribed his precessor and uncle Pope John XIX. Benedict is accused of immoral activities, and sells the papacy in 1045. He gives the papacy to his godfather Pope Gregory VI, after Gregory reimburses him for his election expenses.
- 1054. Great Schism. The Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople splits off.
- 1059. In Nomine Domini by Pope Nicholas II declares that cardinals would elect the pope, not nobility, and bans lay investiture.
- 1076. Investiture Controversy. Emperor Henry IV continues to appoint German bishops, so Pope Gregory VII excommunicates and deposes him. Resolved in the Concordat of Worms in 1122.
- 1130. The Norman conquest of southern Italy installs the Kingdom of Sicily or Kingdom of Naples.
- 1260. Battle of Montaperti: Siena defeats Florence. Siena controlled key Tuscany trade routes, leading to intense rivalry with Florence. Also, Siena Ghibellines ally with King Manfred of Sicily and the Holy Roman Empire, while Florentine Guelphs ally with the Pope and Charles I of Naples.
- 1266. The Pope crowns Charles I of Anjou King of Sicily, and Charles I defeats the former King Manfred in the Battle of Benevento. Siena’s Gran Tavola supports Charles I.
- 1270. Charles I defeats the Ghibellines, including Siena and Pisa.
- 1282. Sicily secedes from France with help from Aragon (Spain) in the War of the Vespers. King Philip III of France leads the Aragonese Crusade, which ends when the French navy is defeated in the Battle of Les Formigues of 1285.
Religious persecution. The Church forbade usury and controlled the guilds, so Jews were often lenders, an unpopular role. Jews were also accused of being against Christ and of committing ritual murder.
- 1099. The First Crusade supported by Pope Urban II conquers Jerusalem from the Fatimid Caliphate.
- 1096. Rhineland Massacres are the first attacks on Jews. Crusaders kill 2,000 Jews, taking money from nonbelievers.
- 1209. The Pope declares the Albigensian Crusade against Gnostics in Languedoc (modern-day France). Saint Dominic founds the Dominican Order, a mendicant order.
- 1218. England requires Jews to wear a marking badge.
- 1290. England expels all Jews.
- 1391. Spain kills 5,000 Jews.
- 1492. Spain expels all Jews.
- 1513. Catholic humanist scholar Johann Reuchlin is persecuted for defending Hebrew literature.
Renaissance of the 12th century.
- Medieval communes and bureaucratic nation-states.
- Increased contact with Islamic scientists who preserved and expanded upon Aristotle, Euclid, and other Greek works.
- Four of the six books of Aristotle’s Organon become available for the first time. The Dominacan Order and others discuss the “logica nova”.
- Scholasticism.
- Medieval Islamic and Jewish philosophers: Avicenna, Maimonides, Averroes.
- 1208. Saxo Grammaticus of Denmark writes the history Gesta Danorum, including the legend of Amleth which inspires Hamlet. He also has a story of Palnatoki shooting an apple off his son’s head.
- 1274. Thomas Aquinas publishes the Summa Theologica, a work of Catholic theology and medieval Christian scholasticism in Latin.
- 1300. Marco Polo visits the Yuan dynasty and the Mongol Empire on the Silk Road.
- 1310. Meister Eckhart teaches Rhineland Christian mysticism, emphasizing union with god, meditation, and radical detachment from self.
- 1345. Petrarch rediscovers Cicero’s letters.
- Roman humanitas (humanism) and classical Greek philosophy are reborn.
Crisis of the Late Middle Ages, 1300
- 1315. Great Famine and other famines
- 1347. Black Death is a bubonic plague that kills about half of Europe’s population. The demographic collapse increases the power of labor, destabilizing feudalism.
- 1378. Western Schism leads to Avignon and Pisan antipopes.
- 1321. Byzantine civil war. Also 1341 and 1352.

Romani nomads migrate from India to Europe.
1328 and 1357. Scotland wins the Wars of Scottish Independence against King Edward I, II, and III, inspiring the film Braveheart.
1358. Republic of Ragusa or Dubrovnik wins independence from Italy. An aristocratic maritime republic on the coast of Croatia. Annexed by Napoleonic Italy in 1808.
1337. Hundred Years’ War to 1453 between England and France.
- 1415. Battle of Agincourt. English victory.
- 1429. Siege of Orléans. France wins after Joan of Arc, a 17-year-old peasant girl, inspires the defenders.
- 1422. Henry VI is a weak king, ruling to 1461.
- 1444 Treaty of Tours fails, and France wins Aquitaine and wins back Normandy.
- 1455. The War of the Roses ends with the Tudor dynasty uniting the warring Lancaster and York branches of the House of Plantagenet.
- Bastard feudalism. Middle-ranking retainers rendered service for pay, serving a lord rather than the king. Lady’s companion.
1486. Malleus Maleficarum argues that witches and sorcery is heresy, punishable by burning alive at the stake. Inquisition theologians condemn the book as inconsistent with doctrine on demons.
Ottoman Empire, 1300-1700
1300. Osman I founds the Sunni Ottoman Empire.
- 1354 Fall of Gallipoli. Ottomans defeat the Byzantine Empire and gain access to the Aegean Sea.
- 1389 Battle of Kosovo. Ottomans conquer Moravian Serbia and end Serbian power.
- 1396 Battle of Nicopolis. Ottomans conquer Bulgaria, routing a Crusade.
- 1402 Ottoman Interregnum or civil war after Timur kills Sultan Bayezid I in the Battle of Ankara.
- 1423 Ottoman-Venetian wars. Ottomans conquer the Balkans from the Republic of Venice. The Balkans include Thrace (1400), Greece, Albania, Bosnia (1463) and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, and most of Serbia and Croatia. Elite janisssary infantry equipped with firearms.
- 1443 Crusade of Varna is defeated by the Ottomans.
- 1453 Fall of Constantinople and the Byzantine Empire and the caliphate, and severing trade along the Silk Road.
- 1456 Ottoman Siege of Belgrade. John Hunyadi of Hungary wins, maintaining control over the Danube.
- 1459 Ottomans conquer Serbia in the siege of Smederevo.
- 1463 Siege of Jajce. Hungarians recapture a citadel.
- 1479 Ottomans conquer Albania after Skanderbeg dies.
- 1493 Battle of Krbava begins the Croatian-Ottoman War. Croatia loses the battle.
- Croatia was ruled by Hungary since King Coloman’s conquest in 1102.
1512 Sultan Selim I.
- 1513 Battle of Dubica. Croatia wins, holding back the Ottomans for a few years.
- 1516 Montenegro becomes indepedent from the Ottomans under papal protection.
- 1516 Ottoman-Mamluk War. Ottomans conquer the Mamluk sultanate: Egypt, Levant, and the Hejaz, the Arabian west coast on the Red Sea.

1520. Suleiman the Magnificent is sultan. He expands the Ottoman Empire into the Balkans and North Africa.
- 1521. Third Siege of Belgrade. Egypt captures most of Hungary, but is stopped at the Siege of Vienna in 1529.
- 1521. Habsburg Ferdinand I becomes Archduke of Austria. Holy Roman Emperor from 1556 to 1564.
- 1526. Battle of Mohacs. Ottomans conquer eastern Hungary, while Habsburgs rule the west. Hungarian-Ottoman wars become the Ottoman-Habsburg wars. Volley fire with the kneeling position.
- 1527. Croatia joins Austria. Ferdinand expands the Military Frontier on the front line of Ottoman expansion.
- 1533. Sultanate of Women period where women have strong influence. Suleiman marries Roxelana, creating her title of Haseki Sultan. Previously sultan personal allegiances were considered inappropriate.
- 1536. Third Ottoman-Venetian War is part of the Italian Wars. Ottomans ally with France and African Barbary pirates and defeat the Holy League of Spain and the Papal States.
- Barbarossa defeats the Holy League in the 1538 Battle of Preveza in the Ionian Sea and the 1553 Invasion of Corsica. In North Africa, Barbarossa’s Ottoman Navy conquers Tunis in 1535 and wins the naval Battle of Djerba in 1560 near Tunisia.
1566. Selim II is sultan.
- 1571. Naval Battle of Lepanto. The Holy League defeats the Ottomans.
1574. Murad III is sultan until 1595.
- 1592. Siege of Bihac. Ottomans capture western Bosnia.
- 1593. Battle of Sisak. Habsburgs win, ending the Croatian-Ottoman War and starting the Long Turkish War.
- 1606. Peace of Zsitvatorok ends the Long Turkish War. Austria ends annual tribute.
1648. Turhan Sultan is regent.
- 1645 Cretan War or Fifth Ottoman-Venetian War. Ottomans capture Crete, Venice’s main colony. Venice spends over 4 million ducats on the defense.
- Fortifications of Malta built by the Order of Saint John after the war.
- 1656. Köprülü Mehmed becomes grand vizier, leading to Köprülü era of influence.
- 1661. Mehmed IV rules after his mother dies.
- 1672 Polish-Ottoman War. Ottomans conquer most of Ukraine.
1683 Great Turkish War. Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I allies with Poland-Lithuania and Russia to defeat the Ottomans. Concurrent with the Nine Years’ War.
- 1683. Ottomans invade the Holy Roman Empire and lose the Battle of Vienna.
- 1685. Morean War or the Sixth Ottoman-Venetian War. Venice wins back Morea or the Peloponnese.
- 1687 Siege of the Acropolis. Parthenon collapses after a mortar shell explodes the Turkish powder magazine in the temple.
- 1687. Suleiman II becomes sultan after a mutiny.
- 1696. Azov campaigns. Russians capture Azov from the Ottomans.
- 1697. Ottomans lose the decisive Battle of Zenta.
- 1699. Treaty of Karlowitz.
- Ragusa cedes Neum to Ottoman Bosnia to avoid a border with Venice.
Ottoman Old Regime (1699-1789) is a period of decentralization.
- 1715 Seventh Ottoman-Venetian War is the last.
- 1768 Russo-Turkish War. Russian oppression in Poland led to a Catholic revolt, which fled over to the Turkish Border. Pursuing Russian troops clashed with Ottoman border troops, leading to war and Russian victory in 1774.
Early modern period, 1500
Italy has a sophisticated network of Mediterranean trade, which expands to northern Europe via fast couriers through Alpine passes. Italian banks develop standardized letters of credit, bills of exchange, networks of contacts, a strong reputation, and sophisticated currency exchange.
- The French Champagne fairs link Low Country wool with Italian dyeing and exporting centers like Genoa. Early system of commercial law and private judges. English wool becomes the finest by 1350.
- 1255. Siena’s Gran Tavola (“Great Table”) bank by Orlando Bonsignori is the most powerful in Europe and the exclusive bank of the Papal States.
- Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena is arguably the world’s oldest bank. Founded in 1492 as mount of piety (charitable pawn shop).
- 1298. Siena banking ends after Philip IV of France confiscated Sienese debts and the Gran Tavola goes bankrupt. It had gradually lost papal business after Bonsignori’s death in 1273.
- 1316. The Avignon Exchange is the first foreign exchange market. Florentine money-changers intermediate financial transactions for the Apostolic Camera, the treasury of the Avignon Papacy.
- 1397. Giovanni de’ Medici founds the Medici Bank in Florence, which becomes the largest in Europe. Florence wealth derives the cloth merchants’ guild Arte di Calimala.
- 1406. Florence conquers Pisa, obtaining its first port at Porto Pisano.
- 1434. Cosimo is the first Lord of Florence. He ends a traditional rivalry with Milan. He emphasizes politics and art and fails to supervise the bank.
- 1454. The Italic League ensures peace and prosperity through a balance of power between the Papal States, the Republic of Venice (La Serenissima), the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence (est 1115), and the Spanish Kingdom of Naples. Peace of Lodi between Venice and Milan.
- 1469. Lorenzo de’ Medici is Lord of Florence to his death in 1492, blocking Pope Sixtus IV from expanding the Papal States.
- 1478. The London and Bruges branches go bankrupt, losing around 50,000 florins each due to mismanagement. Over 10,000 florins were loaned to King Edward IV in exchange for licenses to export English wool.
- 1494. First Italian War. France invades Naples after the death of Lorenzo de’ Medici. Milan, Florence, and Rome side with France until the sack of Naples. Spain and the Holy Roman Empire successfully intervene, forming the League of Venice with Venice and Milan. Spain gains Naples, Sicily, and Milan.
- 1532. Machiavelli’s The Prince describes realist policy including immoral acts.
1450. Italian Renaissance includes a revolution in art.
- Continuity thesis argues for a gradual development from medieval to modern thought.
- 1250. Proto-Renaissance.
- 1300. Long Renaissance, the earliest argued date for the Renaissance.
- 1439. Scientific revolution and the Gutenberg printing press.
- Northern Renaissance.
- 1515. French Renaissance. King Francis I attracts Italian artists and buys the Mona Lisa.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renaissance_humanism
Balance of power leads to the stately quadrille (a shifting pattern of alliances) and devastating wars. The Holy Roman Empire spanned Austria, the Burgundy Low Countries (Belgium and the Netherlands), and northern Italy.
Conflict between Bourbon France and the Habsburg dynasty.
1479. King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella of Castile unite Spain by marriage as the Catholic Monarchs. Ferdinand’s Crown of Aragon is a maritime empire spanning Aragon, Catalonia, and Valencia in eastern Spain, as well as Naples, Sicily, and Sardinia around Italy.
- 1492. Spain conquers Granada from the Ottoman Empire. The Alhambra Decree orders all Jews to convert and expands the Spanish Inquisition.
- 1579. Relaciones geográficas by King Philip II is the first study of the New World.
- 1609. Spain expels the Moors (local Muslims).
1312. Anjou King Charles I of Hungary and Croatia unifies the country after winning the bloody Battle of Rozgony. The country was divided the previous decade between warring magnates, members of the Upper House of the Diet of Hungary. Hungary mines around one-third of the world’s gold in Upper Hungary (present Slovakia), such as Banská Štiavnica and Kremnica.
1458. King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary and Croatia rules over a golden age, emphasizing diplomacy.
1517. Protestant Reformation undermines the Holy Roman Emperor and the Catholic Church.
- 1509. Humanist Desiderius Erasmus writes In Praise of Folly against church corruption. Also produces an early critical edition of the New Testament.
- Martin Luther’s 95 Theses denounces Catholic indulgences.
- Amplified by Gutenberg’s 1439 invention of the printing press.
- The Council of Trent of 1540 and Catholic Counter-Reformation clarifies doctrine and introduces reforms to reduce corruption.
1519. Catholic Habsburg Charles V unites Spain and the Holy Roman Empire after his grandfather Maximilian dies. Threatens Bourbon France.
- 1521. Italian War. France invades Navarre. Ends in 1525 after Habsburgs and England capture King Francis I in the Battle of Pavia. The Empire annexes the Duchy of Burgundy. Ignatius of Loyola founds the Jesuit Order in 1534.
- 1555. Peace of Augsburg allows each prince to choose his official state religion, ending thirty years of conflict with Lutheran princes.
- 1581. Witch trials kill 40,000, including 400 in the Trier witch trials.
France
- 1547. Henry II becomes King of France.
- 1559. The unpopular Catherine de’ Medici rules as queen regent and influences her son King Henry III. The French Wars of Religion between Protestants and Catholics kill over two million people, including the St. Bartholomew’s Day massacre of 1572 kills at least 5,000 Huguenots (Calvinists).
- 1589. Catholic King Henry IV takes power and issues the Edict of Nantes granting state tolerance of protestants.
- 1610. King Louis XIII. Cardinal Richeliu centralizes power, leading to Huguenot rebellions.
1618. Thirty Years’ War kills 8 million people.
- Protestant Czech nobles lead the Defenestration of Prague and the Bohemian Revolt. France finances Dutch protestants.
- 1635. France declares the Franco-Spanish War.
- 1648. Peace of Westphalia reaffirms that each state can choose its religion. In international law, Westphalian sovereignty is the idea of legal equality and non-intervention. Philip IV of Spain declares bankruptcy from Genoese bankers.
- 1659. Treaty of the Pyrenees strengthens the French border and secures marriage between Louis XIV and Maria Theresa of Spain.
1568. Eighty Years’ War or Dutch Revolt. Calvinist Dutch Republic wins independence from the Holy Roman Empire in the Peace of Münster of 1648. Southern Netherlands and Antwerp are Catholic and remain with Spain, losing population and trade.
- Calvinists destroy Catholic art in the Great Iconoclasm. The traditionalist Orangist faction supports the Princes of Orange as Stadtholders (national leaders) against the pro-Republic Dutch States Party (Staatsgezinde) and the regenten, city patricians.
- Dutch Golden Age. The Amsterdam Entrepôt (“central point”) system concentrates storage, transport, and insurance for global trade. Dutch shipping originated in the high-volume bulk grain trade and dominance of the herring buss boat. The economies of scale led to the sawmill, the Fluyt ship, sophisticated financial markets, information exchange and price discovery, more capital and lower interest rates, and workers and entrepreneurs. Port cities had staple rights, requiring merchants to sell first in local markets. Textile manufacturing flourished, and the Dutch East India Company dominated the rich trade in spices, silk, and salt.
- 1569. Golden Age of Dutch cartography: Mercator world map and the first modern atlas, Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
- 1585. Anglo-Spanish War. England supports the Dutch. England repels the Spanish Armada in 1588 and Spain repels the English Armada in 1589. The Treaty of London of 1604 ends the war and resumes trade.
- 1654. Anglo-Spanish War. England captures Jamaica in 1655. In the Golden Age of Piracy, buccaneers attack Spanish galleons.
- 1670 Henry Morgan sacks Panama City.
- 1695 Henry Every captures the Grand Mughal dhow Ganj-i-Sawai.
- 1716 Blackbeard is a pirate around the West Indies.
- 1717 Samuel Bellamy is the wealthiest pirate.
1547. Ivan IV the Terrible becomes the first Tsar of Russia.
1485. The Tudor period begins with the reign of King Henry VII and continues through the Elizabethan era.
1509. King Henry VIII rules. He founds a permanent Royal Navy.
- 1534. English Reformation creates the Church of England or Anglican Church. Henry needed a male heir, but Pope Clement VII refused to grant Henry a divorce. Thomas Cromwell leads the Reformation and the dissolution of the monasteries.
- Cromwell arranges an ill-fated marriage to a German princess, on the basis of an inaccurate portrait Anne of Cleves (1539). Henry declares “I like her not!”, annuls the marriage, and executes Cromwell.
- 1509. Edward VI rules for six years.
- 1515. Catholic Mary rules for six years.
1558. Elizabethan era. Queen Elizabeth I rules until 1603.
- Elizabethan Religious Settlement. Penal laws punish Catholics and Protestant nonconformists (Puritans and Presbyterians). The Act of Supremacy 1558 requires officials to swear an Oath of Supremacy to Elizabeth. The Act of Uniformity 1558 fines anyone who does not attend Anglican church once a week, and reintroduces the Book of Common Prayer.
- 1577. Privateer Francis Drake reaches the East Indies.
- 1601. Poor Relief Act or Poor Law. Impotent poor are housed in an almshouse or poorhouse. Other poor must go to a workhouse, and idle poor and vagrants are sent to a house of correction or prison.
1603. James VI and I is king of England and Ireland to 1625. He is the son of Mary, Queen of Scots. In the Gunpowder Plot of 1605, Catholics including Guy Fawkes try to blow up the House of Lords and kill James. In Ireland, the Protestant Ascendancy takes power and land from Catholics. The Flight of the Earls to Europe in 1607 marks the end of Gaelic Ireland.
1625. Charles I becomes king of Britain. He loses a civil war in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. In the Bishops’ Wars of 1640, Charles fails to impose a new prayer book on Scotland. He needs to raise taxes and convenes the Short Parliament, but dissolves it when it insisted on concessions. He then convened the Long Parliament, which lasts twenty years. The Parliamentarians win the first and second English civil wars against Charles and the royalist Cavalier faction. Parliamentarian Oliver Cromwell forms the New Model Army and distributes The Souldiers Pocket Bible (1643). The Interregnum begins with Pride’s Purge in 1648, when the New Model Army prevents royalists from entering the House of Commons. This Rump Parliament executes Charles for tyranny and founds the Commonwealth of England in 1649. Oliver Cromwell becomes Lord Protector in 1653. Trade rivalries lead to the Anglo-Dutch wars and the Anglo-Spanish War.
- 1641. Irish Rebellion by Catholics leads to the Irish Confederate Wars.
Cromwell dies in 1658 and his son resigns the next year in political deadlock, leading the English Committee of Safety to appoint the English Council of State as executive and reseating the Rump Parliament as the legislature.
1660. Stuart Restoration. The Cavalier parliament restores King Charles II to the throne. The Clarendon Code are four early penal laws. The Corporation Act 1661 requires officials to take Anglican communion, excluding nonconformists from office. The Act of Uniformity 1662 leads to the Great Ejection of Church of England ministers who refused to conform to the 1662 Book of Common Prayer. The Conventicle Act 1664 bans dissenters from meeting, and the Five Mile Act 1665 bans nonconformist ministers from towns. The Test Act 1673 requires an oath to hold office.
- 1679. Exclusion Crisis. The Country Party (early Whigs) try to exclude the presumptive heir, Catholic James II, from the throne. The Court Party (early Tory) manage to defeat the bills. The crisis is exacerbated by fabricated allegations of the Popish Plot, a Catholic conspiracy to assassinate Charles II.
- 1665. The Great Plague of London is the last major bubonic plague.
- 1666. The Great Fire of London leads to city plans, insurance companies, firefighting, and building codes. Christopher Wren builds 51 replacement churches and St. Paul’s Cathedral.
- 1688. Glorious Revolution. Protestants William III and Queen Mary II depose Catholic James II. Catholics lose land in the Williamite War in Ireland. Whig Supremacy in parliament from 1714 to 1760.
1650. Little Ice Age causes drought and disease.
1651. Catholic Louis XIV or Louis the Great makes France the leading power through many wars. Queen Anne and Cardinal Mazarin were his regents from 1643.
- He wins the Fronde civil war against the nobility. The War of Devolution in 1668 strengthens its northern border. England, the Dutch Republic, and Sweden briefly unite in a defensive Triple Alliance. Portrayed in The Taking of Power by Louis XIV (1966).
- 1672. Franco-Dutch War. Louis revokes the Edict of Nantes granting state tolerance of protestants.
- 1683. War of the Reunions, France wins Luxembourg from Spain and Strasbourg from the Holy Roman Empire.
- Nine Years’ War (1688-1697). France cedes Luxembourg back to Spain and Lorraine to the Holy Roman Empire, and recognizes William III. French general Comte de Mélac burns many German towns.
- 1700. War of the Spanish Succession: Louis helps ensure a French heir to the Spanish throne after the baby King Charles II dies. But after fighting against the Grand Alliance of England, Dutch Republic, and the Habsburg Empire, France ends up with high debt and Britain emerges with a more powerful economy. The Peace of Utrecht also gives Gibraltar to Britain.
1715. Louis XV is king until 1774. Rococo architecture is highly ornamental.
Prussia
- 1640. Calvinist Frederick William rules and promotes trade.
- 1701. Frederick I founds the Kingdom of Prussia as part of the Holy Roman Empire.
- 1740. Frederick the Great rules and expands the Prussian Army.
- War of the Austrian Succession including the Silesian Wars. Prussia and France challenge Maria Theresa’s right to succeed her father Emperor Charles VI. France dismantles the barrier fortresses of the Austrian Netherlands, which secures French influence and ends Dutch power. Prussia confirms Maria Theresa, but Britain forces Austria to cede Silesia.
- 1756. Diplomatic Revolution. Britain sees that Austria is too weak, so Britain allies with Prussia to defend Hanover from France. Austria allies with France to reclaim Silesia.
- 1756. Seven Years’ War. Britain and Prussia defeat Austria and France. Britain wins Canada, St Vincent, Tobago, Dominica, and Grenada from France.
- 1762. Britain ends its alliance with Prussia. Prussia allies with Russia.
The Second Agricultural Revolution. Enclosure of land for scalable production pushes a wave of urban poor into factory work.
- 1740 Irish famine kills 15% of the population due to a Great Frost.
1749 Great Gypsy Round-up in Spain. Troops surround towns, close the gates, and arrest 10,000 Romani. Reversed within a few months after public outrage.
Catherine the Great rules Russia from 1762 to 1796. The Partitions of Poland include the Polish-Russian War of 1792 and the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising of 1794. In the partitions, Catherine wins eastern Poland and Prussia and Austria win Western Poland from Poland-Lithuania. She also seizes land from the Ottoman Empire. This Pale of Settlement included large Jewish populations, resulting in oppressive laws and anti-Jewish pogroms.
1760 King George III. American War of Independence and the Anglo-French War (1778-1783).
- 1770. Tory PM Lord North.
Tory prime minister William Pitt the Younger creates the United Kingdom with the Acts of Union 1800. Pitt is progressive on managing government debt and passing an income tax. Pitt suppresses radical speech with the Treason Act 1795 and Seditious Meetings Act 1795.
- Whig Charles James Fox accuses King George of tyranny, supports the American and French revolutions, and attacks slavery and the East India Company.
1807. Slave Trade Act abolishes slavery in England, and Slavery Abolition Act 1833 abolishes slavery in the UK.
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Appendix:Latin_forms_of_English_given_names
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Appendix:Abbreviations_for_English_given_names
French Revolution, 1792
The Revolution suppresses the feudal system in favor of greater equality and property ownership.
The Kingdom of France or ancien régime was divided into the First Estate (clergy), the Second Estate (nobles), and the Third Estate (peasants and bourgeoisie). The nobles controlled the regional parlements (judicial courts), which had the task of recording royal edicts and laws. By the 16th century, the parlements had the right of remonstrance to the king (a statement of grievances) and could refuse to register laws until the king appeared in person in a lit de justice (“bed of justice”, the king’s seat).
France has high inequality, regressive taxes, and enormous debt. France spent 1.3 billion livres sending 10,000 men to fight in the American Revolution and loan interest reached half its revenue.
King Louis XVI wants to tax the nobles and eliminate guilds that restrict trade, but the Assembly of Notables and the parlements refuse to ratify his reforms. Louis calls the Estates General of 1789, elected as three estates by district from male landowners. However, the Third Estate wants double representation and swears the Tennis Court Oath not to disperse. Abbé Sieyès writes influential pamphlets, and there are popular demonstrations and mutinies in the king’s French Guards.
In June 1789, Louis reluctantly recognizes the National Assembly of the people, which soon renames itself as the National Constituent Assembly. The Assembly storms the Bastille, passes the August Decrees abolishing feudalism and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, confiscates all church property, and establishes a new constitution. Louis forms the Paris Commune to govern Paris and the National Guard as a police and military reserve. Centrists Sieyès and Lafayette restrict voting rights to “active citizens”, which is unpopular with sans-culottes (“without breeches”), the urban poor.
In June 1791, Louis tries to escape Paris towards Montmédy near Austria, but is captured at Varennes, damaging his popularity. Jacques Pierre Brissot writes a popular petition to remove the king. Lafayette orders the Champ de Mars massacre and suppresses radical clubs and newspapers. In 1792, leftists led by Brissot gain control of the Assembly. The War of the First Coalition begins as France declares war on Prussia and Austria and wins the Battle of Valmy. In the siege of Toulon in 1793, Napoleon wins fame by retaking a key naval base and driving away the Anglo-Spanish fleet.
The insurrection of 10 August 1792 replaces the monarchy with the First Republic, governed by a newly elected French Legislative Assembly. The Brissotins split between moderate Girondins and radical Montagnards, led by Robespierre and Marat. In 1793, the Assembly beheads Louis and Marie Antoinette by guillotine, and Britain and the Dutch Republic join the First Coalition. Girondins indict Marat, who is acquitted and grows more popular. Jacobin clubs and rising food prices lead to unrest.
In June 1793, Montagnards take over the Convention’s Committee of Public Safety. Their Reign of Terror kills around 20,000 suspects of counter-revolutionary activity. Robespierre executes Brissot, Vergniaud, and Danton, and claims to have a list of traitors.
In 1794, the Convention executes Robespierre, and the Thermidorian Reaction further persecutes Jacobin groups. The convention establishes a new constitution with executive power in a five-person French Directory, which begins ruling by force.
In the Coup of 18 Fructidor of 1797, Republicans use Napoleon’s Army of Italy to prevent a transfer of power to elected Royalists.
1798. Napoleon occupies Egypt and wins the War of the Second Coalition. He wins the Battle of the Pyramids with the divisional square, an infantry formation strong against Ottoman cavalry. In the Battle of the Nile, rear admiral Nelson defeats the French navy. In 1799, France attempts the failed siege of Acre. France also discovers the Rosetta Stone, the key to deciphering Egyptian hieroglyphic and Demotic scripts.
Spain is allied with France in the Anglo-Spanish War (1796-1808).
1799. Coup d’état of 18 Brumaire. Napoleon replaces the Directory with the French Consulate with the help of Sieyès and Talleyrand. He establishes the Legion of Honor, France’s highest honor; signs the Louisiana Purchase; modernizes the administration; introduces the metric system; and abolishes Jewish ghettos. Napoleon conquers most of Italy by 1799, setting up temporary client republics. In 1804, Napoleon becomes Emperor of the French Empire, and raises La Grande Armée at 350,000 men. He forms the Kingdom of Italy in 1805.
- 1805. Napoleon wins the War of the Third Coalition.
- Prime minister William Pitt secures Russian and Austrian alliance.
- Napoleon defeats a confused Austrian army in the Ulm Campaign and the Battle of Austerlitz.
- Napoleon forms the Confederation of the Rhine of western German states, dissolving the Holy Roman Empire. Francis II becomes Emperor of Austria alone.
- Lord Nelson destroys the Franco-Spanish fleet in the Battle of Trafalgar, preventing an invasion of Britain.
- 1805. Napoleon wins the War of the Fourth Coalition.
- 1806. Napoleon wins the War of the Fifth Coalition.
- Peninsular War.
- 1807. Napoleon captures Portugal.
- 1808. Napoleon occupies his former ally Spain and replaces King Charles IV with his brother Joseph Bonaparte. Guerilla (“little war”) fighting breaks out with the Dos de Mayo Uprising in Madrid and the surrender of 24,000 troops in the Battle of Bailén. Britain retakes Portugal in the Battles of Roliça and Vimeiro with 15,000 troops under Arthur Wellesley, future Duke of Wellington.
- 1809. Second Portuguese campaign. French marshal Soult fails to take Portugal. Wellesley builds the Lines of Torres Vedras to defend Lisbon, ordering a scorched earth policy to relocate 200,000 people and destroy all food in front of the lines. General Gerhard von Scharnhorst reforms the Prussian army with conscription, promotion for merit, and organized administration.
- 1809. Napoleon occupies Rome and exiles the pope to France.
- 1812. Napoleon invades Russia with 286,000 men. He wins the Battle of Borodino but allows the Russian army to escape. Napoleon occupies Moscow, but did not prepare food logistics and loses his army leaving Russia in the winter. He wanted to force Tsar Alexander I to reinstate a blockade against Britain. The Alexander Column in Saint Petersburg memorializes the Russian victory.
- The Sixth Coalition defeats Napoleon at the Battle of Leipzig. It is the largest battle in Europe, with 560,000 soldiers. After the Battle of Paris in 1814, Napoleon is exiled to the island of Elba.
- 1815. Hundred Days. Napoleon briefly regains his army but is defeated by the Seventh Coalition at the Battle of Waterloo.
- Prussian general Carl von Clausewitz writes On War (1830).
- “War is the continuation of policy with other means.”
- Conservative Whig MP Edmund Burke writes Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790), A Vindication of Natural Society (1756), A Philosophical Enquiry into the Origin of Our Ideas of the Sublime and Beautiful (1757).
- Thomas Paine writes Rights of Man (1791).
1814. The Concert of Europe stabilizes the balance of power and political boundaries. In the Congress System, disputes are handled through summits, starting with the Congress of Vienna. The Holy Alliance of Austria (led by Metternich), Russia, and Prussia restores a Conservative Order of monarchy over civil rights. The Holy Roman Empire is replaced by the German Confederation mutual defense pact, which includes Austria and Prussia/Germany. Russia gains Congress Poland, formed from the Duchy of Warsaw that France took from Prussia and Austria.
- 1815 Bourbon Restoration in France puts brothers of the king on the throne.
- 1830 July Revolution replaces Louis Philippe with King Charles X.
Ottoman Tanzimat (1789-1876).
- 1801. Janissary commanders seize the Pashalik of Belgrade in Serbia and assassinate the Pasha (governor). They carry out the Slaughter of the Knezes (Serb nobles) in 1804. Karađorđe Petrović leads the First Serbian Uprising, which is successful for a decade.
- 1806. Russo-Turkish War. Russia wins and annexes eastern Moldavia in 1812
- 1813. Turkey briefly reconquers Serbia in 1813.
- 1815. Serbia wins independence in the Second Serbian Uprising and expels Muslims and Albanians.
- 1821. Greek War of Independence from the Ottoman Empire. Russia defeats Turkey in the Battle of Navarino in 1827. Sultan Mahmud II closes the Dardanelles to Russia but is defeated in the Russo-Turkish War of 1828.
- 1831. Wanting to expand, Emperor Nicholas I says the Ottoman Empire is the “sick man of Europe”. In 1833, Turkey agrees to become a vassal of Russia to defend against Egypt. European powers intervene and reestablish the London Straits Convention to settle the Eastern question of Ottoman policy.
- 1854. Crimean War. France, Britain, and the Ottomon Empire defeat Russia.
- In the Battle of Balaclava, light cavalry make an assault on a well-defended Russian artillery battery taking heavy casualties. Tennyson writes The Charge of the Light Brigade (1854). Commander in chief Raglan ordered an attack on a different, more suitable objective, which was misunderstood.
- 1858. Montegro wins the Battle of Grahovac and gains territory from Turkey.
- 1875. Great Eastern Crisis. High debt from the Crimean War leads the Empire to default and increase taxes, causing a wave of independence movements.
- 1875. Turkey brutally suppresses the Herzegovina uprising by the Christian population.
- 1876. Serbia maintains its independence from the Ottoman Empire.
- Turkey suppresses the April Uprising in Bulgaria and commits the Batak massacre, killing 5,000 civilians.
- 1877. Russo-Turkish War. Turkey loses.
- 1878. Congress of Berlin and Treaty of Berlin reorganizes the Balkans.
- Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro win independence.
- Austria rules Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- Bulgaria also becomes de facto independent, annexing Eastern Rumelia in 1885 and declaring formal independence in 1908.
- 1897. Greco-Turkish War. Greek wants Crete. Turkey wins but European powers intervene to found the Cretan State, which unites with Greece in 1908.
1791. Haitian Revolution is a successful slave revolt against France and Spain, winning independence in 1804.
- 1825. Ordinance of Charles X demands 150 million francs (present $21 billion) for claimed property losses, including slaves.
In the Atlantic Revolutions and the Spanish American wars of independence around 1820, other Spanish colonies win independence.
Regency era
- 1811. Regency Act. Eldest son George, Prince of Wales becomes prince regent after George III suffers from bipolar disorder.
- 1815. Post-Napoleonic Depression.
- 1816. Year Without a Summer famine caused by the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia.
- 1829. Catholic Relief Act by the Duke of Wellington. Enacts Catholic emancipation and repeals the penal laws, improving relations with Catholic-majority Ireland.
1850 Second Industrial Revolution. Steam and coal power, steel, and machine tools transform agriculture, manufacturing, and transport.
1837. Victorian Era marks a shift from rationalism to romanticism. Queen Victoria rules until 1901.
- Great Famine in Ireland from 1845 to 1852. Potato blight kills 1 million people. Half of US immigrants are Irish.
- 1846 Repeal of Corn Laws, protective tariffs on grains. Britain shifts to free trade, which increases disposable income and urbanization at the cost of rural landowners.
Great house
- Townhouse and country house
- The parlour is the most formal room. Men socialize in the drawing room after dinner with cards and cigars.
- Servants’ quarters separates the lower classes and are often in a semi-basement. Servants’ hall is the servants’ dining room. Meals could be very formal. The bell pull allows servants to be summoned from a greater distance.
- A nanny provides child care, assisted by a nursemaid. A governess is a private tutor.
- Butler supervises household staff, often in charge of the dining room, wine cellar, and pantry. The valet and lady’s maid are personal attendants. A footman waits tables, attends coaches, delivers messages. A useful man or houseman ranks below footman.
- Cook supervises kitchen staff. is assisted by kitchen maids. Scullery maids, the lowest rank, were dishwashers, floor scrubbers, oven minders. The scullery is a small room for washing pans.
- Housekeeper supervises cleaning staff and reports to the lady of the house, addressed by Mistress. Parlour maids cleaned and served refreshments. The hall boy performs the least desirable jobs. The boot boy, the lowest rank, cleans shoes.
- Property manager supervises the grounds staff, including head gardener and stable master or gamekeeper.
- https://logicmgmt.com/1876/etiquette/etiquette.htm
Politics
- 1852 The Aberdeen coalition ministry is formed after the collapse of Lord Derby’s minority Who? Who? ministry. It loses a vote of no confidence over the Crimean War and the Charge of the Light Brigade.
- 1855 Whig Lord Palmerston forms his first ministry. In the Orsini affair of 1858, an Italian nationalist living in England fails to assassinate Napoleon III. France pressures Britain to pass a Conspiracy to Murder Bill against murder abroad, which is deeply unpopular and fails. Palmerston briefly resigns and Conservative Lord Derby leads a brief second minority ministry with Commons leader Benjamin Disraeli as Chancellor of the Exchequer.
- 1859 Lord Palmerston founds the modern Liberal Party from Whigs and Peelites, representing business and industry interests against landed Tories. He dies in 1865 and is briefly succeeded by Earl Russell.
- 1866 Third Derby ministry. Disraeli is briefly prime minister after Derby has an attack of gout.
- 1868 Liberal William Gladstone is prime minister for four non-consecutive terms until 1894.
- 1873 Return of Owners of Land compiles land ownership.
- 1874 Benjamin Disraeli creates the modern Conservative Party as prime minister from 1874 to 1880, and is skilled at flattery. He favors British imperialism and buys shares of the Suez Canal from the Ottoman Khedive (ruler) of Egypt.
- 1880 Gladstone forms his second ministry after his Midlothian campaign attacking Disraeli’s support for the Ottoman government, the first modern political campaign. In 1894, Gladstone resigns over the rejection of his Home Rule Bill and is briefly succeeded by the liberal Earl of Rosebery.
- 1895 Conservative Lord Salisbury becomes prime minister. The government is very popular during the Second Boer War.
Spain
- 1840. First Carlist War. Liberals supporting a constitutional monarchy defeat conservative supporters of the late king’s brother, Carlos. General Espartero takes power from the regent María Cristina but is unpopular.
- 1843. Parliament recognizes Queen Isabella II at 13. Isabella supports conservative and moderate forces.
The French Revolution of 1848 or February Revolution.
The government bans the campagne des banquets, meetings where liberals criticized the government. Large protests force King Louis-Philippe to abdicate. In 1851, Philippe’s nephew Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte is elected president of the Second Republic, and the next year he declares himself Emperor Napoleon III of the Second French Empire.
- Napoleon III commissions Haussmann’s renovation of Paris, which widens the streets and reduces disease.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_Revolutionary_and_Napoleonic_Wars
The Other Revolutions of 1848 introduce democracy in the Netherlands and a constitution and parliament (Rigsdag) in Denmark.
- 1848 Austria and Prussia crush liberal German revolutions.
- 1848 Austrian Emperor Franz Joseph suppresses the Hungarian Revolution.
- 1838, Giuseppe Mazzini founds the Young Italy movement for a unified Italian republic. In 1848, Austria defeats the First Italian War of Independence by King Charles Albert of Sardinia at the Battle of Custoza. Garibaldi and Mazzini drive Pope Pius IX out of Rome in 1849, but France restores him after winning a two-month siege of Rome.
1854 After losing the Crimean War, Emperor Alexander II abolishes serfdom in the emancipation reform of 1861, promotes local self-government, and puts down the January Uprising of 1863 in Poland.
1864 Russia wins the Caucasian War, which consists of the the Russo-Circassian War in the west and the conquest of Chechnya and Dagestan in the east. After the invasion of Circassia, Russia commits the Circassian genocide, killing 1 million people and sparing just 100,000. In 1859, the Caucasian Imamate surrenders to Russia.
Italian unification
- 1859 Second Italian War of Independence. Sardinian Prime Minister Count Cavour secretly allies with Napoleon III to annex Lombardy from Austria, with France getting Savoy and Nice. Garibaldi leads the military.
- 1860 Cavour persuades Garibaldi to focus on other areas first. Garibaldi sails with the Expedition of the Thousand and overthrows the Spanish Kingdom of the Two Sicilies at the Siege of Palermo.
- 1861 Garibaldi conquers the Kingdom of Naples with massive popular support, and King Victor Emmanuel II founds Italy.
- 1866 Third Italian War of Independence. Italy annexes Venetia from Austria.
- 1870 Capture of Rome. Italy captures the Papal States after Napoleon III moves his army from Rome to fight Prussia.
1866 Austro-Prussian War or Seven Weeks’ War over the German question. Austria wants a unified state, but von Bismark allies with Italy to defeat Austria and establish Lesser Germany. Prussian minister Otto von Bismarck breaks up the German Confederation and creates the North German Confederation. Field Marshal Helmuth von Moltke the Elder emphasizes concentrating forces only after battle begins: “March Divided, Fight United”. Mission command gives goal-based orders and delegates operational details down to unit level. The Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 establishes the diarchy of Austria and Hungary.
1870 Franco-Prussian War. Napoleon III invades Germany and is quickly defeated in the siege of Paris. The German Empire unifies the German states except Austria under emperor Wilhelm I of Prussia and chancellor von Bismarck, and various treaties keep a tenuous peace in La Belle Époque.
- Demimonde: hedonism of drug use, gambling, high fashion, promiscuity, lavish spending. Also associated with courtesans and kept women of wealthy men.
- French Third Republic is founded. In 1871, soldiers of the National Guard briefly found the Paris Commune, which is defeated.
In 1873, von Bismarck creates the League of the Three Emperors with Russia and Austria-Hungary to isolate France. The league dissolves after Russia seeks more influence in the Balkans, threatening Austria-Hungary’s South Slavs, especially Serbs. Anglo-German naval rivalary pushes Britain to France.
In 1879, Germany and Austria enter into the Dual Alliance (Zweibund), followed by the Triple Alliance mutual defense treaty with Italy in 1882. The Triple Entente forms with Britain, Russia, and France.
Revolution of 1868. Liberal military oligarchs remove the unpopular Isabella II of Spain, leading to the Sexenio Democrático.
In the Dreyfus affair of 1894, a Jewish officer is wrongly sentenced to life imprisonment until public pressure leads to an eventual pardon.
Revolution of 1905 after the failed Russo-Japanese War. Tsar Nicholas II massacres protestors on Bloody Sunday. Stalin leads the 1907 Tiflis bank robbery killing 40 people.
Edwardian era is the reign of Edward VII from 1901 to 1910.
- 1900. Labour Party founded.
King George V rules from 1910 to his death in 1936. Edward III abdicates to marry twice-divorced American socialite Wallis Simpson, and his younger brother becomes King George VI.
World War I
Prelude. Allied and Axis powers build entangling alliances. The German policy of Lebensraum (“living space”) involves expansion into Poland.
- 1908. Bosnian Crisis. Austria annexes Bosnia and Herzegovina amidst the chaos of the Young Turk Revolution, angering Serbian nationalists.
- 1908. Bulgaria declares independence from Turkey.
- 1911. Italo-Turkish War. Italy captures Italian Libya. Guglielmo Marconi develops radio for military use, and planes carry out the first recon and bombing missions.
- 1912. Ottomans lose the First Balkan War, ceding Macedonia and Europe to the Balkan League of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria.
- 1913. Second Balkan War settles the Bulgaria-Turkey border, with some gains for Bulgaria.
Western Front
- 1914 July Crisis. A Bosnian Serb assassinates Archduke Ferdinand, heir of Austro-Hungarian. Austria-Hungary declares war against Serbia.
- Germany invades France via neutral Belgium, drawing Britain into the war. In the Rape of Belgium, Germany massacres 6,000 Belgians. Britain imposes a naval blockade of Germany. US ships large amounts of food and munitions to Britain.
- 1915. Germany briefly begins unrestricted submarine warfare. They sink 2 ships a day which had no military benefit. A U-boat sinks the unarmed ocean liner RMS Lusitania, which was carrying 173 tons of war supplies. 1,000 Europeans and 100 Americans die, causing outrage in America, leading to Germany to pause U-boat attacks.
- 1916.
- Battle of the Somme. Bloody trench warfare.
- Battle of Verdun.
- 1916. Naval Battle of Jutland is the last major battleship battle. Britain loses more ships but successfully contains the German fleet.
1915 Battle of 18 March. Ottoman Empire defends the Dardanelles Straits. - 1917. US declares war on Germany after Germany resumes unrestricted submarine warfare. General John J. Pershing leads the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF).
- Zimmermann Telegram: Germany offers a military alliance with Mexico to recapture New Mexico, Texas and Arizona. Britain intercepts the telegram leading to outrage.
- 1918. German spring offensive. Operation Michael is stopped at the First Battle of Villers-Bretonneux and the Battle of the Avre, the first battle with tanks on both sides. The Third Battle of the Aisne advances 55 km with a creeping barrage and poison gas, recapturing the the Chemin des Dames ridge. It reaches 55 km of Paris but is overextended. The Allies stop the offensive, with the first major American involvement in the Battle of Cantigny. The Second Battle of the Marne is the last German attack.
- The Hundred Days Offensive ends the war.
- Battle of Saint-Mihiel: 216,000 Americans breach German lines.
- November 11. Armistice Day or Veterans Day.
On the Eastern front, Germany and Austria-Hungary fight Russia.
https://old.reddit.com/r/MapPorn/comments/1aio2ky/ww1_western_front_every_day/
In total, 17 million die.
Lost Generation experience WWI and the Great Depression.
The League of Nations is founded to promote collective security and rule of law. The mandate system puts colonial administration under principles of non-annexation, non-exploitation, and international observation and courts. The US Senate votes not to join. Resolutions are difficult to enact, requiring a unanimous vote of fifteen Council members.
Britain constructs the Cenotaph at Whitehall as its primary war memorial.
Russian Revolution. Lenin founds the Soviet Union. Hammer and sickle.
- 1917. October Revolution. Tsar Nicholas II led an unpopular war and a bad economy. He rapidly replaces government leaders, losing support from elites.
- February Revolution. Tsar Nicholas II abdicates. Lenin and the Bolsheviks take power with a promise of peace and bread, winning the Russian Civil War against various independence movements. Leon Trotsky is second-in-command and founded the Red Army. Lenin promotes a New Economic Policy that allows limited free markets.
- Basmachi movement is a failed Islamic revolt against the Red Army.
- 1918. Red Terror kills around 100,000.
- 1920. The Baltic states Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia win independence from Russia.
- 1921. Russian famine kills 5 million. Lenin allows a more market-oriented New Economic Policy.
- 1924. Lenin dies.
- 1929. Stalin gains control and exiles Trotsky.
- 1929. First five-year plan includes dekulakization kills a million kulaks (wealthy peasants) and redistributes their land. Millions more are sent to gulags.
- 1932. Holodomor in Ukraine kills 3 million. Pravda becomes the leading Soviet newspaper.
- 1936. Stalin’s Great Purge kills 1 million.
The Revolutions of 1917–1923 follow.
German Revolution of 1918. President Friedrich Ebert founds the Weimar Republic in 1919 after Emperor Wilhelm II abdicates. The Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) allies with German military to suppress the communist Spartacist uprising.
1912. Home Rule Crisis.
1921. Ireland wins independence in the Anglo-Irish Treaty, with Northern Ireland remaining part of the UK. The Sinn Féin party and Irish Republican Army (IRA) rise to power after the brutal suppression of the Easter Rising of 1916.
The 1926 General Strike in the UK is a failed strike by 1.7 million workers over the collapse of coal wages.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spanish_Civil_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Straperlo
Modern Europe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decolonisation_of_Africa
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Third-wave_feminism
1952. European Communities are predecessors to the EU.
- 1950. Schuman Declaration on Europe Day (May 9) pools coal and steel resources into a supranational organization.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Communities
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_integration
The Algerian crisis of 1958 leads to the Fifth Republic with a stronger presidency under the current Constitution of France.
Protests of 1968.
- The Troubles in Northern Ireland. The Protestant government fights the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) and the Irish National Liberation Army (INLA), leading to 3,500 dead.
- In the Good Friday Agreement of 1998, Britain accepts Northern Irish self-government and power-sharing.
- French May 68 unrest with 11 million on strike.
- Italy Years of Lead: political violence. 1968 movement of student protests and Hot Autumn strikes.
Queen Elizabeth II rules from 1952 to her death in 2022. Her children are King Charles III, Anne, Andrew, and Edward.
- 1978. Winter of Discontent: trade union strikes lead to the fall of the Labour PM James Callaghan.
- 1979. Margaret Thatcher breaks the unions.
- 1984. Arthur Scargill leads a failed year-long miners’ strike. He endorses a regional strike and fails to hold a national vote to secure unity.
- Prince Andrew was friends with Jeffrey Epstein and accused of raping Virginia Giuffre.
King Charles III marries Princess Diana Spencer in 1981, having two sons William and Harry, before divorcing in 1996. Diana dies in a car crash in 1997. In 2005, Charles marries Camilla Parker Bowles. William marries Princess Catherine of Wales. Prince Harry marries Meghan Markle.
Socialist François Mitterrand is president from 1981 to 1995.
- 1985 Mitterrand bombs a Greenpeace ship protesting French nuclear testing.
1991 Yugoslav Wars were ethnic conflicts that broke Yugoslavia into Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, and North Macedonia.
- 1992 Bosnian War ethnic conflict between Serbs and Bosnians. 1995 Dayton Accords end the war. The Serbian siege of Sarajevo, the capital, lasts the full three years of the war. NATO Operation Deny Flight enforces a no-fly zone. NATO shoots down four Bosnian Serb fighters near Banja Luka in its first combat action.
- 1999 Kosovo declares independence from Serbia with US support. NATO bombs Yugoslavia until it withdraws from Kosovo.
1993. European Union founded in the Maastricht Treaty.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:History_of_the_European_Union
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Three_pillars_of_the_European_Union
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Commission
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Area_of_freedom,_security_and_justice
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Council_of_the_European_Union
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Democratic_deficit_in_the_European_Union
- Separate
2007. Labour PM Gordon Brown.
2010. Conservative PM David Cameron. Ed Miliband becomes Labour leader.
- Home Secretary Theresa May introduces the hostile environment policy to deport first, appeal later.
2016. Brexit. Cameron resigns. PM Theresa May. In 2015, Jeremy Corbyn becomes Labour leader.
2019. PM Boris Johnson. In 2020, Keir Starmer becomes Labour leader.
2022. PM Rishi Sunak. Liz Truss was briefly PM but resigns after proposing unpopular tax cuts.
2024. Labour PM Keir Starmer wins almost 2/3 of seats with a third of votes. The Conservative party fractures, with 14% hard-right Reform party and 7% Green Party votes. Low turnout.
2018. Yellow vests protests against economic inequality.
Ukraine
2004. Orange Revolution protests against pro-Putin president Yanukovych.
2014. Revolution of Dignity and the Euromaidan protests overthrow Yanukovych.
2014. Russia annexes the Crimean peninsula in the Black Sea, and the Donbas region of Donetsk and Luhansk.
2022. Russian invasion of Ukraine.
America
Geography
America
- American flag
- Cuisine: apple pie, donuts, fried chicken, pizza, hamburgers, french fries, hot dogs, macaroni and cheese, ice cream.
- Thanksgiving dinner: roast turkey, mashed potatoes, cranberry, stuffing.
- Interstate Highway System: Interstate 80 goes from SF to NJ.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megaregions_of_the_United_States
Western US
- The Ring of Fire: the Pacific Plate subducts under the North American Plate.
- Alaska is the largest state.
- Hawaii
- Oahu: Honolulu, Pearl Harbor, Fort Shafter army base, marine corps Camp H. M. Smith, Marine Corps Base Hawaii, Kaena Point remote tracking station, Maui Space Surveillance Complex at Haleakala Observatory
- The American Cordillera is the eastern half of the Pacific Ring of Fire, including the Pacific Coast Ranges.
- Cascadia subduction zone
- The San Andreas Fault is a transform fault or strike-slip fault between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. It includes the Crystal Springs Reservoir.
- Santa Cruz Mountains causes a rain shadow in San Jose
- Hayward Fault
- Calaveras Fault
- Sierra Nevada in California.
- Yosemite Valley
- Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in America.
- Mount Whitney at 14,505’ is the highest in the lower 48.
- Donner Pass
- Creates the endorheic Great Basin desert of Utah and Nevada.
- Creates the Mojave Desert containing the Joshua Tree and Death Valley.
- Rocky Mountains or Rockies are the main Continental Divide.
- Includes Grand Teton National Park and Yellowstone National Park in northwest Wyoming.
- The Columbia River flows past Portland and Vancouver to the Pacific.
- The Colorado River flows from Colorado to the Gulf of California in Mexico.
- The Rio Grande flows from Colorado through Texas to the Gulf of Mexico.
- Peninsular Ranges creates the Sonoran Desert, which contains saguaro and ocean pipe cactus.
- Sierra Madre Occidental range creates the Chihuahuan Desert, dominated by chaparral or creosote bush (Larrea).
- Big Bend National Park on the Rio Grande in West Texas.
- The Yukon River flows from Yukon through Alaska to the Bering Sea. The Bering Strait separates the Pacific and Arctic oceans. The Saskatchewan River flows east to Lake Winnipeg, which drains via the Nelson River to Hudson Bay.
- California is the most populous state at 40 million.
- San Francisco
- 1776 Spain establishes the Presidio (“fort”) deep water port, Mission Dolores, and the Yerba Buena settlement at present-day Portsmouth Square.
- The Golden Gate Bridge (1937) is the longest suspension bridge. It carries 100,000 vehicles per day between San Francisco and Marin County via US Route 101 and California State Route 1.
- San Francisco Ballet (1933)
- The San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge (1936) is a white suspension bridge.
- Embarcadero
- The Ferry Building is a grand, symmetric, ornate Beaux-Arts building with a clock tower on the Embarcadero waterfront. The ground floor arcade features classical columns and a vaulted ceiling with skylights.
- Financial District: Salesforce Tower
- Civic Center: SF City Hall, Asian Art Museum, SF Public Library.
- Union Square
- Chinatown, Japantown and SF Peace Pagoda
- South of Market (SoMa).
- San Francisco Museum of Modern Art.
- Rincon Center: History of San Francisco (1941) by Anton Refregier.
- Moscone Center is the largest convention complex.
- Mission District: Dolores Park.
- Golden Gate Park: Japanese Tea Garden, SF Botanical Garden, and California Academy of Sciences
- Marina district: Palace of Fine Arts.
- Bayview: DCK6 Amazon delivery station.
- SFO airport.
- Berkeley: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)
- Central Valley has rich silt from mountain rivers.
- Sacramento
- Beale Air Force Base
- Los Angeles
- Walt Disney Concert Hall
- Hollywood Bowl
- LAX airport.
- Santa Monica and Venice beaches.
- Edwards Air Force Base
- 1876 Pico Canyon Oilfield is the first successful western oil well.
- 1895 Oil boom grows the town from 50,000 to 1.2 million in 1930.
- Los Angeles City Oil Field produces a million barrels a year, half the oil in California.
- Salt Lake Oil Field produces 50 million barrels. The La Brea Tar Pit is the richest Quaternary paleontological site.
- Santa Barbara
- Vandenberg Space Force Base: NASA and SpaceX launches.
- San Francisco
- Pacific Northwest Corridor (PNW) or Cascadia connects with Vancouver. Temperate rainforest due to warm ocean air.
- Oregon: Willamette Valley flows from through Portland, Salem, and Eugene. Vineyards. Also dominates US blackberry production.
- Washington state
- Seattle
- Seattle-Tacoma or SeaTac airport.
- Joint Base Lewis-McChord near Tacoma.
- Seattle
- Nevada
- Las Vegas: Vegas Sphere, Harry Reid or LAS airport
- Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository is an incomplete deep geological repository. Work stopped in 2011 due to opposition from Western Shoshone peoples.
- Nellis Air Force Base Complex
- Creech Air Force Base
- Arizona
- Grand Canyon carved by the Colorado River.
- Hoover Dam on the Colorado River.
- Davis-Monthan Air Force Base contains the aircraft boneyard.
- New Mexico
- White Sands Missile Range
- Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) is a deep geological repository to store nuclear waste from US nuclear weapons development.
- Colorado
- Air Force Academy near Colorado Springs
- Peterson Space Force Base near Colorado Springs: NORAD HQ
- Cheyenne Mountain Complex: former NORAD HQ
- Schriever SFB and Buckley SFB.
- Utah
- Salt Lake City
- Great Salt Lake Desert includes the Dugway Proving Ground for biological weapons.
- Semi-arid climate and ranching culture west of the 100th meridian.
Midwest US
- Great Plains are the largest area of farmland in the world. Known as America’s breadbasket, the Wheat Belt, or the Corn Belt.
- Tallgrass prairie south of the Great Lakes.
- Shortgass prairie on the west, and mixed-grass prairie in between.
- Black Hills are sacred for Native Americans.
- Devils Tower is a butte and the first national monument.
- The Great Lakes are Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. They flow through the St. Lawrence River to the Gulf of St. Lawrence on the Atlantic Ocean. Also some outflow to the Labrador Sea.
- Lake Superior is the northernmost.
- Lake Michigan: Chicago.
- Lake Erie: Detroit, Cleveland, and Buffalo. The Niagara River and the Niagara Falls flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
- Lake Ontario > Toronto: CN Tower was the tallest in the world.
- Chicago
- Art Institute of Chicago.
- Fermilab.
- O’Hare ORD airport.
- Midway park: original Ferris Wheel built for the World’s Fair of 1893.
- Illinois: Scott Air Force Base near St. Louis.
- The Mississippi River flows from Minnesota to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico, including New Orleans. The Ohio River flows into the Mississippi at Cairo, Illinois.
- The Missouri River flows from the Rocky Mountains into the Mississippi at St. Louis.
- The Allegheny River flows from the Allegheny Plateau to Pittsburgh into the Ohio River.
- The Tennessee River covers the Tennessee Valley, home of the Cherokee people, and flows into the Ohio River.
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory
- North Dakota: Grand Forks Air Force Base
- South Dakota: Mount Rushmore
- Nebraska: Offutt Air Force Base near Omaha.
- Kansas
- Fort Leavenworth: army Command and General Staff College
- Oklahoma
- Oklahoma City capital, with Fort Sill to the southwest.
- Tulsa is the second-largest city in OK.
- New York City boroughs: Manhattan, Queenz, The Bronx, and Staten Island.
- Brooklyn incl. Coney Island: Brooklyn Bridge connects to Manhattan.
- Queens: JFK and LaGuardia (LGA) airports.
- Statue of Liberty (1876): centennial gift from France, designed by Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi as a neoclassical monument to republicanism.
- Hudson River between Manhattan and New Jersey. Erie Canal (1825) to the Great Lakes is part of the Great Loop of waterways that circumnavigate the eastern US.
- Avenues: 1st, Park Ave, Madison Ave, Central Park (5th to 8th).
- Broadway curves east south of Central Park.
- Upper Manhattan: Columbia University and Barnard College.
- Upper West Side > Lincoln Center: Metropolitan Opera houses the American Ballet Theatre, New York City Ballet, Juilliard, .
- Central Park from 59th to 110th St. Metropolitan Museum of Art and The Guggenheim (1959), a large helical ramp by Frank Lloyd Wright on 5th Ave.
- Manhattan schist is a good foundation for skyscrapers.
- Midtown Manhattan is a business center south of the park.
- Carnegie Hall, 57th St
- Museum of Modern Art, 53rd St.
- Rockefeller Center Christmas Tree and skating rink, 50th St.
- Waldorf Astoria, 50th St.
- Times Square, 42nd St.
- Saks Fifth Avenue has rents of $3,000/sq ft.
- Empire State Building (1930) is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper that was the tallest in the world.
- Hudson Yards, 34th St.
- Madison Square and the Flatiron Building, 23rd St.
- Union Square, 14th St.
- Lower Manhattan
- Washington Square Park, 6th St.
- Hudson St next to 1st St and SoHo.
- Whitney Museum hosts the Whitney Biennial, the preeminent US contemporary art show.
- Chinatown
- Civic Center
- Financial District, Wall St and the Raging Bull statue.
- Battery Park
- Broadway theatre: venues with 500 seats.
- Dumbo
- Long Island: Brookhaven National Laboratory.
- Hudson River and Hudson Valley
- West Point or United States Military Academy is the oldest post.
- Rest of New York: Empire Corridor connects Albany, Utica, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo.
Eastern US
- Northeast megalopolis, Northeast Corridor, BosWash, or the I-95 corridor: Boston, New York City, Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Washington, D.C.
- Acela high-speed rail serves 3M pax/yr with $600M revenue. 60 mph with a top speed of 150 mph. Northeast Regional serves 9M pax/yr with $800M revenue.
- Appalachian Mountains or Appalachian Highlands form the Eastern Continental Divide.
- Piedmont (“foot of the mountain”) eastern plains extending to Alabama.
- Blue Ridge Mountains is the eastern ridge.
- Great Smoky Mountains National Park is the most visited, with 13 million visitors a year.
- Shenandoah National Park in western Virginia. The Shenandoah River flows from its west to join the Potomac River, which flows to Chesapeake Bay in Maryland.
- Ridge and Valley
- Appalachian Plateau is a vast dissected western plateau. East-facing Allegheny Front is a sharp slope. Catskill Mountains in southeast New York.
- Cumberland Gap.
- The Appalachian Trail is the longest hiking-only trail at 2,200 miles.
- Adirondack Mountains are a geologically distinct, isolated mountain range covering most of New York.
- Maine
- New Hampshire
- Vermont
- Massachusetts > Boston
- The Boston Common (est. 1634) is the oldest city park in the US.
- Rhode Island, capital Providence.
- Naval Station Newport houses the Naval War College.
- Connecticut
- New Jersey
- Pennsylvania
- Philadelphia on the Delaware Bay.
- 1795. Philadelphia and Lancaster Turnpike is the first road, paved with logs over 62 miles.
- The Delaware River is the longest river in the Eastern US. It flows from New York to Delaware Bay, carving the Delaware Water Gap out of the Appalachians.
- Philadelphia Main Line are a stretch of affluent suburbs along the former Pennsylvania Railroad, now the Keystone Corridor with a top speed of 90 mph.
- Allegheny Plateau and Allegheny Mountains form the PA section of the Appalachians.
- 1755. Braddock Road military trail follows Nemacolin’s Path through the Cumberland Narrows. Superseded in 1818 by the Cumberland Road or National Road.
- 1775. Cumberland Gap: Wilderness Road.
- 1834. Blair Gap: Allegheny Portage Railroad funicular.
- 1854. Kittanning Path: Horseshoe Curve of the Pennsylvania Railroad.
- Bedford Narrows: US Route 30 (part of the Lincoln Highway) and the PA Turnpike.
- Raven Rock Mountain Complex is an underground nuclear bunker.
- Carlisle Barracks houses the US Army War College and is the second-oldest US army post.
- Maryland
- Baltimore is the most populous city in MD. On the Chesapeake Bay.
- Capital at Annapolis: United States Naval Academy.
- Goddard Space Flight Center
- Fort Meade
- Aberdeen Proving Ground
- Fort Detrick used to develop biological weapons.
- Washington DC on the Chesapeake Bay
- United States Capitol, National Mall reflecting pool, Washington Monument, Lincoln Memorial, Jefferson Memorial, Eisenhower Memorial. World War I Memorial, World War II Memorial, Vietnam Veterans Memorial, Korean War Veterans Memorial. US Navy Memorial.
- Smithsonian Institution (SI): Smithsonian Museum of American History
- National Museum of Natural History
- National Air and Space Museum
- National Gallery of Art
- Library of Congress (LOC)
- Potomac River
- Fort McNair or Washington Arsenal is the third oldest post. National Defense University.
- Virginia
- Norfolk on the Chesapeake Bay
- The Pentagon in Arlington County is the world’s second-largest office building, with 6 million square feet and 23,000 workers.
- Fort Belvoir has 50,000 workers.
- Arlington National Cemetery includes the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier and the Marine Corps War Memorial or Iwo Jima memorial.
- Marine Corps Base Quantico: MC University, FBI Academy, HMX-1 presidential helicopter squadron.
- Langley AFB.
- Joint Base Myer-Henderson Hall houses The Old Guard, the oldest regiment which conducts memorials and cermonies.
- Mount Weather Emergency Operations Center or High Point Special Facility: FEMA HQ. Part of the Federal Relocation Arc.
- Warrenton Training Center
Southern US
- Kentucky: Fort Knox
- Texas: west is dry and east is wet. Most of the population in the Texas Triangle:
- Houston
- Houston Space Center
- Port of Houston is the busiest in the US.
- Port of Corpus Christi south of Houston is one of the busiest.
- Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington
- Austin
- San Antonio: Joint Base San Antonio and Lackland Air Force Base.
- Houston
- Florida
- Tyndall Air Force Base, MacDill Air Force Base near Tampa
- Port Canaveral
- Georgia
- Fort Eisenhower is the Army Cyber Command HQ with 30,000 workers.
- Fort Moore
- North Carolina
- Research Triangle
- Raleigh capital
- Duke University in Durham
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Charlotte is the biggest city.
- Fort Liberty houses 52,000 workers including the Army Special Operations Command. Formerly named Fort Bragg after a Confederate general.
- Research Triangle
- South Carolina: Fort Jackson
- Missouri: Fort Leonard Wood
- Louisiana
- Cajun food
- New Orleans
- Creole cuisine: Gumbo, jambalaya, crawfish.
- Social Aid and Pleasure Clubs (SAPCs) organize community help and brass band parades. In jazz funerals, a dirge is followed by a celebration. The second line is a free-form open dance following the main line of a parade, often with colorful suits and parasols.
- Hand grenade: equal parts vodka, rum, gin, rectified spirit, and melon liquer in a tall green plastic tube with a bulbous grenade-textured base.
- Port of South Louisiana around New Orleans is the second-busiest US port.
- Alabama
- Redstone Arsenal army base near Huntsville.
- Maxwell AFB: Air University HQ.
Canada
- Provinces: Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, Quebec, Saskatchewan
- British Columbia
- Vancouver
- Vancouver YVR airport
- Vancouver
- Alberta: Athabasca oil sands are large deposits of bitumen. The Syncrude Tailings Dam is the largest earth structure by volume, at 500 million cubic meters. It is 88 m tall earthen dam.
- British Columbia
- Territories: Northwest Territories, Yukon, Nunavut
Mexico
- Mexico City
- Cancun in the east on the Caribbean Sea.
- Acapulco port. Was a balneario resort but now one of the deadliest cities.
South America

- Caribbean Sea and the West Indies.
- Bahamas: Nassau capital
- Cuba: Havana capital
- Cayman Islands, Jamaica, Haiti, Dominican Republic (Santiago)
- Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands
- Trinidad island: Pitch Lake is the largest asphalt lake.
- Lesser Antilles: Antigua, Barbados, Grenada
- Central America
- Belize: Belize Barrier Reef and the Great Blue Hole
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Nicaragua
- Costa Rica
- Panama: the Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific.
- The Amazon River is the largest. It flows from Peru to Brazil and the Atlantic Ocean.
- The Amazon rainforest is the largest at 2 million square miles. 60% is in Brazil.
- Yanomami are the largest isolated tribe in South America, with around 35,000 people in 200 villages.
- Brazil
- Rio de Janeiro capital: Christ the Redeemer statue and Copacabana Beach.
- Favela is a slum or ghetto.
- Iguazu Falls is taller and wider than Niagara Falls.
- Itaipu Dam is the second largest dam.
- Ecuador
- Galapagos Islands
- Peru
- Machu Picchu, an Inca citadel.
- Andes is part of the American Cordillera.
- Chile
- Atacama Desert is the driest non-polar desert.
- Atacama Giant is the largest human geoglymph.
- Atacama Desert is the driest non-polar desert.
- Venezuela: Lake Bermudez is the second largest asphalt lake.
- Uruguay
- 1828. Independence from Brazil.
- 1973. Military coup.
- 1985. Return to democracy
- 2020. José Mujica: humble,
- Refuses to live in the presidential palace, which he argues is a remnant of feudalism and should be turned into a high school.
- Atheist but admires nature.
- Drake Passage has 40 feet waves with no resistance from land. Antarctic Circumpolar Current at 100 million cubic meters of water per second.
Antarctica
- South Pole
- 1911 Norwegian Roald Amundsen reaches the South Pole.
- 1912 British Robert Falcon Scott dies after reaching the South Pole. A dog team was supposed to relieve him at 82°30’, but Atkinson prioritized helping an ill member of an earlier support team, and Cherry-Garrard did not go to the meeting point.
- 1915 Ernest Shackleton’s ship Endurance is crushed by drift ice. The crew reach Elephant Island and South Georgia on lifeboats.
- West Antarctic: Berkner Island, Byrd, Siple Dome,
- East Antarctic: EDML, Dome Fuji, Vostok, Dome C, Law Dome, Talos Dome
US Government
Federal republic
Federal government
- Legislative branch: Congress sits in the US Capitol.
- House of Represenatives can impeach the president.
- The speaker is second in the line of succession.
- Senate confirms presidential appointments and holds impeachment trials.
- The vice president is the presiding officer and tiebreaking vote
- The president pro tempore is third in the line of succession. Usually the senior senator in the majority.
- The majority caucus is led by the majority leader or chair, the assistant leader or whip gathers votes on important issues, the vice chair, and the caucus secretary, who takes notes. Similarly for the minority.
- House of Represenatives can impeach the president.
- Judicial branch: federal courts. See law.
- Executive branch.
- President is elected by the electoral college every four years with an eight year term limit. Commander-in-chief of the armed forces and can pardon. Lives at the White House at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue.
- Executive Office of the President
- White House Chief of Staff
- White House Office: White House Counsel
- National Security Council
- Homeland Security Council
- Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
- Council of Economic Advisers
- Executive departments led by Cabinet secretaries, by line of succession:
- State
- Treasury
- Department of Defense (DoD) headquartered at The Pentagon
- Armed forces: Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard (USCG).
- National Security Agency (NSA)
- National Reconnaissance Office (NRO)
- Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)
- The Joint Chiefs of Staff is an advisory board.
- Justice Department (DOJ) led by the Attorney General
- Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
- United States Marshals Service (USMS) is the enforcement arm for the federal judiciary.
- Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF)
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
- Bureau of Prisons (BOP)
- Interior
- National Park Service (NPS)
- US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS)
- Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA)
- Bureau of Land Management (BLM)
- Agriculture
- Commerce
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps is a uniformed service.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- Labor
- Health and Human Services (HHS)
- US Public Health Service includes the USPHS Commissioned Corps, a uniformed service.
- Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Transportation
- Energy
- Education
- Veterans Affairs (VA)
- Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
- US Secret Service protect politicians and combats counterfeiting.
- U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE)
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
- Federal Air Marshal Service
- National Incident Management System includes the Incident Command System: operations, planning, logistics (supply, facilities, communication, ground support, food), administration
- Cabinet-level
- Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) leads the Intelligence Community.
- President’s Daily Brief and National Intelligence Council
- Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
- Special Activities Division
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Lead and Copper Rule (1991) limits tap water to 10 ppb.
- Small Business Administration (SBA)
- Office of Science and Technology Policy
- Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR)
- Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) leads the Intelligence Community.
- Independent agencies have rulemaking authority.
- Federal Reserve, Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), Export-Import Bank is the federal export credit agency.
- National Labor Relations Board (NLRB)
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- Federal Election Commission (FEC)
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- US Postal Service (USPS)
- Postal Inspection Service
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- US Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Chemonics
- US Trade and Development Agency (USTDA)
- Peace Corps (PC)
- Social Security Administration (SSA) funded via Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA).
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States_federal_budget
- The General Schedule pay scale ranges from 25,000 to 200,000.
State government
- States are divided into counties and municipalities.
574 Indian tribes govern 326 Indian reservations.
Indigenous
3500 BC The Caral-Supe or Norte Chico civilization develops in coastal Peru. Quipu string-based records and flutes, but no pottery or visual art. 2250 BC Staff God carving. Followed by Andean civilizations.
3500 BC Valdivia culture in Ecuador.
1600 BC Olmec civilization in Mesoamerica.
- 7000 BC Domestication of corn to have full kernels and soft shells.
- 1400 BC. First ballgame court, in Mexico.
- 1200 BC Chavín de Huántar in Peru
- 100 BC-250 CE Teotihuacan near Mexico City. Then-largest city in the Americas with a population of 125,000.
- 250 CE Maya civilization incl. star calendar and writing system south of Mexico.
- 900. Maya abandon many southern cities.
- 1150. Maya Codex of Mexico contrains astronomical tables.
- 800 CE Marajoara culture and Kuhikugu culture in Brazil
- Aztec Empire or Mexica Empire (1300-1521)
- Tlaxcala was an urban republic surrounded by the Aztec.
- Ulama ballgame uses an 8 lb rubber ball. Hit with hips. Goals are large stone rings.
- Inca Empire (1438-1533)
- Children of Llullaillaco are well-preserved mummies
800 BC Paracas culture in the Andes. Extensive irrigation.
- 400 BC Nazca lines are geoglyphs, large designs in the landscape.
800-1600 Mississippian culture built advanced urban settlements, with the largest at Cahokia.
Native Americans grow a post-scarcity culture. The Iroquois had “no poorhouses,” nor sheriffs nor jails. Families, clans, and villages lived together, farmed together, hunted together, and shared all they had. They met their needs and were content to eat well, sleep comfortably, live quietly, play with children, laugh and be merry. The idea of “female subordination in all things was conspicuously absent in Iroquois society”. Husbands joined their wife’s family. When a woman wanted a divorce, she set her husband’s things outside the door.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mythologies_of_the_Indigenous_peoples_of_the_Americas
Apotamkin
There were 45 million Indigenous people between Mexico, the Andes, and other parts of the Americas. There were around 3 million Indigenous people in the US.
Eastern Woodlands
- Iroquois Confederacy (70k) includes Mohawk, Oneida. Great Law of Peace.
- Algonquian (50k) includes Wampanoag and Powhatan. Also Cree in Canada.
- Wendigo are gaunt hungry spirits.
- Five Civilized Tribes: Choctaw (125k), Creek (pop 50k), Cherokee (30k)
- Three sisters farming: beans growing on corn and squash to retain moisture
- Forced out in the Trail of Tears
- Great Basin: Shoshone (pop 60k)
Plains Indians: Blackfoot Confederacy (60k), Crow (50k), Comanche (40k), Osage (15k)
- Medicine Lodge Treaty of 1867 sends Plains Indians to Indian reservations.
- Apache (60k): martial culture
- Comanche (40k) allied with the Confederacy in the civil war. General Sherman sends a cavalry unit, which wins the Comanche campaign (1871).
- Lakota Sioux (pop 100k) conquered the Cheyenne (10k) in 1776, then allied against the US in the Great Sioux Wars.
Southwest
- Pueblo (pop 300k) including Hopi.
- Navajo is currently the largest US tribe with 400k people.
- Second Battle of Fort Defiance (1860): US infantry repel Navajo warriors, then Lt. Col. Chaves raid Navajo land.
- Long Walk of the Navajo. Kit Carson rounds up all 10k Navajo by burning crops and shooting all males on sight.
Arctic people
- 1000. Thule people are ancestors of the Inuit. Eskimo is not preferred.
- Yupik in Alaska.
Colonialism
In the 1400s, a calamity spreads across the world, known as the Age of Exploration or Age of Discovery. Competing feudal monarchies in Europe discover sailing and stocks. They enslave and decimate hundreds of cultures in pursuit of profit and power. In sub-Saharan Africa, Portugal enslaves hundreds of tribes in sugar plantations. To deter organized resistance, slavers obliterate the heritage of language, dress, custom, family and village relations. In 1652, the Dutch East India Company establishes the Dutch Cape Colony in the Cape of Good Hope, which is captured by the British in 1806. In the Bahamas, Cuba, and Haiti, Columbus enslaves and exterminates the Arawak Indians in search of gold. The East India Company strangles the Indian economy and fosters opium addiction in Asia. In Mexico, Peru, Puerto Rico, Spanish conquistadores massacre cities and whole civilizations in search of El Dorado (“the golden”). In the English colonies, Puritans raze village after village. “A depraved appetite after the great vanities, dreams, and shadows of this vanishing life…” in need of wealth as if starving and dying of thirst. All the blood and money goes toward hiring more mercenaries to wage more war, and in the end the people are not richer.
In contrast, the enclosure of land in Europe for scalable production flooded the cities with vagrant poor. In response, rulers passed laws to whip the poor, imprison them in poorhouses, and send them out of the country. The system of class oppression metastasized to America. Merchants built fortunes from shipping out the poor to become indentured servants, landless serfs, and commodities of profit to the landed elite.
The elites feared frequent revolts by slaves, Indians, servants, and farmers, especially the potential for the oppressed to combine. The law was an instrument of power: people needed to show papers to prove that they were free men; striking workers were sentenced to lashes; etc. But racism and dehumanization was a more powerful tool of class control. To rule, the upper class bought the loyalty of the middle class with concessions and social acceptance, at the cost of the lower class. They emphasized racial purity to prevent the mixing of poor whites and blacks. And finally, they invent a new nation and new politics where “artisans and even laborers” can participate in the political process.
The Spanish treasure fleet steals mountains of precious goods, but all the wealth fuels massive destructive wars, and Spain does not end up richer.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First_wave_of_European_colonization
Colonial period 1607-1765
- 1492 Columbus discovery.
- Columbian Exchange
- New World tobacco, corn, tomato, potato, beans, vanilla, chocolate
- Old World horses, cows, pigs, sugarcane, wheat, rice, coffee
- 90% of Native Americans die from smallpox, measles, influenza, typhus, yellow fever, bubonic plague
- Columbian Exchange
- Britain established three types of colonies by royal charter.
- Proprietary colonies were governed by a sovereign lord proprietor.
- Charter colonies were run by a joint-stock company for profit, and experimented more with elected governors and legislators. These include Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut.
- Crown colonies were directly run by the Crown. Most colonies were eventually converted to Crown colonies.
- 1587 Lost Colony of Roanoke founded with 100 colonists, who disappeared by 1590, leaving only a carved “croatoan”.
- 1605 French Acadia colony founded at Port Royal (present Annapolis Royal).
- 1610 Newfoundland colony.
- 1607 Jamestown, Virginia is the first permanent English colony in America. Captain John Smith led the colony through the Starving Time in winter 1609, where 80% of colonists died. Colonists expand into Powhatan land and grow tobacco which degrades the soil.
- Pocahontas is a princess of the Powhatan Confederacy and talked with Smith when he was captured.
- 1620 Plymouth colony settled by Pilgrims on the Mayflower. Only half the colonists survived the first winter. Thanksgiving thanks the Native Americans for helping the colony survive.
- 1628 Massachusetts Bay Colony around Salem and Boston founded by Puritans, who wanted to purify the Church of England of Catholic practices. The colony had around 100 slaves by 1680.
- 1692 Salem witch trials kills 20 people. Giles Corey dies after three days of pressing, only requesting “more weight”. He refused to plea guilty or not guilty, allowing his sons to inherit his estate.
- 1688 King William’s War is the American theater of the Nine Years’ War, with fighting between French and English colonies.
American Indian Wars
- 1609. Beaver Wars: Iroquois fight the French and the Algonquians. Wendat leader Kondiaronk arranges the Great Peace of Montreal (1701).
- 1622. Jamestown massacre kills 347 settlers, beginning the Anglo-Powhatan Wars.
- 1830. Indian Removal Act by Andrew Jackson.
- 1849. Apache Wars against Mexico and the US army led by Geronimo.
Mercantilism
Slavery
- Atlantic slave trade is a triangular trade: manufactured goods to Africa, slaves to America, raw materials to Europe.
- In the Middle Passage, slave ships packed slaves tightly in chains with minimal food, water, or air on a two-month journey. Slaves often had to urinate or defecate where they lay, leading to rampant disease. Around 12.5 million slaves were transported, with a 15% mortality rate.
- Slave resistance. Passive resistance included working slowly or carelessly, or pretending ignorance or sickness. In Petit marronage, slaves would escape for days or weeks then return. Grand marronage was permanent escape.
- 1791. Haitian Revolution.
- 1811. German Coast uprising is the largest, at 200 slaves.
- Hoodoo or voodoo spirituality
Seven Year’s War (1756-1763). Colonial rivalry between opposing alliances of Great Britain and France. The French and Indian War is the American theatre of the war. In the Treaty of Paris, France loses North America, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Tobago to Great Britain. Great Britain ended up with around 200% debt-to-GDP, and taxes the colonies to help pay for British troops.
The Mayflower arrives in Portsmouth. Puritans have a high literacy rate because they believe that scripture is an individual journey.
1734. Great Awakening is an evangelical revival movement emphasizing religious piety and devotion. Congregational minister Jonathan Edwards preaches justification by faith alone in Northampton, Massachusetts. He delivers Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God (1741) with vivid imagery.
American Revolution
Ben Franklin publishes The Pennsylvania Gazette from 1729 and Poor Richard’s Almanack from 1732. Hundred dollar bill.
- “Love, and be loved.”
- “Dost thou love life? Then do not squander time, for that is the stuff life is made of.”
- “Whate’er’s begun in anger ends in shame.”
- “The Sting of a Reproach, is the Truth of it.”
- “Wink at small faults; remember thou hast great ones.”
- “Early to bed, early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise”
- “Well done is better than well said”
1765-1783
- 1651. The Navigation Acts require the colonies to trade only with England.
- 1765. The Sugar Act and Stamp Act leads to some boycotts of British luxuries. Colonists petition for “no taxation without representation”.
- 1767. Townshend Acts tax colonial imports from Britain, and help the British East India Company compete with smuggled Dutch tea. Protestors tar and feather tax collectors and blow up the Gaspee, a customs ship.
- Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania (1767) by John Dickinson, “Penman of the Revolution”, unites colonists against the Townshend Acts.
- 1773. Boston Tea Party. The Sons of Liberty board East India Company ships and throw the tea into the harbor in response to the Tea Act, which allowed the British East India Company to sell its tea directly to America, undercutting colonial merchants who would buy the tea at the London Tea Auction.
- 1774. Intolerable Acts or Coercive Acts close Boston Port and revoke the Massachusetts charter, giving the governor direct control. The First Continental Congress petitions the king, unsuccessfully.
April 1775. The Revolutionary War begins with Battles of Lexington and Concord. 700 British regulars in Boston row to Cambridge and march to Concord to capture military supplies. They row from Boston to Cambridge, inspiring Henry Longfellow’s poem The Midnight Ride of Paul Revere (“one if by land, two if by sea”). Lexington minutemen stand in formation by the road watching the British army. The British army confronts them without firing, until someone fires “the shot heard round the world”. In the return march, militiamen kill nearly 50 British soldiers from behind trees and walls.
The siege of Boston begins afterward. George Washington leads the Continental Army. Conneticut militia capture the largely undefended Fort Ticonderoga, and Colonel Henry Knox moves the heavy artillery to overlook Boston harbor, forcing the British to evacuate by ship to Nova Scotia.
In May 1775, the Second Continental Congress convenes in Philadelphia. It initially drafts the Olive Branch Petition which is rejected by King George.
Thomas Paine writes Common Sense (1776), which argues for independence and is wildly popular.
Johnny Appleseed is a kind missionary who grows over a thousand acres of apple nurseries in Pennsylvania and surrounding states.
1776. Declaration of Independence by the Continental Congress.
- We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.
General Howe occupies the Port of New York in the Battle of Long Island. The Continental Army retreats across the state, shrinking from desertions and poor morale. On Christmas Eve, Washington ambushes the Hessian camp in Trenton, capturing almost 1,000 Hessians and inspiring reenlistments and inspiring the painting Washington Crossing the Delaware (1851). Hessians are German mercenaries hired by the British. Washington winters at Morristown.
1777. Articles of Confederation by the Continental Congress.
1777. Battle of Saratoga. General Burgoyne surrenders his army of 8,000, securing French entry into the war. He aimed to capture Albany. Instead of supporting Burgoyne, General Howe occupied Philadelphia after winning the Battle of Brandywine, the largest battle with 15,000 troops per side. Washington spends a harsh winter at Valley Forge. The British army moves back to New York City, with Washington raiding. The Battle of Monmouth ends in a draw.
1778. The British change to a southern strategy and capture Savannah. In the siege of Charleston of 1780, Britain captures all 6,000 US soldiers in the south. Benedict Arnold defects to the British in a failed plot to surrender the fort of West Point.
1781 Siege of Yorktown. General Cornwallis surrenders to Washington and Comte de Rochambeau, ending the war. The French navy under Comte de Grasse prevents the British fleet from reinforcing Cornwallis in the Battle of the Chesapeake. The Treaty of Paris of 1783 formally ends the war.
Confederation Period. The federal government is very weak, requiring unanimous agreement to act. In Shays’ Rebellion of 1787, tax protestors occupy the courts and attempt to seize the federal Springfield Armory. The government cannot finance troops to restore order.
1780 First Industrial Revolution mechanizes the British textile industry with water power. Europe transitions from cottage industry and the domestic workshop or putting-out system to urban factories.
Westward Expansion
Constitutional Convention of 1787.
US Constitution (1789): ensures separation of powers and checks and balances between executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
- Federalism divides powers between federal and state government.
- Supremacy Clause: federal laws take priority over state laws.
- Necessary and Proper Clause
- McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) establishes implied powers.
- Connecticut Compromise: proportional representation in the House, and equal representation in the Senate.
- Three-Fifths Compromise: slaves counted as 3/5 of a person for apportioning seats in the House, Electoral votes, and direct taxes. The Fugitive Slave Clause provided that slaves that escaped to a free state did not become free.
- Commerce Clause: federal government has broad power to regulate interstate commerce.
Bill of Rights
- First amendment: freedom of speech, religion, press, assembly, petition, association.
- Second amendment: right to bear arms.
- Third amendment restricts quartering of soldiers in wartime.
- Fourth amendment bans unreasonable search and seizure.
- Fifth amendment: right to due process. Also bans double jeopardy and self-incrimination and requires grand jury indictment to bring charges for felonies.
- Sixth amendment: right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury with the assistance of counsel, and right to confront one’s accuser and compel witnesses.
- Gideon v. Wainwright (1963): public defender must be provided to criminal defendants unable to afford an attorney.
- Seventh Amendment: right to jury trial
- Eight Amendment bans excessive bail, excessive fines, or cruel and unusual punishments.
- Ninth Amendment: all powers not delegated to the government are retained by the people
- Tenth Amendment: federal government has specific delegated powers, and the states have the rest.
Federalists like Madison and Hamilton write the Federalist Papers, while Anti-Federalists oppose a strong central government.
First Party System, 1792-1824: Federalists promote a strong central bank, trade, and better relations with Britain, while Jeffersonians or Democratic-Republicans emphasize farmer interests and liberty and better relations with France.
George Washington is the first president from 1789 to 1797. Appears on the dollar bill and quarter.
- 1791. Washington passes the whiskey tax, the first tax on a domestic product, to pay war debt. This hurts frontier farmers. In the Whiskey Rebellion, over 500 armed men beat up a tax collector. Washington leads an army of 13,000 militiamen to enforce the tax, though the rebellion disbands before he arrives.
- 1791. Hamilton founds the First Bank of the United States to increase public and private credit. Appears on the ten dollar bill.
- 1794. Jay Treaty reopens trade with Britain and delays war for ten years. Britain relinquishes forts on US territory around the Great Lakes, while debt and border disputes would be resolved in arbitration. John Jacob Astor becomes the first US multimillionaire through a fur trade monopoly.
Federalist John Adams is the second president from 1797 to 1801. He is an abolitionist and the only founding father not to own slaves. He is a Congregationalist. Abigail Adams pushes for women’s rights because men are “naturally tyrannical”. Thomas Jefferson is vice president.
- 1797. XYZ Affair. The French foreign minister Talleyrand demands bribes to open negotiations. Pinckney responds: “No, no, not a sixpence!” US backlash leads to the Quasi-War, an undeclared naval war with France in the Caribbean.
- 1798 Federalists pass the Alien and Sedition Acts in fear that French immigrants would overthrow the government.
- Alexander Hamilton is the first Secretary of the Treasury, promoting a national bank.
- Adams tries to pack the judiciary by appointing midnight judges, which are promptly fired by Jefferson.
Democratic-Republican Thomas Jefferson is the third president from 1801 to 1809. Two dollar bill and nickel.
- 1787 Jefferson lives in Paris as Minister to France. He takes his 14-year-old slave Sally Hemings and impregnates her.
- 1800 Louisiana Purchase doubles the US for $15 million. Jefferson wanted to secure Mississippi River shipping, and France could not defend the territory.
- The Lewis and Clark Expedition documents the new land.
- Sacagawea interprets for the expedition, finds edible camas roots, and guides them through Gibbons Pass and Bozeman Pass. Appears on the dollar coin.
- 1801 First Barbary War. US bombards Tripoli, pays ransom for captured soldiers, and celebrates a victory.
- Marbury v. Madison (1803) establishes the principle of judicial review.
War of 1812. During the Napoleonic Wars, Britain restricts US trade with France and impresses deserters on US ships into the Royal Navy.
- 1806. Non-importation Act imposes sanctions on Britain.
- 1807. Chesapeake affair.
- Embargo Act of 1807. US bans trade with both France and Britain. It mostly hurts the US, though it increases industrialization in the longer term.
Tecumseh’s confederacy resists American expansion and is defeated in the Battle of Tippecanoe. In 1814, Britain burns Washington before US wins the Battle of Baltimore, inspiring The Star-Spangled Banner. In 1815, US repels an attack on New Orleans and signs the Treaty of Ghent, allowing an independent economy free of British mercantilism. Europe food production was depleted from war, increasing demand for US food, fueling a land bubble. The Federalist Party opposed the war and collapses.
James Madison is the fourth president from 1809 to 1817.
- 1815. Second Barbary War. US navy wins against pirates.
- 1816. Second Bank of the United States. Madison adopts a key Federalist program after difficulties funding the war.
Democratic-Republican James Monroe is president from 1817 to 1825. He promotes national unity in an Era of Good Feelings, which is still highly factional.
- Monroe Doctrine opposes European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere.
- Panic of 1819 caused by deflation due to a gold shortage and a collapse of the land bubble.
- 1820. Missouri Compromise admits Missouri as a slave state, Maine as a free state, and prohibits slavery in remaining territory north of the 36°30′ parallel. Northern states want a protective tariff and a national bank.
- 1821. Sequoyah invents the Cherokee syllabary.
Second Party System
Democratic-Republican John Quincy Adams is the sixth president from 1825 to 1829. Supported the Jay Treaty and left the Federalist Party.
- Webster’s Dictionary (1828).
Democrat Andrew Jackson is the seventh president from 1829 to 1837. Twenty dollar bill. Free Banking Era.
- Jackson emphasizes the spoils system and replaces 10% of the government, inspiring the phrase “to the victor belong the spoils”.
- 1828. Jackson’s very high Tariff of Abominations precipitates the South Carolina Nullification crisis, supported by John C. Calhoun. The Compromise Tariff of 1833 resolves the crisis.
- 1830. Daniel Webster’s second reply to Hayne celebrates nationalism.
- 1830. Indian Removal Act and the Trail of Tears.
- Expands suffrage to all white men.
- Petticoat affair. The wives of prominent cabinet members refuse to socialize with Peggy Eaton, the wife of Secretary of War John Eaton. Jackson defends his friend Eaton and Vice President John C. Calhoun resigns.
- National Republican Party, later the Whig Party, founded by Andrew Clay. Conservative: wanted a protective tariff, national bank, and infrastructure; against Manifest destiny and presidential power.
- 1835.
- Tocqueville tours America and writes Democracy in America (1835) on American exceptionalism.
- Frontiersman Davy Crockett becomes a folk hero.
Democrat Martin van Buren is the eighth president from 1837 to 1841.
- William Henry Harrison is the ninth president but dies after 31 days. He is worn down by the press of patronage, gets caught in the rain, catches pneumonia.
Whig John Tyler is the tenth president from 1841 to 1845.
- 1822. Under a Spanish impresario contract, Stephen F. Austin colonizes eastern Texas with the Old Three Hundred families and slaves.
- 1836. Texas Revolution. US colonists and Tejanos (Hispanic Texans) secede from Spain, opposing Mexican abolition, immigration ban, and import tariffs.
- Battle of the Alamo. Mexican troops kill all 200 defenders. “Remember the Alamo” on the reverse of the seal of Texas.
- The Republic of Texas is independent for 10 years, giving the nickname The Lone Star State.
- Cyrus McCormick invents the reaper, improving farm productivity and urbanization.
Democrat James K. Polk is 11th president from 1845 to 1849, defeating Whig Henry Clay. Polk wins as a dark horse candidate on the popular platform of annexing Texas and Oregon. Van Buren was against annexation, and Whig Henry Clay was ambivalent.
Manifest Destiny is a belief that America is divinely ordained to bring democracy and civilization across the continent, as portrayed in American Progress (1872) by John Gast.
- Oregon Trail. 300,000 settlers make the 5 month, 2,200 mile journey from Independence, Missouri to the Willamette Valley in Portland, Oregon. The trail follows the Missouri River, Platte River, Independence Rock, and Sweetwater River to the South Pass in Wyoming, which goes through the Rockies. From there the trail follows the Green River, Fort Bridger, Bear River, Big Hill, Soda Springs, Fort Hall, and Snake River. Finally, migrants had to raft the Columbia River around Mount Hood. 5% die of drowning and starvation. Made fires with buffalo chips (dung). Chloera killed thousands, especially on the brackish Platte River, as many people shared the same camping spots on freshwater springs with no sewage treatment.
- Eastern seaboard -> Allegheny Mountains -> Pittsburgh -> Ohio River -> St. Louis, Missouri.
- 1843. Great Migration of 1843 is the first wagon train of 700 people.
- Santa Fe Trail goes from Independence to Santa Fe, crossing the northwestern corner of the Comancheria territory. El Camino Real goes from Santa Fe to Mexico City.
- Panic of 1837 causes a depression and settlers look west for better opportunities.
- 1830. Joseph Smith founds the Mormon church in Independence. Mormons are wealthier and abolitionist and are evicted following the 1838 Mormon War. They migrate to Illinois, where in 1844 Smith orders the destruction of an anti-Mormon printing press and gets killed by a mob. Brigham Young leads Mormons to Salt Lake City, Utah via the Mormon Trail, which forks from the Oregon Trail at Fort Bridger.
- 1845. US annexes Texas and wins the Mexican-American War in 1848.
- 1846. Oregon Treaty sets the US border at the 49th parallel.
- 1849. California gold rush leads to mass immigration into Gold Country in the Sierra Nevada and northern California. Gold is discovered at Sutter’s Mill in Coloma on the American River. Sacramento becomes a large trading port on the Sacramento River. Saloons. SF grows to 36,000 people. Chinese immigration surges in the opium wars.
- California Trail: Salt Lake Cutoff -> Humboldt River -> Forty Mile Desert of 1 ft of loose sand. Hard to cross with half the wagons abandoned. Then Truckee River -> Donner Pass across the Sierra Nevada -> Bear Valley, or Carson River -> Carson Pass -> American River.
- Placer mining of stream bed placer deposits, where gold accumulates due to gravity.
- Gold panning: stratification by agitating the deposit in water.
- Rocker box: quarter-inch sieve, baffle, riffles, and carpet.
- Sluice box: riffles trap small gold particles.
- Placer deposits of
- 1850. The Donation Land Act promotes settlement in the Oregon Territory.
- Legend of John Henry, who wins a duel a steam-powered rock drill only to die as his heart gives out.
Whig Millard Fillmore is 13th president from 1850 to 1853. The Compromise of 1850 delays civil war:
- The Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 requires federal officers to help return fugitive slaves.
- Admits California as a free state.
- Bans the slave trade in the District of Columbia.
- The US assumes $10 million of Texas debt and Texas surrenders its claim to New Mexico.
- Slavery in the territories would be decided by popular sovereignty.
- Authored by Whig senator Henry Clay and Democratic senator Stephen A. Douglas. Supported by Whig Daniel Webster.
Democrat Franklin Pierce is 14th president from 1853 to 1857.
The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 repeals the Missouri Compromise, instead allowing states to decide slavery for themselves.
- Bleeding Kansas: electoral fraud and murders by proslavery “border ruffians” and antislavery free-staters. Depicted in Tragic Prelude (1942).
- Democrat Thomas Hart Benton of Missouri and former Democrat Sam Houston of Texas oppose slavery.
- 1856. Republican Charles Sumner denounces the act as “rape of a virgin Territory” and is caned in the Senate. Abolitionists and slaveholders accused each other of being sexually motivated.
- Minister Henry Beecher raises funds to send rifles to Kansas, leading them to be called Beecher’s bibles, saying that border ruffians had “a supreme respect for the logic that is embodied in Sharps rifles”.
- 1856. John Brown defends an free-stater settlement in the Battle of Black Jack. In 1859, he raids Harpers Ferry, Virginia hoping to incite a slave revolt.
Democrat James Buchanan is 15th president from 1857 to 1861. He favors states’ rights.
- The Know Nothing party is anti-immigrant and anti-Catholic and neutral on slavery.
Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857) increases tensions. Scott sues for his freedom after living in free territories. The court holds that Black people are not citizens and thus lack standing to sue in federal court. It strikes down the Missouri Compromise arguing that Congress had no power to regulate slavery in the territories.
- Lincoln rejects that “the right of property in a slave is distinctly and expressly affirmed in the Constitution”, pointing out that the Constitution refers to slaves as people, not property.
1858. Lincoln-Douglas debates. Lincoln runs against incumbent Stephen Douglas for Illinois senate. Douglas supports popular sovereignty.
- House Divided speech: A house divided against itself, cannot stand. -Matthew 12:25
Civil War, 1861 - 1865
Republican Abraham Lincoln is 16th president from November 1860 to 1865. He opposes the expansion of slavery into the western territories. In February 1861, eleven states secede and form the Confederacy. In his inaugural address in March, Lincoln says that he does not intend to invade Southern states but will use force to keep federal forts. Even in 1862, Lincoln emphasizes that his official duty is to save the Union, and not to save or to destroy Slavery.
- Copperheads oppose the Civil War and want immediate peace with Confederates.
- 1861. Trent Affair: US Navy captures two Confederate envoys from a British ship. Lincoln releases them to avoid war with Britain.
- 1861. Lincoln revokes the Frémont Emancipation, which frees slaves of Confederate supporters in Missouri. Lincoln wants to prevent Missouri and other border states from seceding.
- On the five dollar bill and penny.
1861. Battle of Fort Sumter. Lincoln sends an unarmed ship to resupply the fort. Confederate forces capture the fort, and Lincoln calls a Union army and blockades Confederate ports.
July 1862. First Battle of Bull Run. General Patterson failed to prevent Confederate reinforcements from arriving and routing the Union Army. Both sides prepare for a larger, longer conflict. Stonewall Jackson gets his name from breaking the Union attack. General McClellan replaces McDowell as army general.
Lincoln imposes martial law in Maryland, which had voted to close its rail lines to Union soldiers. West Virginia splits from Virginia to join the Union.
Kentucky declared neutrality, so the Union army staged in Ohio until Kentucky aligned with the Union.
Peninsula Campaign. McClellan slowly battles through Williamsburg and Seven Pines. In the Valley Campaign, Stonewall Jackson prevents the Union army from reinforcing McClellan. Lee defends Richmond against McClellan, McClellan stays put, Lincoln appoints Pope to lead the Army of Virginia, Lee defeats Pope at the Second Bull Run and invades Maryland.
Battle of Antietam, McClellan wins.
Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation prevents European interference.
- Juneteenth. June 19, 1865. Union troops free the last slaves in Texas.
At the Battle of Chancellorsville in May, Lee defeats Hooker’s larger army with heavy losses. Hooker’s goal is to attack Lee and keep his army between Lee and Washington DC to the northeast. Hooker moves slowly. On June 3, Lee heads north toward Pennsylvania to capture horses, equipment, and food and increase pressure for a treaty.
Battle of Brandy Station on June 9, the largest cavalry battle. To help the Confederate Army slip away, Stuart prepares to raid Union forward forces. Hooker surprises Stuart with a preemptive attack: Buford makes a predawn raid across the river and Gregg threatens Stuart’s rear. But Stuart fends off the attacks and Hooker does not discover the Confederate army.
Battle of Gettysburg
General Meade halts Lee’s advance over three bloody days in July 1863.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gettysburg_campaign
https://archive.is/2NbR9
Background. Lee’s army advances north in three corps under Longstreet, Hill, and Ewell. On June 28, Lincoln replaces Hooker with Meade, who promptly advances north to Gettysburg. In the lead are three corps under Reynolds, Sickles, and Howard. Meanwhile, Stuart’s cavalry is delayed riding fully east of the entire Union army for many days to raid supplies, depriving Lee of intelligence. Spy Henry Thomas Harrison reports that the Union army is very close, so Lee concentrates his army and orders his generals to avoid a large battle. On June 30, Buford’s cavalry and a brigade under Heth see each other in town. Buford calls for reinforcements and holds three layers of low ridges west of town for a delaying action: Herr Ridge, McPherson Ridge and Seminary Ridge. Hill thinks this is a local militia and sends some units to investigate.
Day 1. In the morning, Heth leads two brigades against Buford. Reynolds’ corps arrives (becoming Doubleday’s corps after Reynolds dies). In the afternoon, Howard’s corps reinforces to the right of Doubleday, facing attacks by Ewell’s corps (Rodes’ division and Early’s division to its east). Finally, Hill’s corps fully arrives, and the Union army makes a chaotic retreat through town to Cemetery Hill. Ewell does not try to take the hill, and Howard accepts the fantastic defensive position instead of falling back mid-battle to prepared defenses at Pipe Creek.
Day 2. Union forces are entrenched behind steep hills and stone walls, in a fishhook shape with short interior lines. Sickles (III) holds the left flank at Little Round Top; Hancock (II), Newton, and Howard extend up two miles of Cemetry Ridge to Cemetery Hill; and Slocum and Sykes (V) hold the right flank at Culp’s Hill. Longstreet urges Lee to leave for better ground, but Lee wants to keep the initiative. Lee attacks the Union left flank, unaware that it extended down to Little Round Top. Longstreet attacks from the south, Hill attacks from the west, and Ewell pins down units on the right flank. Against orders, Sickles overextends west to slightly higher ground in a peach orchard. With an attack imminent, Meade sends Sykes to support, weakening the rest of the line. Sickles takes heavy losses retreating through the peach orchard and the wheat field, and Longstreet takes heavy losses in Devil’s Den and Plum Run Valley (the “Valley of Death”) to the south. Hancock and Sykes barely hold Cemetery Ridge and Little Round Top, resorting to bayonet charges by Colvill and Chamberlain. Stuart finally arrives around noon and have no role in the second day’s battle. Ewell takes some trenches at Culp’s Hill.
Day 3, Union reinforcements push Ewell out of Culp’s Hill. Lee orders a massive, ineffective bombardment against the Union center. Pickett’s Charge covers a mile of open terrain and is destroyed, marking the high-water mark of the Confederacy. Lee retreats and Meade does not pursue, eventually stopping for winter. Lincoln complains that “Our army held the war in the hollow of their hand and they would not close it!”
Gettysburg Address. The nation was conceived in Liberty and equality. Mentions the dedication of the cemetery and honors the dead. Asks the audience to continue the work and achieve “a new birth of freedom-and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth”.
Grant vs. Lee
In March 1864, Grant gets command and proceeds to encircle Lee on three sides.
Sheridan moves cautiously to ensure Lincoln’s reelection in 1864, then defeats Early at the Battle of Cedar Creek. Sherman’s Western March to the Sea in Atlanta is a bloody success. Lee is unable to break out and surrenders at Appomattox Court House.
McClellan would lead the Union Army of the Potomac through Virginia toward Richmond.
Post Civil War
Lincoln wins reelection in 1864 on unity platform, naming Tennessee senator Andrew Johnson as his vice president.
- on changing political parties: “it was not best to swap horses when crossing streams”
The Thirteenth Amendment bans slavery. Lincoln and Secretary of State Seward bribe lame-duck Democrats with federal jobs and campaign contributions in exchange for votes. Lincoln also creates the Freedmen’s Bureau to provide temporary food, clothing, and shelter for newly freed slaves.
First-wave feminism focuses on legal rights and is primarily led by middle class white women.
- The Culture of Domesticity values piety, purity, submission, and domesticity.
- The Angel in the House (1862) represents Victorian views.
- 1890s bicycle craze with pneumatic tires.
- The New Woman is educated, economically independent with sexual autonomy.
- 1900. Finishing school teaches young women etiquette and grace.
- Mary Wollstonecraft. A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (1792) argues that women are equal to men if given the same education. Also Original Stories from Real Life (1788).
- Frances Wright organizes popular speeches and publishes Course of Popular Lectures (1829).
- Margaret Fuller is a transcendentalist and feminist. Woman in the Nineteenth Century (1843).
- Sojourner Truth: Ain’t I a Woman? (1851) by an ex-slave.
- 1863. Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony found the Women’s Loyal National League to campaign for the Thirteenth Amendment.
- 1848. Seneca Falls Convention. Susan B. Anthony, Lucretia Mott, and Elizabeth Cady Stanton advocate for women’s suffrage and abolition.
- Anna J. Cooper: A Voice from the South (1892) pioneers Black feminism.
- Godey’s Lady’s Book is the most popular antebellum magazine, with a circulation of 150,000. Editor Sarah Hale advocates for women’s education and moral leadership.
- 1920. The Nineteeth Amendment gives women the right to vote.
Abolition
- Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852) by Harriet Beecher Stowe is the best selling book of the century. It humanizes slaves and emphasizes Christian love and nonresistance.
- Frederick Douglass: writer and statesman, 1845-1881.
- Harriet Tubman: conductor on the Underground Railroad starting in 1849.
- Minstrel shows are popular after the Panic of 1837. Blackface performers would portray a Jim Crow stereotype who is dim, lazy, and happy-go-lucky. They influence vaudeville, variety shows, comedy, and blues music.
Native-American relations
The Treaty of Fort Laramie of 1851 established Cheyenne and Lakota Sioux territories. Pike’s Peak Gold Rush in Colorado in 1859, which was Cheyenne territory. The Treaty of Fort Wise of 1861 is signed by a minority of Cheyenne chiefs, leading to the Colorado War of 1864 and the Sand Creek Massacre.
In 1863, gold is discovered in Alder Gulch, Montana. Miners blaze the Bozeman Trail branching north from the Oregon Trail through Wyoming Sioux territory. Red Cloud’s War consists of many Sioux raids, including the Fetterman Fight which kills 81 US soldiers. The Crow ally with the US because the Sioux occupied some of their territory.
The Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868) ends Red Cloud’s War. It establishes the Great Sioux Reservation including the Black Hills, large amounts of Crow tribe land, and the Ponca Reservation. The Crow Indian Reservation covers 3,600 square miles in south Montana.
The Great Sioux War of 1876. The Black Hills Gold Rush begins in South Dakota, and Grant sends 570 men to attack the Sioux. In the Battle of the Little Bighorn, also known as Custer’s Last Stand, Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse kill 270 soldiers.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indian_removal
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lenape
Reconstruction, 1865 - 1877
Andrew Johnson is 17th president from 1865 to 1869, taking office after Lincoln is assassinated. Johnson tries to readmit rebel states without protection for newly freed slaves. He pardons all the Confederates.
Republicans briefly control the South.
- 1862. The Ironclad Oath requires members of Congress to swear that they never supported the Confederacy.
- Black voting bloc organizes via Union League men’s clubs and the black-and-tan faction, leading to freedmen leaders.
- Conservative whites brand the leaders as carpetbaggers (Northerners who recently moved south) and scalawags (southerners who supported Reconstruction). The Lily-White Movement eventually rules the Republican party.
Radical Republicans in Congress take charge of reconstruction over Johnson’s veto. Include Benjamin Wade.
- Thaddeus Stevens helps Lincoln fund the war and pass the 13th Amendment.
- Civil Rights Act of 1866
- Reconstruction Amendments
- Reconstruction Acts require rebel states to pass the Fourteenth Amendment to be readmitted to the Union.
- Johnson dismisses pro-Reconstruction Secretary of War Edwin Stanton ignoring the Tenure of Office Act and escapes impeachment by one vote. Republican Edmund Gibson Ross makes the deciding vote and loses reelection two years later.
The Fourteenth Amendment of 1868 includes:
- Equal Protection Clause
- Due Process Clause: incorporates the Bill of Rights to state governments.
- Citizenship Clause: all people born or naturalized in the US are citizens, reversing Dred Scott v. Sandford.
Republican Ulysses S. Grant is president from 1869 to 1877, presiding over the Reconstruction era. Grant passed Enforcement Acts to send federal troops to curb white supremacist Ku Klux Klan (KKK) violence and ensure fair elections. He creates the Department of Justice to prosecute the KKK. He appointed many friends, leading to corruption scandals. Appears on the fifty dollar bill.
- 1869. Jay Gould and James Fisk try to corner the gold market, and Grant releases federal gold, leading to the Black Friday stock market crash and low food prices.
- Panic of 1873 leads to five years of Long Depression.
1869 Transcontinential Railroad. Chinese laborers provide much of the labor, and introduce chop suey 杂碎.
The Fifteenth Amendment of 1870 prohibits denying the right to vote based on race. In response, Southern states used poll taxes, literacy tests, white primaries, grandfather clauses, and KKK violence to deter black voters.
The Great Chicago Fire kills 300 people. Insurance executive Arthur Ducat promotes better fire standards.
Gilded Age, 1877 - 1896
Republican Rutherford B. Hayes is 19th president from 1877 to 1881. He ends reconstruction.
- The Solid South or Southern bloc realigns Democratic.
- Jim Crow laws, lynchings, and the KKK enforce racial segregation.
- Sundown towns ban colored people.
- Literacy tests and poll taxes exclude black voters. Grandfather clauses exempted white voters.
- Black Codes force black workers to continue working on farms.
Republican James Garfield is 20th president for half a year in 1881 but gets assassinated.
Republican Chester Arthur is 21st president from 1881 to 1885.
- 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act bans immigration from China.
- 1875 Page Act bans immigration of “immoral Chinese women”.
- 1892 Geary Act denies citizenship to Chinese immigrants.
- 1883 Wong Chin Foo founds the Chinese Equal Rights League.
- 1883 Pendleton Act mandates most federal positions should be awarded on the merit system instead of the spoils system.
Grover Cleveland is 22nd president from 1885 to 1889, and 24th president from 1893 to 1897.
- 1893. Americans overthrow the Hawaiian Kingdom of Queen Liliʻuokalani.
- 1898. Newlands Resolution. US annexes Hawaii.
Republican Benjamin Harrison serves as the 23rd president from 1889 to 1893. He passes the unpopular McKinley Tariff of 1890 which raised import taxes to 50%.
The Tammany Hall political machine controls New York politics. Boss Tweed controls patronage and city jobs and embezzles millions of dollars.
- Thomas Nast attacks Tammany Hall with political cartoons, reaching illiterate Americans.
Robber barons consolidate monopolies, manipulate markets, and lobby politicians.
- 1818. Lehigh Coal is the first vertically integrated US company, including transport and manufacturing.
- 1860. Cornelius Vanderbilt builds a railroad empire.
- 1860. Leland Stanford leads the Central Pacific and Southern Pacific railroads.
- 1860. Jay Cooke builds the first investment bank and finances the Civil War.
- 1880. Rockefeller becomes the richest person by establishing the Standard Oil monopoly through differential pricing, horizontal and vertical integration, and secret rail rebates.
- 1890. Andrew Carnegie builds a steel empire through the Bessemer process, vertical integration of raw suppliers, rail rebates, and lobbying for trade tariffs. In 1894, Philadelphia City Hall becomes the tallest building in the world.
- 1890. J. P. Morgan drives massive consolidation. He owns the Pullman Company, 21 railroads, and forms U.S. Steel in 1900. Drexel Morgan finances the US Army in 1877 and bails out the US government in the Panic of 1893, Panic of 1895, and Panic of 1907.
- Joseph Pulitzer (New York World) and William Randolph Hearst consolidate the newspapers. They cut prices, sell department store ads, and sensationalize news with yellow journalism.
- James Bryce observes vast inequality in The American Commonwealth (1888).
Coal
The Coal Region in northeast PA is the world’s largest anthracite coal deposit.
- Geography
- Lehigh Valley is formed by the Lehigh River. Part of the Great Appalachian Valley.
- The Lehigh River joins the Delaware River at Easton, PA and Phillipsburg, NJ.
- The Delaware River is the border between PA and NJ.
- 1818. Lehigh Coal is the first vertically integrated US company, including transport and manufacturing.
- 1820. Lehigh Canal ran south from White Haven to Easton, PA, where the Delaware Canal. Some sections on the Lehigh River, and other sections parallel to avoid rapids and shallows.
- 1825. Schuylkill Canal moves coal barges from Port Carbon to Pottsville to Philadelphia. Closed in 1931.
- 1826. Main Line of Public Works creates the Pennsylvania Canal System and the Allegheny Portage Railroad, which connect Philadelphia to Pittsburgh and the Ohio River.
- Allegheny and Conemaugh rivers.
- 1829. Morris Canal runs east from Phillipsburg, NJ to Jersey City, NJ, allowing access to NYC. Closed in 1924.
- First US canal to use water-driven inclined planes, to cross 900 ft of New Jersey hills.
- 1832. Delaware Canal runs south from Easton to Briston, PA, parallel to the Delaware River.
- 1837. Lehigh and Susquehanna Railroad moves coal from the North Branch PA Canal to the Lehigh Canal.
- 1857. Bethlehem Steel was the world’s second-largest steel manufacturer. Also a major shipbuilder. Mostly closes in 1982.
- 1891. Coal Creek War in Tennessee.
Progressive Era, 1896 - 1917
Also known as the Fourth Party System. The Republican vision of stronger central government, gold standard, and protective tariffs triumphs.
Labor movement.
- 1886. Samuel Gompers founds the American Federation of Labor (AFL).
- 1886. Haymarket affair. Workers strike for an eight-hour work day, which inspires International Workers’ Day or May Day.
- 1887. Great Railroad Strike is the first national strike. It is put down by federal troops.
- Led by the Knights of Labor, an industrial union. Unlike craft unions, it is inclusive of unskilled labor.
- 1894. Pullman Strike. Pullman developed the sleeping car. With lower wages after the Panic of 1893, workers in the company town demand lower rent. Cleveland orders the army to defend the trains, and Eugene V. Debs is sentenced to six months in prison.
- 1905. Bill Haywood founds Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), a radical antiwar union advocating One Big Union. Syndicalism promotes unions and socialism.
- 1918-1920 New York City rent strikes.
- 1919. Luigi Galleani stokes anarchist bombings which contribute to the First Red Scare.
- 1919. AFL steel strike with 350,000 workers fails.
- 1935. Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) focuses on unskilled workers excluded from AFL unions. They merge in 1955.
- 1962. Cesar Chavez and Dolores Huerta found the National Farm Workers Association (NFWA), which becomes the United Farm Workers (UFW) union.
- 2022. Amazon Labor Union by Chris Smalls and Derrick Palmer.
Muckrakers target corporate monopolies and political machines.
- Ida Tarbell writes The History of Standard Oil (1904), which spurs antitrust law and the Hepburn Act of 1906 and Mann-Elkins Act of 1910 that regulated railroad prices.
- Ida B. Wells investigates lynching and inequality, 1884-1920.
- Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle (1906) depicts poverty, harsh working conditions, and lack of social support. The Federal Meat Inspection Act of 1906 requires that meat is processed in sanitary conditions.
- 1911. Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire kills 146 garment workers. Unions organize for better working conditions.
- 1930. Mary Heaton Vorse publicizes and participates in strikes.
1890. Sherman Antitrust Act bans anticompetitive agreements (e.g. cartels) and monopolization.
1914. Federal Trade Commission polices anticompetitive behavior.
1914. Clayton Antitrust Act bans price discrimination, exclusive dealings, tying, and mergers when they harms competition. It exempts organized labor: boycotts, strikes, picketing, collective bargaining.
- Meat Cutters v. Jewel Tea (1965)
- Connell Construction Co. v. Plumbers (1975): a “limited nonstatutory exemption” protects collective bargaining agreements. The NFL Draft was illegal Smith v. Pro Football (1978) until the National Football League Players Association (NFLPA) approved it.
- Jung v. Association of American Medical Colleges (2002)
The Norris-La Guardia Act of 1932 bans employers from interfering with unions.
Republican William McKinley is the 25th president from 1897 to 1901.
The Cuban independence movement had support from landowners and laborers. Landowners wanted lower taxes, while laborers wanted more political representation. Rural people often sheltered rebels. In 1896, Spain moves 500,000 rural people into Reconcentration camps, where half died of starvation and disease.
Spanish-American War of 1898. The US supports the Cuban War of Independence as a moral act. In addition, the US wanted a naval base near the Panama canal, and US magnates purchased most of the sugar and tobacco plantations in Cuba when they were devastated by high taxes. Spain gives Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines to the US in the Treaty of Paris of 1898. American foreign policy becomes more global.
The Teller Amendment blocks the US from acquiring Cuba. Teller ensured that Cuban sugar would not compete with Colorado beet sugar. However, the Platt Amendment allowed the US to dictate Cuban foreign policy and required Cuba to provide Guantamo Bay to the US, leading to resentment. The US wins the Philippine-American War of 1899, and the Philippines are finally independent in 1946. Cuba is very instable, with the US having to intervene after a revolt in 1906 to supervise new elections.
Republican Theodore Roosevelt is the 26th president from 1901 to 1909. He wins fame leading the Rough Riders against Spain in Cuba. Boss Platt places him as governor of New York, where he promotes the Square Deal of public responsibility of large corporations, moderate reform, and protection for the poor. Platt has him chosen as Vice President to get rid of him. Booker T. Washington is the leader of the black community, and has dinner with Roosevelt. Roosevelt brings antitrust suits aggressively and creates the Department of Commerce and Labor. He resolves the Panic of 1907 by allowing U.S. Steel to purchase a struggling steel company and save a major bank. Roosevelt forces coal owners to arbitration to resolve the coal strike of 1902. Roosevelt establishes the US Forest Service, five National Parks, the Antiquities Act of 1906 which creates National Monuments, and 150 National Forests, often by executive order. He also prosecutes corruption in the Indian Service, the Land Office, and the Post Office. He believes that war is noble.
- 1904. Paul Bunyan is a superhuman lumberjack.
- 1904. Harry Houdini escapes from handcuffs in front of 4,000 people. The Daily Mirror had challenged him to escape from the extra-secure handcuffs.
Roosevelt installs William Taft as the 27th president from 1909 to 1913. Taft’s handling of the Payne-Aldrich tariff of 1909 alienates both liberals and conservatives. Roosevelt runs with the Progressive Bull Moose Party which ensures Taft’s defeat.
Democrat Woodrow Wilson is president from 1913 to 1921. He opposes federal laws on women’s suffrage and child labor. He narrowly wins reelection on an anti-war platform, and does not prepare for war.
- 1916. Naval Act authorizes 50 destroyers and 67 submarines.
World War era
World War I: see Europe
- Uncle Sam poster (1917) by J. M. Flagg.
Interwar
Roaring Twenties, 1918-1929.
- Flapper women wear short knee-length skirts, boyish straight lines, bob cuts, and heavier makeup. Jazz and partying culture.
- Coco Chanel popularizes pearl jewellery, petite handbags, the little black dress, and the women’s perfume Chanel No. 5 (1921). Cloche (“bell”) hat.
- 1920 Prohibition (18th amendment). Moonshine, bathtub gin, bootlegging, muscle cars, speakeasies.
- 1933 21st amendment ends Prohibition.
Republican Warren G. Harding is the 29th president from 1921 to 1923. The Teapot Dome scandal sees his Secretary of the Interior imprisoned for accepting bribes. In addition, he attacks the Great Railroad Strike of 1922 of 400,000 union workers. Secretary of the Treasury and oil baron Andrew Mellon pushes tax cuts for the rich and lower national debt.
- 1921 Emergency Quota Act establishes the National Origins Formula to restrict Southern and Eastern Europeans.
Republican Calvin Coolidge is the 30th president from 1923 to 1929. He rises to prominence as governor of Massachusetts by attacking the unpopular Boston police strike of 1919. He signs the Indian Citizenship Act of 1924 and supports women’s suffrage. Congress passes the Bonus Act of 1924 paying up to $500 for WWI vets over Coolidge’s veto.
- 1924 Immigration Act founds the U.S. Border Patrol and includes the Asian Exclusion Act.
Great Depression, 1929-1941
Migrant Mother (1936) by Dorothea Lange.
The Fifth Party System (1932-1980) begins with a Democratic landslide. Democrats begin prioritizing civil rights and gaining black voters.
Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) is president from 1933 to 1945. The popular New Deal expands the federal government, building the New Deal liberal coalition of labor unions, blue-collar workers, and minorities against rich people, businesses, and Protestants. Appears on the dime.
- 1933. The Good Neighbor policy promotes noninterference in Latin America.
- 1934. National Housing Act creates the Federal Housing Administration to underwrite mortgages to reduce foreclosures.
- Redlining denies mortgages in African American neighborhoods by classifying them as high-risk.
- 1935. Social Security
- 1935. Works Progress Administration
- 1935. National Labor Relations Act creates the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB), protects the right to unionize, and bans unfair labor practices.
- 1938. Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) creates a minimum wage and overtime pay.
- 1938. Fannie Mae (Federal National Mortgage Association) focuses on single-family mortgages. Later Freddie Mac (Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation). Supervised by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA).
- 1942. Only president to serve more than two terms.
Eleanor Roosevelt is a civil rights activist. She hosts hundreds of Black guests at the White House and speaks against anti-Japanese prejudice. In 1948, she leads the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- US Lend-Lease Act $31B of supplies to the UK, $11B to the Soviets, $3B to France, and $2B to China.
- Greatest Generation fights in WWII and is civic-minded.
- The G.I. bill helps veterans get college education.
The United Nations is founded on June 1945 at the United Nations Conference on International Organization.
- The permanent members of the UN Security Council are the US, China, Russia, UK, and France. Each can veto Security Council resolutions.
- June 1941. The Declaration of St James’s Palace by European powers commits to a peace based on the “willing cooperation of free peoples”.
- August 1941. Atlantic Charter by the US and UK calls for “no territorial changes made against the wishes of the people”.
- 1942. Declaration by United Nations signed by all Allies reaffirms the Charter.
- 1972. Stockholm Declaration
- At the UN Conference on the Human Environment which created the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
- 1987. Our Common Future emphasizes sustainable development.
- 1992. Earth Summit produces the Rio Declaration and Agenda 21.
Truman’s Marshall Plan rebuilds Europe. It is named after Secretary of State George C. Marshall, who wins a Nobel Peace Prize.
1957. European Economic Community.
Sustainable development
- Participatory development
- Capability approach
- Muhammad Yunus of Bangladesh popularizes microfinance. 2006 Nobel Peace Prize.
1940s Bobby soxer subculture. Rise of teen culture in the swing era.
1950s Baby boom.
Cold War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Cold_War
Democrat Harry Truman is 33rd president from 1945 to 1953. The Truman Doctrine pledges US support for democracies against authoritarian threats. George Kennan devises a policy of containment against communism.
- 1945. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists founded by Albert Einstein. Keeps the Doomsday Clock.
- 1949. Geneva Conventions establish legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war and define war crimes.
Second Red Scare
- 1950. Joseph McCarthy claims to have a list of communists in the State Department.
- House Committee on Un-American Activities investigates Hollywood, which blacklists the Hollywood Ten.
- 1954 Army-McCarthy hearings. Army lawyer Joseph Nye Welch ends the Scare: Let us not assassinate this lad further, Senator. You’ve done enough. Have you no sense of decency, Sir, at long last? Have you left no sense of decency?
- 1953. CIA director Allen Dulles leads Project Artichoke and MKUltra experiments for interrogation and mind control using torture and high-dose LSD.
- 1956. FBI director J. Edgar Hoover leads COINTELPRO to illegally spy on, infiltrate, and discredit political organizations, including sending the FBI–King suicide letter. It is exposed by the Washington Post in 1971 after a breakin.
- Hoover compiled the FBI Index tracking 10 million people, including Communists, Rabble Rousers and Agitators, and Sexual Deviants.
- 1959. Advise and Consent by Allen Drury explores the Senate confirmation of a possible communist.
- 1973. William Colby becomes CIA director. He orders the Family Jewels report on illegal CIA activities.
- 1975. Senate Church Committee exposes CIA, FBI, NSA, and IRS abuses.
- 1940. Project Shamrock photographed and shared all international cablegrams without a warrant. At the time, it is “the largest government interception program affecting Americans ever”.
1946 Greek Civil War is a failed communist uprising caused by the White Terror persecution of communists.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is founded in 1949.
- Turkish straits crisis. The Soviet Union tries to force Turkey to give up control over the straits, leading Turkey to join NATO.
The October Revolution of 1944 is a Guatemalan revolution establishing democracy. The second president begins the Decree 900 land reform program, returning United Fruit Company land to poor farmers. In the 1954 Guatemalan coup d’état, the CIA installs a military dictator.
1946 First Indochina War. Ho Chi Minh founds the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, and Việt Minh, Soviet, and Chinese forces defeat France at the Battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954.
1950 Korean War. Japan occupied Korea in WWII, and the USSR and the US accepted the Japanese surrender in two zones divided at the 38th parallel. Kim Il-sung becomes leader in 1948, establishing a totalitarian Leninist Juche regime emphasizing self-reliance. Kim invades most of South Korea until the Battle of the Pusan Perimeter in August, where 140,000 UN troops hold the port of Busan against 98,000 North Korean troops. In the September Battle of Inchon, the UN makes an amphibious landing, captures Seoul, and pushes near the Chinese border. China intervenes in the November Second Phase Offensive, leading to a two-year stalemate. In 1953, Stalin dies and the Soviet Union withdraws support, leading to an armistice establishing the Korean Demilitarized Zone DMZ.
Nikita Khrushchev rules after Stalin dies in 1953. He ousts the Stalinists and allows some reforms. His 1956 speech On the Cult of Personality and its Consequences criticizes Stalinism and causes the Sino-Soviet split.
He crushes the Hungarian Revolution of 1956.
In 1960, the Soviet Union shoots down a U-2 spy plane and captures pilot Gary Powers alive, disrupting a thaw in US-Soviet relations.
1953. Eisenhower’s New Look emphasizes tactical nuclear weapons, covert operations, and the Strategic Air Command. The Army was cut, and develops the Pentomic concept, which is too spread out and too complex to command.
1954. Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb test at Bikini Atoll is the largest at 15 megatons and causes fears in Japan about eating contaminated fish.
President Gerald Ford issues Executive Order 11905 banning political assassinations. TODO
Ford suppresses the House Pike Committee report and edits the Rockefeller Commission.
The Committee for State Security (KGB) was the Soviet secret police from 1954 to 1991.
The Federal Security Service (FSB) is the main security agency of Russia. Its spetsnaz special forces includes Alpha Group and Vympel.
The GRU is the Soviet and Russian military intelligence.
1957. Sputnik crisis begins the space race.
Spies
- FBI counterintelligence officer Robert Hanssen exposes GRU officer Dmitri Polyakov, who provided information on the Soviet-China split.
- CIA counterintelligence officer Aldrich Ames exposes 25 Soviet officers, including KGB London bureau chief Oleg Gordievsky.
- In 1967, Navy communications officer John Walker starts sharing encryption keys with Russia, allowing them to read one million naval messages. Russia reduces propeller cavitation to avoid sound tracking.
- In 1968, North Korea captures the US spy ship USS Pueblo containing KL-47, KW-7, KWR-37, and KG-14 cipher machines, and key lists allowing Russia to decrypt two months of classified messages.
- In 1987, the Toshiba-Kongsberg scandal exports controlled machining tools that helped Russia mill quieter propellers, leading to a ban on Toshiba imports.
Cuba
- 1952. Cuban coup by anti-communist general and dictator Batista, supported by the US.
- 1959. Cuban Revolution, communist Fidel Castro overthrows Batista after the US ends arms sales to Batista. In 1953, Castro declares History will absolve me and founds the 26th of July Movement in prison, with Che Guevara rising to second in command. Castro nationalizes US-owned Cuban oil refineries, leading to a US embargo against Cuba, and Cuba increasingly trades with the Soviet Union.
- 1961. Guerrilla Warfare by Che Guevara based on popular support and the foco, a small group of revolutionaries in the countryside.
- 1961. JFK Bay of Pigs invasion fails to overthrow Castro, and the CIA carries out Operation Mongoose assassinations on key leaders.
- Kennedy creates the White House Situation Room.
- 1962. Cuban Missile Crisis. Khrushchev builds ballistic missile sites in Cuba, and Kennedy declares a “quarantine” of Cuba, since a blockade would be a declaration of war. Khrushchev agrees to remove the missiles and the US agrees not to invade Cuba and to remove PGM-19 Jupiter missiles from Turkey.
- 1968. Revolutionary Offensive nationalizes all remaining small businesses and targets increased sugar production. This leads to Freedom Flights that bring 300,000 Cuban refugees to Miami.
1963 Kennedy Ich bin ein Berliner speech.
- 1964. Leonid Brezhnev and KGB chair Semichastny force Khrushchev to retire. Brezhnev Doctrine is a policy of intervention in the Soviet Bloc to support socialist rule, ending a thaw.
- 1968. Prague Spring begins with the election of Alexander Dubček, who supports free democracy. In response, the Soviet Union invades Czechoslovakia.
Vietnam War or the Second Indochina War.
- 1958. Viet Cong fights a guerrilla war against South Vietnam. USSR ally North Vietnam invades Laos and build the Ho Chi Minh Trail to supply the Viet Cong.
- 1964. Johnson uses the Gulf of Tonkin incident to conduct a ground invasion with 200,000 troops, large-scale bombing, and Agent Orange. The My Lai massacre kills 500 civilians.
- 1968. The Tet Offensive destroys US support. Johnson halts some bombing and begins the Paris Peace Accords. Nixon asks Vietnam to delay the peace to support his election.
- 1971. Daniel Ellsberg leaks the Pentagon Papers to The New York Times, showing that Johnson had lied to Congress.
- 1975. The Fall of Saigon reunifies Vietnam under Communism. Communists also win the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War. That year, 130,000 Vietnamese refugees immigrate to the US, and actress Tippi Hedren helps many open nail salons.
1975 Third Indochina War
- 1975. Cambodian genocide. Pol Pot and the Khmer Rouge kill 2 million or 20% of the population.
- 1978. Ba Chuc massacre. Khmer Rouge kill 3,000 Vietnamese villagers
- 1978. Cambodian-Vietnamese War. Vietnam occupies Cambodia for a decade.
- 1978. Vietnamese border raids in Thailand after Khmer Rouge flee across the border.
- 1978. Sino-Vietnamese War. China captures several border cities and withdraws. Border conflicts until relations normalize in 1991.
Richard Nixon.
- Kissinger uses triangular diplomacy and linkage to promote detente and project US power.
- 1972. Nixon visits China after table-tennis diplomacy.
- 1968. Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). Non-nuclear states agree never to acquire nuclear weapons and nuclear states (US, China, Russia, UK, France) agree to share the benefits of peaceful nuclear technology. Israel, India, Pakistan, North Korea didn’t sign.
- 1974. Threshold Test Ban Treaty bans nuclear tests above 150 kilotons.
- 1975. Biological Weapons Convention bans biological weapons.
- 1994. Budapest Memorandum. Ukraine gives up its nuclear weapons and Yeltsin agrees to respect Ukraine’s borders.
- 1991. Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START) from the SALT talks.
The Reagan Doctrine supports resistance movements against the Evil Empire (the Soviet Union) to roll back communism.
- 1983. Evil Empire speech against the Soviet Union.
- 1987. Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall! speech had no contemporary impact.
- 1989. the US invades Panama to depose Panama dictator Noriega.
- 1991. The first Haiti President Aristide promotes substantial reforms. An army general stages a coup until the US military intervenes. The Bush administration boycotts Haiti, and in 2004 a coup overthrows the president.
Gorbachev promotes glasnost and perestroika. Economic collapse leads to nationalist movements.
Revolutions of 1989. Fall of communism in Germany (fall of the Berlin Wall and Peaceful Revolution), Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia (Velvet Revolution), Romania, Bulgaria, Mongolia, Albania.
- 1991 Boris Yeltsin signs the Belavezha Accords dissolving the Soviet Union against Gorbachev’s wishes. Yeltsin was an alcoholic and resigns in 1999.
- 1993 Dissolution of Czechoslovakia into Czech and Slovak republics.
- 1999 Vladimir Putin becomes leader. Putin is a former KGB foreign intelligence officer.
Civil Rights
- 1909 W. E. B. Du Bois, Ida B. Wells, and others found the The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).
- The Souls of Black Folk (1903) and Black Reconstruction by Du Bois.
- Walter White leads the NAACP from 1929 to 1955.
- 1917. East St. Louis massacre kills 100 in the nadir of American race relations.
- 1917. NAACP Silent Parade of 10,000 in New York.
- 1919. Red Summer: racial riots in most cities.
- 1921. Tulsa race massacre. White mobs raze 35 blocks of “Black Wall Street”.
- 1925. A. Philip Randolph founds the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters, the first Black-led labor union.
- 1930. Great Migration of 1 million Black farmers from the rural south to the northeast and midwest: Chicago South Side. Harlem Renaissance develops Black culture.
- The Warmth of Other Suns (2010) by Isabel Wilkerson.
- 1940. Second Great Migration of 5 million African Americans across the northeast and west: LA Central Avenue. Often from Southern cities.
- 1941. Executive Order 8802 bans discrimination in defense industries during World War II.
- 1942. Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) pushes for nonviolent resistance.
- 1942. Double V campaign promotes victory at home for civil rights.
- 1943. Harlem riot after police shoot a Black man. Detroit race riot, LA Zoot Suit Riots.
- 1947. Jackie Robinson becomes the first African American to play in Major League Baseball.
- 1960. Mexican American Political Association (MAPA) supports the Chicano Movement.
Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower is 34th president from 1953 to 1961.
1953 Chance for Peace speech: Every gun that is made, every warship launched, every rocket fired signifies, in the final sense, a theft from those who hunger and are not fed, those who are cold and are not clothed. This world in arms is not spending money alone. It is spending the sweat of its laborers, the genius of its scientists, the hopes of its children. The cost of one modern heavy bomber is this: a modern brick school in more than 30 cities. It is two electric power plants, each serving a town of 60,000 population. It is two fine, fully equipped hospitals. It is some fifty miles of concrete pavement. We pay for a single fighter with a half-million bushels of wheat. We pay for a single destroyer with new homes that could have housed more than 8,000 people. . . . This is not a way of life at all, in any true sense. Under the cloud of threatening war, it is humanity hanging from a cross of iron.
1953 Atoms for Peace exports over 25 tons of highly enriched uranium (HEU) to fuel research reactors.
1954 Shippingport Atomic Power Station is the first nuclear power plant.
1961 Farewell address warns against the military-industrial complex.
1955. Lynching of Emmett Till, an African American boy.
1955. Rosa Parks refuses to give her seat to a white person. In 1956, Browder v. Gayle decides that bus segregation is unconstitutional under the Equal Protection Clause.
1955. Martin Luther King organizes the Montgomery bus boycott and later founds the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). “Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.”
1960. Greensboro sit-ins forces Woolworth to desegregate its stores.
1963. March on Washington by Bayard Rustin and A. Philip Randolph
- King’s I Have a Dream speech.
- King’s Letter from Birmingham Jail argues that rights are too urgent to wait for.
1965. Immigration and Nationality Act ends discrimination in immigration policy.
1965. Pauli Murray writes Jane Crow and the Law arguing for sex as a protected category. She was also arrested in 1940 for refusing to sit in the back of a bus.
1971. Saul Alinsky writes Rules for Radicals for community organizers.
Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) establishes separate but equal.
1954 Brown v. Board of Education bans racial segregation in public schools.
- Brown II (1955) orders desegregation with “all deliberate speed”, from Francis Thompson’s poem The Hound of Heaven.
- 1957. The Little Rock Nine attend a previously all-white school. Eisenhower federalizes the Arkansas National Guard to override state opposition.
- Loving v. Virginia (1967) bans anti-miscegation laws.
- 1971 Desegregation busing: the Supreme Court mandated mixing of public schools in the Swann decision.
- Leads to white flight from cities to suburbs and private schools.
Black power movement advocates more violent resistance.
1959. Nation of Islam led by Elijah Muhammad and Malcolm X. Advocates Black separatism and Back-to-Africa movement.
Black Panther Party publishes their platform, the Ten-Point Program (1966).
Black Power salute at the 1968 Olympics.
1992. Rodney King riots after LA police officers are acquitted of beating
- Rooftop Koreans defend their property
1994. Black jurors acquit O. J. Simpson of killing his ex-wife Nicole Brown Simpson, expressing anger at LAPD racial bias. Ford Bronco chase. Simpson is defended by Robert Kardashian and later publishes If I Did It (2006).
1994. California Proposition 184 three-strikes law. Mandates life imprisonment after conviction on three felonies.
John F. Kennedy (JFK) is president from 1961 to 1963. He orders CIA Project Mockingbird to wiretap the national security reporter for The New York Times and another Washington reporter. He writes A Nation of Immigrants (1958). Appears on the half dollar coin.
- Popularizes “don’t get mad; get even”.
- 1956. Profiles in Courage by speechwriter Ted Sorensen. 1957 Pulitzer Prize.
- 1961. Foreign Assistance Act creates USAID (United States Agency for International Development).
- 1961. Peace Corps by executive order.
- 1962. “We choose to go to the Moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard”
- Kennedy assassination investigated by the Warren Commission.
Modern US
1950s Silent Generation includes conservatives and hippies.
- 1950s Beat Generation or Beatniks are spiritual, anti-consumerist, psychedelic, sexually liberated.
1960s counterculture: civil rights and antiwar movement.
- Hippie movement: communal living in harmony with nature. Artistic, psychedelic, and sexual experimentation.
- British Swinging Sixties: consumerist pop and fashion.
- Mod subculture around jazz clubbing and Vespa motor scooters. Mary Quant popularizes miniskirts and hotpants (very short shorts).
- Rockers or greasers are biker culture with rock and roll and leather jackets.
- UK underground: drugs and radical thinking.
- Skinheads emphasize working class jeans and Dr. Martens boots.
Democrat Lyndon B. Johnson (LBJ) is president from 1963 to 1969. He launches the Great Society as a War on Poverty, and loses the Vietnam War.
- Civil Rights Act of 1964 bans discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin.
- 1965 Hart–Celler Act ends the National Origins Formula.
- 1968 Fair Housing Act bans discrimination in sale or rental.
- Cuts top marginal tax rate from 91% to 71%.
- 1964 Economic Opportunity Act launches Head Start providing preschool for poor children.
- 1965 Voting Rights Act bans racial discrimination in voting.
- 1965 Social Security Act creates Medicare and Medicaid despite campaigns by the American Medical Association against “socialized medicine”.
- National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities created in 1965.
- Clean Air Act of 1963.
- Demonstrations against the Vietnam War include burning draft cards, burning American flags, and rioting.
- The Chicago Seven are acquitted of conspiracy in the 1968 DNC protests.
Republican Richard Nixon is the 37th president from 1969 to 1974.
- Southern strategy achieves a Republican electoral realignment via racist dog whistles including “states’ rights” and “law and order”.
- Nixon “emphasized that you have to face the fact that the whole problem is really the blacks. The key is to devise a system that recognized this while not appearing to.” -Nixon chieff of staff
- 1952. Checkers speech. Nixon denies charges of bribery and states that he will not give back his dog Checkers, a gift.
- 1972 election. After news that his running mate Eagleton had clinical depression, Democrat George McGovern endorses Eagleton “1000 percent” shortly before dropping Eagleton.
In 1973, Nixon leads the war on drugs, increasing black prison rates by 5x. Drug laws 100:1 racial disparity in sentencing: 5 grams of crack cocaine gets the same sentence as 500 grams of powder cocaine. He also founds the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Watergate scandal. In February 1971, Nixon installs a White House tape system. In 1972, Nixon records his coverup of the break-in of the Democratic National Committee headquarters in the smoking gun tape. FBI Associate Director Mark Felt, codenamed Deep Throat, tells Washington Post reporter Bob Woodward of Nixon’s involvement. The Senate committee learns about the tape system in 1973, and special counsel Archibald Cox subpoenaes the tapes. Nixon is contemptuous and vindictive. In the Saturday Night Massacre in October, Nixon fires the Attorney General and Deputy Attorney General in order to fire the Cox, and claims “I am not a crook”. In August 1974, Nixon resigns to avoid impeachment.
New social movements focus on social change over politics and class struggle. Culture, social relations, identity, quality of life, and human rights.
- Negative and positive rights
- Three generations of human rights
- Two Concepts of Liberty (1958)
- capability approach
- Identity politics
- Gay rights
- 1950. Mattachine Society: early gay rights organization.
- 1969. Stonewall riots after police raid a gay bar lead to pride parades.
- Environmental movement with Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring (1962) about DDT killing birds. EPA (1970). Greenpeace (1971). Clean Water Act (1972), Endangered Species Act (1973), Safe Drinking Water Act (1974). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (1992), Kyoto Protocol (2005), Paris Agreement (2016).
- 1963. CITES: Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species.
- 1970. Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA).
- 1985. Don’t Mess with Texas campaign against littering.
- Disability rights: Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990.
- New Urbanism. Jane Jacobs writes The Death and Life of Great American Cities (1961) and fights against urban renewal and slum clearance.
- Second-wave feminism from 1960s to 1980s critiques broader social issues: sexuality, family, domesticity, domestic violence, marital rape, the workplace, reproductive rights, de facto inequalities, custody laws, divorce laws. Builds rape crisis centers and women’s shelters.
- The Feminine Mystique (1963) by Betty Friedan.
- The Second Sex (1949) by Simone de Beauvoir discusses the subordination and oppression of women.
- Kimberlé Crenshaw discusses intersectionality in 1989.
- Rape culture: sexualization and objectification, “no means yes”, victim blaming or “asking for it”, slut-shaming
- toxic masculinity: misogyny, homophobia, toughness or machismo.
- Feminist sex wars. Around 1985, Women Against Pornography leaders Catharine A. MacKinnon and Andrea Dworkin argue that porn subordinates and degrades women, perpetuating violence and discrimination. In 1981, Ellen Willis argues that authoritarianism and sexual repression.
- Baby Boomers live through economic prosperity and trend conservative to preserve their status quo.
- Black Lives Matter organizes against police brutality, with the slogan of “defund the police”. Associated with the killing of Breonna Taylor and George Floyd. NFL quarterback Colin Kaepernick kneels during the national anthem.
1974. Republican Gerald Ford is the 38th president. Ford pardons Nixon.
1977. Democrat Jimmy Carter is the 39th president.
- 1979 Department of Education split out from HHS.
- vice president Walter Mondale
1981. Republican Ronald Reagan is the 40th president to 1991. He promotes Reaganomics, neoliberalism, trickle-down economics, deregulation, and tax cuts on the rich.
In 1987, Reagan helps abolish the FCC fairness doctrine requiring broadcasters to present controversial issues in a manner that fairly reflected differing viewpoints. This enables Fox News and conservative talk radio such as Rush Limbaugh to air hateful content and conspiracy theories that increases emotional engagement and political polarization. Radio and TV are still required by the equal-time rule to provide equivalent access to competing political candidates.
- Yuppie culture (young urban professional) emphasizes city life over comfort or security.
New Journalism is literary reporting, with more immersive storytelling, dialogue, and scene-setting.
- Joan Didion suggests that the Central Park Five, five black teens falsely convicted of rape, are innocent in 1991.
- Gay Talese: Frank Sinatra Has a Cold (1966) and Honor Thy Father (1971)
- Tom Wolfe writes statusphere journalism that critiques the wealthy and captures their language and mannerisms. The Right Stuff (1979) and The Bonfire of the Vanities (1987).
- Hunter S. Thompson pioneers gonzo journalism, where the reporter is part of the story: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas (1971), Hell’s Angels (1965).
- Norman Mailer: The Armies of the Night (1967) and The Executioner’s Song (1979).
1989. Republican George H. W. Bush is 41st president.
- He campaigns on “Read my lips: no new taxes”, but is forced to raise taxes.
1993. Democrat Bill Clinton is 42nd president to 2001. He portrays himself as a centrist New Democrat. Madeleine Albright is secretary of state.
- Vice president Al Gore.
- 1993 Don’t ask, don’t tell policy allows closeted gay people.
- 1996 Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA) bans federal recognition of gay marriage and allows states to refuse to recognize gay marriages granted in other states.
- 1998 Lewinsky scandal. Clinton is impeached and acquitted for sexual relations with a 22-year-old intern. He says “I did not have sexual relations with that woman, Ms. Lewinsky.” and “it depends on what the meaning of the word is is”.
- 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) expands Mexico’s economy.
- 1995 Hillary Clinton gives a sharp speech at the UN Conference on Women, popularizing the phrase “women’s rights are human rights”.
Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich increases polarization by emphasizing ideological differences, raising culturally charged issues, and using combative and hateful language. This nationalizes and homogenizes politics, marginalizing local issues and political independents. He added term limits on committee chairs, which prevented chairs from developing a separate power base, consolidating the power of the Speaker and increasing conformity. He forces an unsuccessful 1990 government shutdown and wins large gains in the 1994 midterms.
The 1994 Crime Bill is the largest in history. Clinton pushes a “tough on crime” policy.
- Federal Assault Weapons Ban that lasted ten years.
- Federal rape shield law, banning evidence relating to the past sexual behaviour of the victim.
- Wetterling Act requiring sex registries and Megan’s Law making registries public.
- Conditions funding on state truth-in-sentencing laws, where violent criminals must serve 85% of their sentence before being eligible for parole.
Carol Moseley Braun is the first female Black Senator.
2001. Republican George W. Bush is 43rd president to 2009. Colin Powell and Condoleezza Rice serve as secretary of state. Vice president Dick Cheney.
- Karl Rove pioneers the push poll.
- Shadow Company (2006) documents private military companies like Blackwater, later renamed to Academi and then Constellis.
- In 2008, an Iraqi throws his shoes at Bush. In 1992, Bush vomited into the lap of Japanese prime minister Miyazawa.
- 2001 President’s Surveillance Program involves unprecedented collection activities. Codenamed Stellar Wind.
- DOJ attorney Yoo writes a factually flawed memo. He is the only Office of Legal Counsel (OLC) member read in. Attorney General Ashcroft approves the program the same day.
- In 2003, Yoo resigns, and his replacement Philbin asks new Assistant Attorney General Goldsmith to be read in, and Goldsmith asks Deputy Attorney General James Comey to be read in. They find that Yoo’s memo did not describe or justify some Other Intelligence Activities in the PSP. Philbin and Goldsmith bring concerns to Ashcroft, who agrees that there are problems. Ashcroft gets pancreatitis, DOJ tells White House Counsel Alberto Gonzales and Chief of Staff Andrew Card to stop some PSP activities. Gonzales and Card try to get Ashcroft to reauthorize PSP at his hospital bedside, and Ashcroft direct them to Comey.
- On March 11, 2004, Bush reauthorizes the PSP without DOJ concurrence. The next day, Director Robert Mueller withdraws the FBI from the PSP. On March 17, Bush discontinues the unsupported Other Intelligence Activities, and Goldsmith approves the modified program on May 6.
- 2005. CIA destroys videotapes of torture after a judge asked them to provide the tapes to defense lawyers.
- FBI Terrorist Screening Database includes a million names, mostly foreigners.
- FBI No Fly List includes a million entries, including 10% Muhammad.
- TSA Secondary Security Screening Selection (SSSS) targets people for enhanced pat-downs.
- Generation X (Gen X): work-life balance, individualism and entrepreneurialism. Slacker stereotype of bleak, cynical, and disaffected.
Democrat Barack Obama is 44th president from 2008 to 2016.
- 2004. DNC speech. “there is not a liberal America and a conservative America — there is the United States of America”.
- Hope poster. three-quarters view looking slightly up and out. Bold lines and colors. Aesthetic touchups. Red, white, and blue palette to deracialize Obama. Modified Futura font.
- Occupy movement protests economic inequality and the 1%.
- 2010. Don’t ask, don’t tell is repealed, allowing openly gay people to serve.
- 2010. New START treaty halves the number of strategic nuclear missile launchers and replaces the Strategic Offensive Reductions Treaty (SORT) treaty of 2003.
- 2010 Panetta Review by the CIA director sharply critizes CIA use of torture (“enhanced interrogation techniques”) in the Bush administration. In 2014, the Senate Intelligence Committee somehow copied the review. CIA general counsel Robert Eatinger requested a criminal inquiry into the committee staff. In March, CIA director John O. Brennan denies hacking Intelligence Committee computers. In July, the CIA confirmed that it hacked the computers.
- 2011 SEAL Team Six kill Osama bin Laden.
- Energy Secretary Steven Chu
- Millenial or Gen Y: slower economic growth, electronic devices, alienation, declining fertility rates, internet.
Republican Donald Trump is president from 2016 to 2020, defeating Hillary Clinton. FBI director James Comey announces a new investigation into Clinton’s emails eleven days before the election. Clinton feels that Bernie Sanders stayed in the primary race longer than needed, hurting her in the general election.
- 2019. A jury finds that Trump sexually assaulted E. Jean Carroll.
- 2016. Access Hollywood tape: “when you’re a star, they let you do it. You can do anything. … Grab ’em by the pussy.”
- 2023. Trump is convicted on 34 felony counts of falsifying business records about payments to Stormy Daniels after an investigation by district attorney Alvin Bragg.
- 2016. Mueller investigation. Campaign chair Paul Manafort, personal attorney Michael Cohen, national security advisor Michael Flynn, advisor George Papadopoulos, and advisor Roger Stone all plead or are found guilty of felonies regarding Russian contacts.
- Donald Trump tries to enact a Muslim ban.
- 2017. Women’s March is the largest US protest.
- 2018. Withdraws from the 2015 nuclear deal with Iran and reimposes sanctions. The EU declares the sanctions to be illegal.
- 2019. Withdraws from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty of 1987.
- 2020. Kills Qasem Soleimani, leader of the Quds Force and second most powerful Iranian.
- 2017. Justice Neil M. Gorsuch
- 2019. Ends the 1988 Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF treaty) claiming Russian noncompliance.
- Amy Coney Barrett
- Brett M. Kavanaugh
- 2022. Drone kills al-Qaeda leader Ayman al-Zawahiri.
- A Georgia grand jury also indicts Trump and 18 others on 13 criminal charges of election racketeering brought by Fulton County district attorney Fani Willis.
- Special counsel Jack Smith also brought two federal cases against Trump. A grand jury in the Southern District of Florida indicts Trump on 40 federal felony counts of mishandling of classified documents and a grand jury in DC indicts Trump on four felony counts including conspiracy to defraud the US and obstructing an official proceeding for his attempt to overturn the 2020 election and the January 6 Capitol attack.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trump_Tower
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/40_Wall_Street
2017 #MeToo movement.
- Harvey Weinstein is jailed for rape.
- 2018 Christine Blasey Ford accuses Supreme Court justice nominee Brett Kavanaugh of sexual assault.
- Tennis player Peng Shuai accuses retired Vice Premier Zhang Gaoli of sexual assault and gets disappeared.
- Kevin Spacey is accused of sexual assault. Louis CK apologizes for masturbating in front of multiple women.
- Democratic Senator Al Franken resigns after a model accuses of forcibly kissing her.
2018 Parkland shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Florida.
Greta Thunberg calls for climate action.
2020. Joe Biden is president to 2024.
- Vice President Harris is the first with less Washington experience. Typically they provide connections and guidance.
- Chief of staff Ron Klain.
- Sanders is briefly the frontrunner as moderates are split between many candidates. Jim Clyburn delivers South Carolina for Biden, and Buttigieg and Klobuchar drop out before Super Tuesday.
- 2022 Ketanji Brown Jackson is the first Black woman on the Court.
Kamala Harris is the Democratic nominee for 2024.
- Biden resigned because 70% of voters felt he was too old (versus 36% in 2020). In contrast, Harris polls as a nameless generic Democrat, with 50% popularity. Voters have no major reservations about her.
Gen Z: slow living, less alcohol, greater mental health awareness, more sleep deprivation.
Gen Alpha just being born.
Internet culture
Economic impact
History of computing
- 2001. Wikipedia by Jimmy Wales.
- English 8B views/mo, Japanese Russian Spanish 900M, German 800M, French 700M, Italian 500M, Chinese 400M
- transclusion includes another document by reference. Substitution is less common, and ensures that the output is independent of template changes.
- Regenerate a page in case of stale dates: ?action=purge
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:AWB
- nowiki tag shows text without wiki or html rendering. HTML special characters are escaped so the original text shows up. Newlines are treated as spaces by HTML. Allows raw markup characters at the beginning of lines.
- 2003. Badgers, O RLY? owl.
- The Room: “Oh hi, Mark”, “You’re tearing me apart, Lisa!”
- Nick Denton founds Gawker, Deadspin, Kotaku, Lifehacker, and Gizmodo. Thiel finances a lawsuit that ends the company in 2017 after it outed him in 2007.
- 2005. Pepe the Frog.
- 2006. Google buys YouTube. Hitler’s Downfall. Lolcat including I Can Has Cheezburger?.
- 2007. iPhone, Tumblr, rickrolling, Success kid.
- 2008. asdfmovie animated clips such as “I like trains”. Loss comic.
- 2009. Wojak or Feels Guy, and NPC Wojak. Thanks Obama. Slenderman creepypasta.
- 2010. Navy Seal copypasta.
- 2011. Silk Road by Ross Ulbricht is the first bitcoin drug market, shut down two years later.
- 2013. PewDiePie becomes the most subscribed channel; he makes comedic Let’s Plays and talks to his audience as peers.
- 2014. Twitch Plays Pokemon: most participants on a single-player online videogame, at 1 million people.
- 2014. Gamergate harasses women in the video game industry.
- Remix. culture
- . mashups or YouTube poop (YTP)
Mexico
Yucatán: Chichen Itza, a Mayan city.
Mexican food
Corn tortilla made with masa dough from ground nixtamalized corn.
Salsa
Taco
pupusa is a thick filled flatbread.
tamale: filled masa steamed in banana leaves.
Empanada is a filled turnover.
Asado grilled
Chorizo pork sausage
1810. Mexican War of Independence from Spain. Priest Miguel Hildalgo issues the Cry of Dolores and bans slavery in Guadalajara.
- 1821. Plan of Iguala makes three guarantees: official religion of Roman Catholicism, political independence, and full social equality. Also bans slavery.
- 1821. Treaty of Cordoba ends the war.
1824. First Mexican Empire loses army support and abdicates to the First Mexican Republic.
1829. Vicente Guerrero is second president for a year before being killed in a coup. He bans slavery.
1832. Santa Anna becomes president. Mexico grants land to American settlers in Comanche territory. Santa Anna loses the Texas Revolution in 1836 and the Mexican-American War in 1848, and sells the Gadsden Purchase in 1853 for $10 million.
1854. Plan of Ayutla. Liberals oust Santa Anna.
1864. the Second French intervention in Mexico installs Austrian Archduke Maximilian.
1867. liberal President Juarez restores the Restored Republic.
1876. General Porfirio Díaz stages a coup and invites foreign investment.
1910. Mexican Revolution. Francisco I. Madero rebels against Díaz.
1913. General Victoriano Huerta kills Madero with support from US ambassador Henry Lane Wilson. The US occupies Veracruz, leading to anti-American backlash. The US withdraws after the Niagara Falls peace conference brokered by Argentina, Brazil and Chile.
1914. Carranza proclaims the Plan of Guadalupe and his Constitutional Army defeats Huerta and his Federal Army, with support from Pancho Villa, Zapatistas, and others. He wins a brief civil war against other revolutionaries and drafts the 1917 Constitution.
1920. Army generals proclaim the Plan of Agua Prieta and overthrow Carranza.
1995. Chiapas conflict. Zapatista Crisis protests the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). Presidential candidate Luis Donaldo Colosio is assassinated.
2018. President Lopez Obrador increases transfers to poor people.
2024. President Sheinbaum
Frida Kahlo: Mexican painter of pain, suffering, and identity.
South America
Brazil
- 1889 The military overthrows the Empire of Brazil.
- 1964 Anticommunist military dictators overthrow elected president Goulart. The US and the Catholic Church supports the coup.
- 1985 Democratic government with the election of opposition candidate Neves.
- 2003 Left-wing Lula is president.
Argentina
- 1946 President Juan Peron is dictatorial and shelters many Nazi war criminals. He develops Peronism, which emphasizes social justice and economic independence and remains popular.
- 1955 Revolucion Libertadora. Military junta overthrows Peron.
- 1963 Physician Arturo Illia becomes president, investing 23% of the budget in education and reducing unemployment.
- 1976 Military dictator Jorge Videla overthrows Isabel Peron and forms the Argentine Republic. 300% annual inflation for a decade. Dirty War represses communists and kills 20,000. US-supported.
- 1982 Falklands War. Argentina invades and loses.
- 1983 Argentine general election returns to democracy. Trial of the Juntas jails dictators.
Bolivia
1825. Simón Bolívar wins the Bolivian War of Independence against Spain and Spanish Peru during Spain’s Peninsular War.
1920. Saavedra overthrows the Liberal Party, but his Republican party soon splinters.
1952. Bolivian Revolution. The Revolutionary Nationalist Movement (MNR) overthrows the Bolivian oligarchy with liberal and communist support.
1964. Bolivian coup by army commander Barrientos with CIA help. Che Guevara is executed trying to overthrow Barrientos.
In the Central American crisis, the US supported right-wing governments against left-wing guerrillas.
1979 Nicaraguan Revolution. Sandinistas overthrow the US-backed Somoza dictatorship.
1979 Salvadoran coup d’état by US-aligned military leads to civil war in El Salvadore by FMLN guerrillas, killing 75,000. Authoritarian President Nayib Bukele arrests over 75,000 alleged MS-13 (Mara Salvatrucha) gang members, leading to 90% approval.
Grenada
- 1974. Independence from the UK.
- 1979. Communists stage a coup but faces internal fighting.
- 1983. The US invades to install a democracy.
1980s Latin American debt crisis or La Década Perdida has high debt and inflation. Mexico borrowed against future oil revenues with debt in US dollars.
Chile
- 1970 Salvador Allende becomes the first Marxist president of Chile. He implements a planned economy, which leads to 150% inflation.
- 1973 Right-wing military dictator Pinochet overthrows Allende. Milton Friedman and the Chicago boys promote neoliberal shock doctrine of free markets, privatization, and austerity to end inflation.
- 1975 Operation Condor represses liberals.
- 1982 monetary crisis caused by overvalued Chilean peso, low tariffs, and high interest rates. Leads to Jornadas de Protesta Nacional protests.
- 1988 Chilean presidential referendum returns Chile to a democracy.
Venezuela: Hugo Chavez is president from 1999 to 2013.
Africa
Geography
- North Africa: Western Sahara, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt
- good economic development.
- Nile River flows from Lake Victoria in Tanzania to the Mediterranean via Kenya, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt.
- West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia (Gambia River), Guinea-Bissau, Windward Coast or Pepper Coast or Grain Coast from melegueta pepper, the “grain of paradise” (Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast), Ghana (formerly Gold Coast), Slave Coast (Togo, Benin, Nigeria).
- The Niger River in West Africa flows from the Guinea Highlands through Mali, Niger, and Nigeria to the Niger Delta on the Atlantic.
- The Senegal River flows west between Mauritania and Senegal.
- Cape Verde islands
- UK Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha islands.
- Sahara desert
- Sahel coup belt: Guinea, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Chad, Sudan.
- Central Africa: Central African Republic, Rwanda, Burundi
- west coast: Cameroon (Mount Cameroon), Equitorial Guinea, Gabon, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola
- São Tomé and Príncipe islands off Gabon.
- The Congo River drains central Africa to the Atlantic.
- East Africa
- Uganda
- Kenya: Maasai Mara part of the Serengeti migration.
- Tanzania
- Serengeti is the largest annual animal migration in the world, with 1.5 million blue wildebeest.
- Mount Kilimanjaro
- Ngorongoro Crater is the largest inactive intact caldera.
- east coast: Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Somalia, Mozambique
- Rwanda, Zambia, Zimbabwe. Victoria Falls on the Zambezi River.
- Seychelles island
- Madagascar in the south with low development.
- Southern Africa: South Africa, Namibia
- Botswana: Okavango Delta is an inland delta
Hadza people in East Africa are around 1,000 hunter-gatherers with no known genetic relatives. They live in bands of 20-30 people. They predate the Bantu expansion and speak a click language isolate.
2000 BC to 0 CE. Bantu expansion. Bantu speakers around Cameroon displace other hunter-gatherer groups and become the dominant language family, spoken by 300 million people. Bantu are associated with iron, millet, and sorghum.
700 Kanem-Bornu Empire in Central Africa.
700 Gao Empire in the Niger River valley.
1226 Mali Empire in the Niger River valley, West Africa
1696 Omani Empire in East Africa.
- 1808 UK ends the slave trade and begins the Blockade of Africa.
- 1820 Back-to-Africa movement founds Liberia and Sierra Leone.
- 1821 Britain founds the Gold Coast colony.
Scramble for Africa.
- 1830. French conquest of Algeria.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_colonial_empire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Imperialism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Civilizing_mission
South Africa
- Native Zulu people
- 1888 Cecil Rhodes founds De Beers to excavate the Kimberley diamond mine or Big Hole in South Africa. He becomes prime minister of South Africa in 1890 and takes land from black people.
- 1899 Boer War. Britain conquers the two Boer Republics in South Africa during the Witwatersrand Gold Rush. The South African Republic became independent from Britain in the small-scale First Boer War of 1880.
- 1948 Apartheid in South Africa begins when the National Party defeats the United Party on a platform of segregation. Nobel Laureate Nadine Gordimer writes novels on apartheid, including Burger’s Daughter (1979).
- 1960 Sharpeville massacre kills 7,000 black people protesting against pass laws that restricted movement and enforced segregation. The government bans the African National Congress.
- 1961 Nelson Mandela founds the Umkhonto we Sizwe (“Spear of the Nation”, MK) to perform acts of sabotage. He is jailed after the CIA reveals his location, and delivers his “I Am Prepared to Die” speech in 1964. In 1989, F. W. de Klerk becomes president and releases Mandela from prison.
- 1990 Namibia wins independence from South Africa in the South African Border War. Germany colonized the area in 1884 as German South West Africa.
- 1994 Nelson Mandela becomes president and wins a Nobel Peace Prize. Archbishop Desmond Tutu organizes against apartheid and leads the Truth and Reconciliation Commission.
1957 Kwame Nkrumah achieves Ghana independence in the Positive Action campaign.
1960 Congo gains independence from France.
1993 Congo Civil War: Sassou Nguesso and his Mbochi Cobra militia wins the ethnic conflict against Nibolek (Cocoye militia) and Lari (Ninja militia).
1975 Angolan Civil War after it becomes independent from Portugal kills over 500,000. In 2002, the communist People’s Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) wins.
1988 Somali Civil War begins with armed rebels fighting the military junta. In 1922, 37,000 UN soldiers controls the southern half of Somalia, including the capital, trying to build a nation. In 1993, the UN ends up fighting against the Somali National Alliance. In a raid, the SNA inflicts 100 US casualties, downing two Black Hawks with RPGs and ambushing the relief convoy in multiple places.
- 2006 War in Somalia. Ethiopia and the US overthrow the Islamist government.
- 2009 Somali civil war. Somlia government and the African Union fight Sunni Islamist Al-Shabaab militants.
Liberia peace settlement required ceding local power to bad people.
Sudan
- 1956 Sudan gains independence from Britain, and Arab elites in Khartoum in the north hold outsized power. The First Sudanese Civil War kills one million.
- 1972 South Sudan wins independence in the Addis Ababa Agreement.
- 1983 The Second Sudanese Civil War kills two million.
- 2005 The Comprehensive Peace Agreement tries to develop a democratic national government.
- 2003 The War in Darfur in the east kills hundreds of thousands.
- 2009 The International Criminal Court charges Sudan president Omar al-Bashir with war crimes against civilians in Darfur. The Darfur Peace Agreement of 2020 ends the war.
- 2011 South Sudan gains independence from Sudan.
- 2013 South Sudan Civil War.
- 2019 Sudan coup. The Transitional Military Council led by Abdel Fattah al-Burhan removes President al-Bashir.
- 2023 Rebel Rapid Support Forces around Darfur resume the Sudan civil war.
In 1991, President Robert Mugabe of Zimbabwe implements anti-colonial land reforms that result in a flight of capital, banking collapse, a drop in food production. Mugabe continues printing money to fund the Congo War and corruption, leading to hyperinflation. Most transactions are now conducted in US dollars.
1992 Algerian Civil War. Military coup d’état after Islamists win elections. Islamic rebels start with popular support but are defeated after ten years of civil war killing 100,000. Partly caused by economic problems from the oil glut. It spills over as the Islamist insurgency in the Maghreb and the Islamist insurgency in the Sahel region: Mali War, Niger, and Burkina Faso. A Coup Belt forms from disatisfaction with handling the insurgency.
- 2012 Mali War. The government fights Sunni Islam Tuareg separatists (MNLA or CMA) in the north. The separatists capture Timbuktu.
- 2012 Malian coup d’état. Soldiers depose president Touré and replaces him with elected president Keïta.
- 2020 Malian coup d’état. Army officer Goïta deposes Keïta.
- 2021 Malian coup d’état. Goïta deposes elected interim president N’daw.
- January 2022 Burkina Faso coup d’état. Damiba deposes president Kaboré, and is then couped by Traoré.
- 2021 Guinean coup d’état. Army officer Doumbouya deposes elected president Condé.
1885. Berlin Conference gives King Leopold II of Belgium rule over present DRC. Belgium colonized the entire country to extract rubber killing 10 million people, mostly due to famine.
1960. Congo Crisis. DRC gains independence from Belgium. White officers led by Force Publique army commander Janssens continue to repress black soldiers, who mutiny. President Mobutu Seko overthrows the elected president Kasa-Vubu in 1965 and crushes Soviet-supported communist resistance. Hutu Banyamulenge militias help Mobutu defeat the Simba rebellion.
1971. General Amin overthrows President Milton Obote. In 1972, Obote orders an abortive invasion of Uganda.
1979. Uganda-Tanzania War. Uganda National Liberation Front (UNLF) leader Milton Obote overthrows Amin.
1980. Ugandan Bush War. Dictator Museveni overthrows Obote.
1986. Ugandan Civil War against Museveni. Rebels include Joseph Kony’s army, which uses 66,000 child soldiers.
1994. Rwandan Civil War. In the Rwandan genocide, Hutu militias kill around 500,000 Tutsi minorities. Rwanda president Juvénal Habyarimana and Burundian president Cyprien Ntaryamira, both Hutu, are killed when their plane is shot down. The Tutsi Rwandan Patriotic Front wins the war. Mobutu welcomes the Hutu extremists, who escalate violence.
1996. Congo War. Rwanda, Uganda, and Burundi invade to pursue some rebel groups, joined by Angola and Eritrea. Rebels include Tutsi Banyamulenge. The occupation replaces president Mobutu with the rebel leader Kabila, and starts a second war when Kabila tries to expel them. Kabila gets military help from the Southern African Development Community (SADC), including Namibia, Zimbabwe, Angola, Chad, Libya and Sudan, resulting in 5 million excess deaths through disease and malnutrition. In 2003, a democratic Transitional Government is shakily established, though it is weak and corrupt.
1974 Ethiopian Civil War. Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF) overthrows the communist Derg military junta. 1 million die from famine.
1993 Eritrea gains independence from Ethiopia.
1998 Eritrean-Ethiopian War. Eritrea invades Ethiopia.
2018 Opposition leader Abiy Ahmed defeats the TPLF and gives Badme to Eritrea, ending the border conflict.
2020 Tigray War. TPLF condemns the peace and fights the government for two years.
2002 African Union. The African Standby Force intervenes in peacekeeping missions.
2007 Kenyan crisis. Ballot-stuffing on both sides leads to violent mass protests. Kofi Annan brokers a coalition government.
2010 Somaliland opposition candidate Ahmed Mohamoud defeats President Kahin.
1960 Nigeria gains independence. It is the most populous country and leading oil producer in Africa.
2009. Islamist Boko Haram insurgency includes the 2014 Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping.
2015. Nigeria opposition candidate Buhari defeats incumbent President Goodluck Jonathan.
1992. Ghana becomes a democracy.
2016. Ghana has a peaceful transfer of power from John Mahama to Nana Akufo-Addo.
2017. Gambia: president Barrow defeats incumbent Jammeh, who leaves after Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) military intervention.
2020. Malawi opposition candidate Chakwera defeats incumbent Mutharika.
2021. Zambia opposition candidate Hichilema defeats incumbent Lungu.
1989. First Liberian Civil War. Dictator Charles Taylor overthrows dictator Samuel Doe.
1991. Sierra Leone Civil War. Revolutionary United Front (RUF) and Charles Taylor take over diamond mines and commit war crimes. In 1992, Captain Valentine Strasser overthrows the government. In 1996, Julius Maada Bio overthrows Strasser and Ahmad Tejan Kabbah is elected president.
1993. Second Liberian Civil War. Taylor resigns in 2003 and Ellen Sirleaf is elected president.
2024. Libera opposition candidate Boakai defeats George Weah.
Gabon
- 1967 Omar Bongo is the second president.
- 2009 Ali Bongo is the third president.
- 2023 Military coup following protests against election fraud.
Niger
- 1922 French colony.
- 1960 Independence from France.
- 2023 Niger coup by General Tchiani, who asks US soldiers to leave. ECOWAS threatens military intervention but does not intervene.
Law
Judicial branch: federal courts. Judges are appointed for life.
- Supreme Court: chief justice and eight associate justices.
- 13 courts of appeals: 11 circuits, DC, and Federal.
- 94 district courts
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_Rules_of_Civil_Procedure
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_Rules_of_Evidence
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Evidence_law
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contract
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legal_instrument
Financing instrument
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legal_principle
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legal_doctrineTrial
- A trial court has original jurisdiction and holds trials.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/General_jurisdiction
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evidence_(law)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testimony
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Procedural_law
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jury_trial
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bench_trial
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Court_clerk
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harmless_error
Appellate courts hear appeals. Most do not hear testimony or take evidence, but instead rule solely on matters of law.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equity_(law)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estoppel
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clean_hands
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maxims_of_equity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equitable_interest
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doctrine_of_marshalling
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laches_(equity)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equitable_conversion
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breach_of_confidence_in_English_law
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consideration
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subrogation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Injunction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Specific_performance
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tolling_(law)
Learned Hand served on the 2nd circuit appeals court from 1924 to 1961. He is the most quoted lower-court judge.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Intellectual_property
- standard for copyright eligibility is low: “some minimal degree of creativity” suffices.
- Idea-expression distinction: copyright applies to creative expression, not to facts or ideas.
- merger doctrine: if there is very little choice about how to express some fact or idea, the expression merges with the fact.
- Scènes à faire (“scene that must be done”): elements of a creative work that are customary to the genre are not protected.
- Photography
- construction of the scene.
- composition: cropping, color, depth of field
- rendition: angle of shot, light and shade, exposure, effects achieved by means of filters, developing techniques, etc.
- timing
- Fair use
- purpose and character, especially whether the new work is transformative, adding a further purpose or different character, altering the first with new expression, meaning, or message. adding new information, new aesthetics, new insights and understandings.
- Some courts limit to transformative nature to parody or commentary.
- Also: commercial vs. educational
- Some courts consider bad faith: removing copyright notice, failing to credit including when registering the copyright
- nature of the copyrighted work.
- more creative vs. more informational
- scope for fair use is narrower for unpublished works
- amount used out of the whole copyrighted work
- whether the use competes with the potential market for the work.
- traditional, reasonable, or likely to be developed markets
- excludes people who wish to use the plaintiff’s work in transformative ways.
- ensures that copyright does not limit First Amendment freedom of expression.
- purpose and character, especially whether the new work is transformative, adding a further purpose or different character, altering the first with new expression, meaning, or message. adding new information, new aesthetics, new insights and understandings.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_affairs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Think_tank
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carnegie_Endowment_for_International_Peace
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brookings_Institution
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chatham_House
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Sex_and_the_law
Education
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxbridge
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ivy_League
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven_Sisters_(colleges)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swarthmore_College
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bryn_Mawr_College
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haverford_College
Literature
High level is more abstract and general.
Low level is more detailed.
Granularity: degree to which a system is composed of distinguishable pieces.
Emergence.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organization
Unit of analysis: entity being studied. Discuss conclusions in terms of the unit of analysis.
- person, partnership, family, household, neighborhood
- Meso groups: clan, tribe, community, village, town, city, organizations, institutions
- Macro: state, society, civilization
- Unit of observation: data points, which may be then be analyzed in aggregate.
- Level of analysis: scale of relationships, context, and framework
1959. The Two Cultures by C. P. Snow argues for more dialogue between science and humanities.
Keywords: A Vocabulary of Culture and Society (1976) by Raymond Williams.
Thomas Schelling writes The Strategy of Conflict (1960) on action-based communication to demonstrate credible commitment in war and diplomacy. He proves the existence of a focal point or Schelling point that people assume in the absence of communication. People default to meet at noon at the information booth at Grand Central Terminal, heads over tails, ABC letter order, and $50 for splitting money. Micromotives and Macrobehavior (1978) pioneers agent-based computational economics proving a tipping model of racial segregation.
Classical realism theory by Hans Morgenthau (1948) studies the international relations of self-interested states. It holds that multipolar systems are more stable than bipolar systems through alliances and petty wars.
Neorealism theory by Kenneth Waltz (1979) assumes that states fundamentally care about survival and thus power. Because states cannot trust others’ future intentions, they face a security dilemma where one state’s increase in security reduces the security of others’, causing an arms race. This prisoner’s dilemma can lead to tension, escalation, or conflict. The dilemma is stronger when offensive weapons have an advantage over defensive weapons and when offensive and defensive weapons are hard to distinguish. Multipolar systems are more unstable because of greater complexity in diplomacy, higher change of misreading others’ intentions, chain-gaining where allies are drawn into unwise wars provoked by their partners, and buck-passing where states hope others will pay the costs of balancing against a threatening power. Offensive neorealism theory by John Mearsheimer (2001) argues that all states pursue offensive power.
Fukuyama’s The End of History (1992) argues that liberal democracy and free-market capitalism is the final form of sociocultural organization.
The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962) by Thomas Kuhn argues that science involves paradigm shifts, not just an accumulation of knowledge.
Diffusion of innovations (1962) by Everett Rogers: innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, and laggards.
Imagined Communities (1983) by Benedict Anderson on the spread of nationalism.
Guns, Germs, and Steel (1997) argues that differences in development originate in environmental differences that are amplified in positive feedback loops. Eurasia has more suitable plants and animals for domestication, more east-west orientation allowing economy of scale. Density and trade led to higher immunity to disease.
Hard Choices (1998) on humanitarianism, with contributions from Kofi A. Annan.
Steven Pinker writes The Better Angels of Our Nature (2011) that violence has declined over time due to state monopolies on force, commerce, humanitarianism, communication, rights revolutions. Empathy, self-control, moral sense, and reason triumph over practical violence, dominance, revenge, sadism, and ideological justification.
Sapiens (2011) by Yuval Noah Harari argues for growing political and economic interdependence and unification driven by money, empire and capitalist globalization, and universal religion.
The Dawn of Everything (2021). Rejects the State as a colonial construct. Favors flexible politics without domination (control over violence and information). Favors freedom of movement, freedom to disobey arbitrary authority, and freedom to reimagine society.
The Human Past by Chris Scarre
Anthropology
- The Interpretation of Cultures (1973) by Clifford Geertz.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_largest_cities_throughout_history
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_100
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_100:_The_Most_Important_People_of_the_Century
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_System_(economic_plan)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-structuralism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_African-American_history#1970%E2%80%932000
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lincoln%E2%80%93Douglas_debates
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Women%27s_Hall_of_Fame
https://www.youtube.com/@mapsinanutshell
https://vimeo.com/128373915
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prehistoric_technology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_history_of_the_world#Early_Modern_Era
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outline_of_economics#Economic_history
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_relations_(1814%E2%80%931919)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neutrality_Acts_of_the_1930s
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balkans_campaign_(World_War_II)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khedivate_of_Egypt
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Imperialism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scramble_for_Africa
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Italo-Turkish_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moscow_theater_hostage_crisis
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russo-Georgian_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romania_in_World_War_II
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Revolutions_of_1917%E2%80%931923
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russian_Civil_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chechen%E2%80%93Russian_conflict
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_Chechen_War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beslan_school_siege
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_Security_Service
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adolf_Tolkachev
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lockheed_Martin_X-35
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stabilizer_(aeronautics)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vertical_stabilizer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Directional_stability
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%E2%80%93Lagrange_equation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classical_mechanics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unification_of_theories_in_physics#Unification_of_gravity_and_astronomy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Gascoyne-Cecil,_3rd_Marquess_of_Salisbury#Prime_minister:_1895%E2%80%931902
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long_Depression
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_Italian_War_of_Independence#War
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geneva_Conventions
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serenity_Prayer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Legionary_State
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kingdom_of_Romania
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trial_of_the_century
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Brief_History_of_Europe/TOC
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_Dream
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Average_Joe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fee_simple
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freehold_(law)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Making_false_statements
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSDCORB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prison_reform
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demurrage
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Language_isolate
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_abolition_of_slavery_and_serfdom
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/100_Greatest_Britons
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Evidence-based_practices
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Golden_ages_of_China
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Chinese_Military_Texts
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Foreign_alliances_of_France
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byzantine_Empire_under_the_Palaiologos_dynasty
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_Bulgarian_Empire
dominant power in the Balkans until 1256
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Latin_Empire
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adriatic_Sea
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turkish_Croatia#Legacy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Science_and_Civilisation_in_China
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pre-Columbian_transoceanic_contact_theories
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Cities
Rede Lecture
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Renaissance_navbox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Early_Modern_Europe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron_triangle_(US_politics)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_selection_(politics)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_eponymous_laws
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Culture_of_the_United_States
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Environmental_social_science
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Social_sciences
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:History_of_Mexico
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Register_of_Historic_Places
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orientalism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canal_age
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Howard_Hughes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Culture_of_ancient_Rome
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Journal_of_African_American_History
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Journal_of_Social_History
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Journal_of_Black_Studies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Journal_of_African_American_Studies
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Wikipedia_directories