Contents
- Cellular
- Genetics
- Cell cycle
- Embryonic development
- Signaling
- Photosynthesis
- Metabolism
- Medicine
- Emergency medicine
- Endocrine
- Reproductive system
- Digestion and gastrointestinal
- Kidney
- Nutrition
- Cardiology and circulatory
- Lung respiratory pulm
- Orthopedics and musculoskeletal system
- Muscle
- Anatomy
- Physical therapy PT
- Dermatology and skin
- Immune system
- Infectious disease
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Oncology
- Neuroscience and neurology
- Eye
- Psychiatry
- Addiction and substance use disorder
- Psychology
- Cognitive biases
- Radiology
- Histology and pathology
- Lab analysis and biotech techniques
- Devices
- Companies
- History of medicine
Biology
See also: study design.
Tinbergen’s four questions in terms of past and present:
- Proximate view: organism development and mechanistic description
- Evolutionary view: environmental adaptations and species evolution
Cellular
Cell structure
- Cell wall: rigid cellulose layer, only in plants.
- Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer. It contains proteins for transport, receptors, and cell adhesion. Some proteins are modified with glycans for cell-cell recognition.
- Cytoplasm or cytosol
- Cytoskeleton: network of protein fibers for structure and movement
- Actin microfilament is 7 nm diameter
- Formin promotes nucleation and elongation at the fast-growing barbed end.
- Rho GTPase actives formin via its GTPase-binding domain (GBD).
- Stress fibers are contractile bundles of actin and non-muscle myosin II needed for adhesion, migration, and morphogenesis.
- Intermediate filament is 10 nm diameter
- Microtubules are 25 nm diameter and up to 50 μm long. Used for intracellular transport.
- Kinesin: anterograde transport towards the (+) end. Walks hand-over-hand.
- Dynein: retrograde transport towards the (-) end.
- Myosin I motor proteins transport vesicles. They walk with a 10 nm step size.
- Actin microfilament is 7 nm diameter
- Organelles
- Nucleus contains DNA and has two lipid bilayer membranes. Nuclear pores allow materials to move.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- Rough ER is continuous with the outer nuclear envelope. studded with ribosomes for making proteins
- Smooth ER makes lipids
- Golgi apparatus is close to the smooth ER. It modifies proteins and transports them in vesicles.
- Mitochondrion produces ATP as the “powerhouse of the cell”.
- Mitochondrial DNA is only passed down maternally.
- CoRR hypothesis (co-location for redox regulation) states that mitochondria have their own genome allows direct regulation of energy production genes based on redox state.
- Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, only in plants.
- Vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste. Plants have a large central vacuole, while animal cells may have many smaller ones.
- Lysosome contains hydrolytic enzymes and buds off the Golgi apparatus. Only in animal cells.
- Peroxisome contains oxidative enzymes that generate hydrogen peroxide. Self-replicating and found in all eukaryotes.
Cell adhesion
- cell-adhesion molecules (CAM) like selectin are transmembrane proteins.
- Focal adhesion includes integrin between extracellular matrix and F-actin. Regulated by PTK2 or focal adhesion kinase (FAK).
- Anchoring junctions
- Desmosomes connect intermediate filaments of adjacent cells. Strongest.
- Adherens junctions connect actin filaments
- Cadherin (“calcium-dependent adhesion”) is a cell-surface receptor protein.
- E-cadherin - β-catenin - α-catenin - actin cytoskeleton.
- β-integrin - talin - (amino terminus) vinculin (carboxy-terminus) - actin
- Hemidesmosomes anchor a cell to the basal lamina, a sheet of extracellular matrix.
- Gap junctions form channels to allow small molecules and ions.
- Tight junctions seal between epithelial cells, preventing the passage of fluids and solutes.

Cilium or flagellum.
- The axoneme or axial filament is a ring of 9 microtubule doublets. Nexin binds between doublets.
- Motile cilium has dynein and two inner doublets.
Cell stains
- Acidophile structures contain protein and stain with eosin dye. Includes cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers.
- Basophilic structures stain with basic dye, such as hematoxylin, which is dark blue, purple, or black. Includes nucleus, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, collagen, myelin, elastic fibers, and acid mucins.
- H&E stain is hematoxylin and eosin.
- Orange G stains keratin in the Pap stain, and erythrocytes in trichrome stains.
Cell culture
- An immortalised cell line has mutations allowing indefinite division without cellular senescence.
- HeLa is the oldest human cell line, derived from cervical cancer cells taken from Henrietta Lacks, a Black woman, in 1951.
Genetics
Mendelian inheritance
- Replaces Lamarckian inheritance or the inheritance of acquired characteristics.
- dominant and recessive genes
- inbreeding depression: recessive diseases become more frequent.
- homozygous, heterozygous
- Genetic cross, Punnett Square, F1 generation, F2 generation
- Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium: genotype frequencies remain constant in the absence of influences.
- Pedigree
- Non-Mendelian inheritance
- Incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits
- Gene map and genetic linkage: recombination frequency is proportional to chromosomal distance, violating Mendel’s law of independent assortment.
- Sex-linked inheritance.
- horizontal gene transfer
- phenotypic plasticity
- genetic assimilation, where an environmental adaptation later becomes genetically encoded through selection.
- Baldwin effect: selection can reinforce learned behavior and learning ability
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pleiotropy
DNA
- Human have 3 billion base pairs of DNA.
- The exome is the 1.5% of DNA comprising the 22,300 protein-coding genes.
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, including an X or Y sex chromosome or allosome pair.
- X-linked dominant inheritance: all daughters and no sons of an affected father are affected.
- X-linked recessive inheritance: males are quadratically more affected
- Klinefelter syndrome: male has an extra X chromosome. Causes low testosterone (hypogonadism), high gonadotropin levels, less muscle, less facial hair, increased breast tissue.
- DNA is a double helix with antiparallel strands, containing a deoxyribose-phosphate backbone and nucleotides adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). RNA uses uracil, a demethylated thymine.
- DNA supercoiling adds more twists. DNA is usually negatively supercoiled to be more compact. It is positively supercoiled when replicated or transcribed.
- In eukaryotes, DNA is wrapped up as chromatin around histone proteins.
- DNA replication is semiconservative. It consists of initiation, elongation, and termination. The leading strand is synthesized continuously and the lagging strand is synthesized in Okazaki fragments.
- Origin recognition complex binds at an AT-rich origin.
- Helicase unwinds the helix at the replication fork.
- DNA topoisomerase cleaves DNA to relieve the torsional stress.
- Primase synthesizes a short primer.
- DNA polymerase adds nucleotides 5’ → 3’. It can only add to an existing strand. It can also proofread and one incorrect base as a 3’ → 5’ exonuclease.
- Replication ends at a ter site.
- Terminal transferase
- TLS
Mutations
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is a single germline substitution.
- Microsatellite or short tandem repeats (STRs) have a high mutation rate and high diversity.
- Structural variation affects at least 50 bp. Insertion, deletion, inversion, translocation, and Copy number variation (CNV)
- Chromosome abnormality
- Chromosomal translocation. Reciprocal translocation swaps parts between non-homologous chromosomes. In Robertsonian translocation, two different chromosomes stick together. In an unbalanced translocation, some genes are deleted or silenced.
- Transposons
- Retrotransposons encode reverse transcription to copy their DNA and insert into new positions.
- DNA transposons encode transposase to jump to different locations.
- Down syndrome: trisomy (third copy) of chromosome 21 causes intellectual disability, flat head, and a small chin.
The central dogma states that genetic information flows as DNA -> RNA -> protein, with reverse transcription and RNA replication possible in special cases.
Transcription to mRNA is 5’ → 3’.
- Promoter regions control transcription of their downstream gene.
- TATA box in 25% of promoters and initiator element (Inr) in 50% bind transcription factor II D (TFIID) which recruits RNA polymerase II. The TATA box is 25 bp upstream while Inr overlaps the transcription start site.
- TATA-binding protein (TBP)
- The transcription preinitiation complex (PIC) positions RNA polymerase II, unwinds the DNA and forms the transcription bubble. It is needed for transcription and contains the mediator complex which interacts with transcription factors.
- TFIIB helps form the PIC.
- TATA box in 25% of promoters and initiator element (Inr) in 50% bind transcription factor II D (TFIID) which recruits RNA polymerase II. The TATA box is 25 bp upstream while Inr overlaps the transcription start site.
- RNA polymerase starts at the promoter and ends at a poly-U/hairpin loop termination sequence.
- pre-mRNA primary transcript contains exons and non-coding introns. RNA-binding proteins carry out post-transcriptional modifications and RNA editing.
- The spliceosome contains small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNP) and SR protein and removes introns, and also removes some exons in alternative splicing. The reading frame is the span of DNA between the start and stop codons that is not removed.
- Proteins add a 5′ cap prevents degradation by 5′ exonuclease. Cap-binding complexes bind with the nuclear pore complex and export the RNA.
- Polyadenylation factors add a poly-A tail.
Translation to a protein is N → C.
- Methionine AUG start codon.
- The ribosome forms peptide bonds between a complementary aminoacyl-tRNA at its A site and a growing protein at its P site. The tRNA moves to the exit E site and leaves. The ribosome contains 18S and 28S rRNA subunits.
- A stop codon UAA, UAG, or UGA releases the protein.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/
Post-translational modifications include protein phosphorylation, acetylation, and N-linked glycosylation. The latter is essential for cell recognition and adhesion. Kinase phosphorylates proteins and phosphatase dephosphorylates proteins.
- Telomerase extends telomeres, a repeat sequence at the 3’ end which distinguishes DNA ends from a double-strand break.
DNA repair
- Single-strand damage
- Base excision repair: oxoguanine glycosylase (OGG1) removes the damaged base, creating an AP site. AP endonuclease nicks the backbone to recruit DNA polymerase.
- Nucleotide excision repair (NER): 12-24 nucleotide-long strand is removed.
- Mismatch repair detects and cuts errors.
- MutSα proteins identify T:G mismatch.
- Double-strand break
- Homologous recombination repairs the damage using a homologous chromosome as a template.
- non-homologous end joining (NHEJ): specialized DNA ligase joins the ends.
Gene Regulation
- Histone phosphorylation can loosen or condense chromatin. Heterochromatin is condensed. Histone acetylation loosens chromatin.
- Transcription factor proteins bind to 10 bp DNA sequences to regulate transcription.
- TATA-binding protein binds the TATA box.
- Zinc finger domains bind to specific DNA sequences.
- EGR1 (Early growth response protein 1) is a master regulator transcription factor. It recruits TET1 (ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase 1) which demethylates DNA.
- Epigenetics are heritable genome changes that do not change the DNA sequence.
- DNA methylation of cytosine blocks transcription factor binding.
- CpG islands are in 70% of promoters.
- Cytosine has an electron-rich nitrogen which easily converts to 5-methylcytosine. The guanine provides a hydrogen bond donor to stabilize the methyl group.
- Methylated cytosines often deaminate to thymine.
- Cis-Regulatory Elements (CRE) are on the same strand. DNA can fold, bringing regions 1 Mbp away close to the gene.
- Enhancers bind transcription factors that increase transcription.
- Silencers and operators bind repressors.
- Insulators block enhancers or act as barriers to prevent silencing from the spread of heterochromatin.
- Trans-Regulatory Elements (TRE) are on a different molecule. They usually are transcribed to RNA or protein, act on a wide range of genes, are more conserved, and act indirectly via cis-regulatory elements.
- microRNA are 21 to 23 bp ssRNA hairpin loops. microRNA pairs with and silences its complementary mRNA via cleavage, shortening the poly(A) tail, or reducing translation.
- lac operon is an inducible operon for lactose metabolism. lac repressor binds and blocks the operator. Lactose inactivates the lac repressor.
- trp operon is a repressible operon for tryptophan synthesis. tryptophan activates the repressor.
Human Genome Project sequences the full genome in 2003.
ENCODE: Encyclopedia of DNA Elements
- map of open chromatin or DNase 1 hypersensitive sites
- 8.4 million DNA motifs for protein binding, around 50 bp long.
- interaction network of human transcription factors.
GOLD: Genomes On Line Database
Cell cycle
The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis. Cells can also be resting phase G0 (quiescence) outside the cell cycle.
Interphase.
- G1 phase. Cell increases protein synthesis and grows in size.
- The G1 restriction point. Mitogens promote passage through the restriction point by producing cyclins. Cyclins activate cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK), which phosphorylates proteins for DNA replication and centrosome duplication. Once activated, the cell commits to cell division and no longer needs extracellular signals.
- p53 (TP53) suppresses tumors and is mutated in a majority of cancers. It promotes p21, a CDK inhibitor, by binding to p53 response elements (p53RE). p53 also promotes DNA repair proteins, apoptosis, or senescence. It is activated by cellular stress, including DNA damage, oxidative stress, osmotic shock, ribonucleotide depletion, viral infection, and deregulated oncogene expression.
- Synthesis S phase. DNA replication forms sister chromatids.
- Chromatin assembly factor 1 (CAF-1) deposits histone behind replication forks to mark heterochromatin for somatic cell identity.
- G2 phase. Cell completes DNA replication.
- G2-M DNA damage checkpoint. DNA damage suppresses M-phase CDK which promotes spindle assembly.
Mitosis.
- Prophase. Chromosomes condense and become visible under a microscope. The nuclear envelope begins to break down, and the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) duplicates, forming centrioles in animal cells. The nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align in a central plane at the metaphase plate to ensure equal distribution to daughter cells.
- Spindle fibers, composed of microtubules, capture chromosomes by their kinetochores, protein complexes on the centromeres of chromosomes.
- Spindle checkpoint. When kinetochores on sister chromatids are attached to opposite spindle poles, M-phase CDK stimulates the anaphase-promoting complex, which destroys cyclins and proteins holding sister chromatids together.
- Anaphase: Separation of sister chromatids towards opposite poles of the cell by microtubules and dynein. This is a critical step in ensuring each daughter cell receives a complete genome.
- Telophase: The separated sister chromatids arrive at the poles and begin to decondense back into chromatin. A new nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two daughter nuclei.
- Cytokinesis: The final stage, where the cytoplasm and organelles are physically divided into two daughter cells. This can occur by cleavage furrow formation (pinching inward) in animal cells or cell wall formation in plant cells.
Meiosis
- Before meiosis: duplication into two sister chromatids attached at the centromere.
- Prophase I. Homologous chromosomes pair up and crossover in synaptonemal complexes. Homologous recombination swaps parts of homologous chromosomes.
- The Holliday junction joins two dsDNA strands to allow exchange.
- Homologous chromosomes align (metaphase) and separate (anaphase), and the cell divides (telophase), creating haploid cells. Somatic cells are diploid, containing one chromosome from each parent.
- Meiosis II. Sister chromatids separate.
Embryonic development
23 Carnegie stages cover the first 60 days of a human embryo.

Germinal stage is the first week.
- Day 1. Fertilized single-cell zygote demethylates its DNA, travels down the fallopian tube, and divides via cleavage.
- Day 2. 4 cells.
- Day 3. 8 cell.
- Day 4. Morula is a solid ball of 16 identical totipotent cells.
- Day 4. Blastocyst is a hollow sphere with an inner cell mass which methylates.
- Trophoblast (hypoblast) outer layer develops into the yolk sac or chorion and amnion membranes that surround the embryo. The placenta derives from chorion and uterine tissue.
- Day 7. Inner cell mass develops a bilaminar embryonic disc with epiblast (ectoderm) and hypoblast (endoderm). The disc becomes pear shaped.
- Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent stem cells from the inner cell mass, which can differentiate into any of the germ layers.
Day 14. A primitive streak forms at the narrow caudal end. The disc differentiates into a gastrula with blastopore, archenteron, and three germ layers:
- Ectoderm: nervous, sensory, epidermis.
- Mesoderm: muscle, skeleton, blood, urogenital, dermis.
- Mesenchyme becomes:
- Hemangioblast becomes angioblast (endothelium) and HSC.
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) or stromal cells can differentiate into muscle and connective tissue.
- Mesenchyme becomes:
- Endoderm: gut, lungs and liver.
Neuralation
- Day 19. Neural plate.
- Day 25. Neural groove and neural folds.
- Day 28. Neural tube closes via Twist-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cell type. It will become the brain and spinal cord. Dorsal to the notochord.
- Endoderm -> gut tube ventral to the notochord.
- Axial mesoderm -> notochord (replaced by spine).
- Paraxial mesoderm -> somites, paired blocks along the neural tube. BMP, fibroblast growth factor (FGF).
- dermatome -> dermis
- myotome -> skeletal muscle
- sclerotome -> vertebrae, rib cage
- syndetome -> tendons and cartilage
- Intermediate mesoderm -> urogenital
- Lateral plate mesoderm at the periphery. Created by ectoderm BMP-4. Splits into two layers:
- Outer somatopleuric mesenchyme -> body wall
- splanchnopleuric mesenchyme -> circulatory system.
- Sonic hedgehog protein SHH is a morphogen. Mutations can cause holoprosencephaly, where the brain does not split along the ventral midline.
Facial development from ectoderm
- Frontonasal process down from the top of the head
- Week 6. Two nasal placodes invaginate into nasal pits, which give rise to the olfactory epithelium. The raised margins become the nose, palate, and upper lip.
- Two maxillary prominences from the cheeks.
- Two mandibular prominences for the chin and lower lip.
- Cleft lip occurs if these fail to fuse.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Development_of_head_and_neck
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Development_of_respiratory_system
Week 9. Fetus.
Tissue types
Epithelial tissue
- Simple: squamous, cuboidal, columnar, ciliated, glandular
- Stratified
Nervous
Muscle
Connective
Germ cells undergo meiosis and give rise to gametes. Somatic cells are not heritable.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) are created by reprogramming somatic cells.
- Yamanaka factors: Oct4 induces pluripotency and Sox2 maintains it. Klf4 remodels chromatin to promote pluripotency genes. c-Myc.
- NANOG represses histone markers and helps recruit Oct4 and Sox2.
Signaling
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) cAMP pathway. Hormone binds -> Gs-alpha subunit detaches -> adenylyl cyclase -> ATP to cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate).
cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA). Also CREB.
metabotropic receptors
85% are rhodopsin-like receptors, mostly olfactory receptors.
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK). When activated, RTKs dimerize and autophosphorylate tyrosine residues on its cytoplasmic tail.
Most kinases are serine/threonine protein kinases, which phosphorylates the OH group.
Cytokines are small, widespread immune signaling proteins: interleukins, lymphokines.
- Interferon (IFN)
- Type I: IFN-α, IFN-β. IFNAR receptor -> JAK1 and TYK2
- Type II: IFN-γ. IFNGR receptor -> Jak1 and Jak2
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activates NF-κB, MAPK, and weakly leads to apoptosis.
- Chemokines attract leukocytes and endothelial cells.
- Constitutive or in response to inflammation.
- IFN-γ -> CXCL9,10,11 attract T-lymphocytes
- CCL11 binds to eosinophil CCR3 receptor.
- CCL2 attracts monocytes.
- CXCL1 and CXCL8 (IL-8) -> Akt and ERK1 -> attract neutrophils, promote angiogenesis, promote wound healing. Found in endothelial cells.
JAK-STAT pathway responds to cytokines. IFN.
- IL-2 -> IL-2 receptor -> JAK1 and JAK3
- IL-6, Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), IL-11, IL-27, oncostatin M (OSM), cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC) -> glycoprotein gp130 -> Jak1 -> Stat3
- IL-10 -> IL-10 receptor -> JAK1 and Tyk2
- IL-12 -> IL-12 receptor -> Jak2 and Tyk2
- cytokine binding -> receptor dimerizes -> Janus kinases (JAK) transphosphorylate each other and the receptor
- receptor binds SH2 domain of STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription protein) -> JAK phosphorylates the STAT -> STAT dissociates from the receptor, dimerizes, and move to the nucleus -> protein expression.
- JAK activates PI3K through its SH2 domain.
- JAK activates Grb2 and MAPK through the Grb2 SH2 domain.
MAPK pathway regulates cell growth, differentiation, and death.
- All activated by cytokines and growth factors.
- All cause proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism.
- p38 and JNK are stress-activated and cause inflammation and apoptosis.
- Activated by MEKK1-4, TAK1 (aka MAP3K7), ASK1 (MAP3K5), MLK3 (MAP3K11).
- Gadd45 stress sensor -> MEKK4 (aka MAP3K4).
- CDC42 Rho small GTPase -> MLK3.
- MKK4,7 -> JNK1,2,3 (c-Jun N-terminal kinase, MAPK8-10) -> c-Jun
- MKK3,4,6 -> p38α/β/γ/δ (MAPK14,11,12,13). Can cause growth.
- Activated by MEKK1-4, TAK1 (aka MAP3K7), ASK1 (MAP3K5), MLK3 (MAP3K11).
- ERK activated by mitogens.
- Ras (a MAPK) is a membrane-bound small GTPase.
- guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) activates membrane-bound Ras-GDP to Ras-GTP.
- Ras, calcium -> RAF1 (c-Raf), ARAF, BRAF -> MEK1,2 (MAP2K) -> ERK1,2 moves to the nucleus (extracellular signal-regulated kinase, MAPK3,1) -> serum-response factor (SRF)
- SRF -> proto-oncogenes Myc, Jun, Fos, EGR -> cyclins.
- ERK1,2 cause migration, morphogenesis, growth.
- Ras (a MAPK) is a membrane-bound small GTPase.
- MEKK2,3 -> MEK5 -> ERK5. Mitogen and stress-activated, not activated by cytokines.
- Epidermal Growth Factors (EGF) like TGF-α activate ERK.
- EGF binds to EGFR (an RTK) -> binds the SH-2 domain on Grb2 (Growth factor receptor-bound protein) -> activates Sos (a GEF).
- Atypical MAPKs:
- Stress, growth factors, CDC42 -> PAK -> actin migration, morphogenesis, differentiation.
- ERK7 (MAPK15) causes autophagy.
PKB or Akt pathway increases protein synthesis and inhibits apoptosis.
- IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor) -> IGF-1R (an RTK) -> PI3K.
- Insulin -> insulin receptor (an RTK) -> PI3K.
- PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase) -> phosphorylate PIP2 to PIP3 -> PDK1 -> Akt.
- PKB (protein kinase B)
- activates mTOR via Akt ⊣ TSC1 ⊣ Rheb -> mTORC1.
- inhibits GSK3 by phosphorylating it
- inhibits p27 by phosphorylating it which moves it out of the nucleus. p27 is a tumor suppressor that promotes G1 arrest.
- inhibits apoptosis via Akt ⊣ BAD ⊣ Bcl-2 ⊣ apoptosis and Akt ⊣ Caspase9 ⊣ Caspase 3/7 -> apoptosis.
- inhibits FOXO metabolism and stress resistance.
- mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). Rapamycin is an immunosuppressant.
- activates p70S6K (ribosomal protein S6 kinase) -> S6 -> cell division.
- inhibits 4EBP1 ⊣ elF4E -> cell division.
- inhibits Ulk1 autophagy gene.
- PTEN is a tumor suppressor that dephosphorylates PIP3 to PIP2.
IGF-1
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) activates ERK-1/2 and Akt.
NF-κB inflammation pathway.
- Full name: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.
- Dimer. The monomers have a Rel homology domain (RHD) for DNA binding and dimerization:
- RelA, RelB, and c-Rel also have a C-terminal transactivation domain which binds coactivators of transcription. c-Rel is a myeloid checkpoint protein.
- p50 and p52 do not activate transcription. They are generated from p105 and p100 via removal of ankyrin repeats.
- NF-κB is usually inactive, bound to IκBα in the cytosol.
- Inflammation or stress signals -> receptor -> IκB kinase (IKK) active.
- IKK phosphorylates IκBα, causing addition of ubiquitin and degradation.
- Free NF-κB translocates to the nucleus and binds response elements (RE) -> DNA transcription -> inflammation.
Wnt pathway.
- Wnt growth factor binds to its Frizzled receptor and LRP5/6, activating Dishevelled or Dvl protein to inhibit GSK3 and degrading Axin. Dvl inhibits GSK3 by phosphorylating it.
- Noggin -| BMP, specifying boundaries.
- Axin and GSK3 (Glycogen synthase kinase) are part of the destruction complex which continually degrades β-catenin.
- GSK3 inhibits glycogen synthase.
- GSK3 phosphorylates cyclin D1, blocking cell cycle progression.
- Lithium inhibits GSK3, which promotes inflammation.
- GSK3 inhibitors induce cell cycle arrest
- Accumulating β-catenin moves to the nucleus and interacts with TCF/LEF transcription factors to express Myc, Lef1, and cyclin.
Notch: proliferation and differentiation.
- Reelin -> Notch-1. Reelin -> Disabled-1 (Dab1) -> proto-oncogene c-Crk.
- Delta and Jagged ligand binds to Notch receptor, causing two cleavages.
- Free Notch intracellular domain (NICD) moves to the nucleus and activates RBPJ.
Chordin -> Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) causes bone growth via Smad1/5/8 and Co-Smad (Smad4) -> serum response factor (SRF), ternary complex factor (TCF), activator protein 1 (AP1), activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2).
hox
Calcium signal transduction pathway
Calcium activates calmodulin (CaM).
Calcineurin (CN) is a calmodulin-activated protein phosphatase which dephosphorylates NFAT, exposing a nuclear localization signal (NLS).
CaMKII (calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) activates CREB.
CREB transcription factor essential for neuroplasticity and memory. Binds to cAMP response elements.
- CREB increases ΔFosB and JunD. ΔFosB and JunD represses c-Fos, allowing accumulation of ΔFosB. ΔFosB in the nucleus accumbens causes addiction.
c-Src is a proto-oncogene that promotes proliferation and angiogenesis. Non-receptor tyrosine kinase.
- CSK (C-terminal Src kinase) inactivates c-Src. CSK phosphorylates the tyrosine group, which binds with the c-Src SH2 domain.
Addition of ubiquitin causes degradation by proteasomes.
- Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose, 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Nodal signaling pathway, cerberus, Lefty (TGF-β family). left-right asymmetry.
Cluster of differentiation (CD) are cell surface molecules which can be used to classify cells types (immunophenotyping).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_of_differentiation
Senescent cells have permanent cell cycle arrest, resistance to apoptosis, and have the senescence-associated secretory phenotype.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Senescence-associated_secretory_phenotype
Photosynthesis
Metabolic pathways.
Photosynthesis
- Light-dependent reactions create a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts.
- Chlorophyll is a porphyrin that absorbs red and blue light.
- Carotenoids are red, orange, or yellow tetraterpenoids. They include carotene, orange-yellow luteine (leafy greens), lycopene (tomato).
- Photosystem II uses plastoquinone
- photosystem I
- Light-independent reactions fix carbon.
- Calvin cycle
- C3 carbon fixation came first and is still used in 95% of plants.
- RuBisCO uses ATP: RuBP + CO2 + H2O -> 2x 3-phosphoglycerate
- Gas exchange requires open stomata, which loses up to 97% of the water taken up.
- In dry areas, plants shut their stomata, resulting in higher O2 concentration. This increases the rate of wasteful photorespiration, where RuBisCO produces 2-phosphoglycolate and releases previously fixed carbon.
- C4 carbon fixation: concentrate CO2 around Rubisco.
- CAM carbon fixation: fix CO2 at night, when it is cooler and O2 levels are lower
- C3 carbon fixation came first and is still used in 95% of plants.
- Calvin cycle
Metabolism
Cellular respiration
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the cell’s main energy store.
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide) are electron carriers that donate high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain.
NADH = 3 ATP, FADH2 = 2 ATP. Fermentation recycles NAD+.
The electron transport chain is an aerobic process that converts electron carriers to a proton gradient and then to ATP. Complex I takes 2 electrons from NADH and pumps four protons into the intermembrane space. Complex II takes 2 electrons from FADH2. Coenzyme Q moves electrons from Complex I/II to Complex III, which pumps four protons per electron. Cytochrome C brings four electrons to Complex IV, which pumps two protons and reduces two oxygen to two water. The proton gradient drives ATP synthetase.
Citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle converts glucose into 2 ATP and electron carriers (NADH and FADH2). It takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. Glucose is first converted to 2 pyruvate -> 2 acetyl-CoA + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH. In the Krebs cycle, 2 acetyl-CoA -> 8 NADH + 2 FADH2 + 2 ATP + 6 CO2. Acetyl-CoA (2C) + oxaloacetate (4C) -> citrate (6C), which is rearranged and decarboxylated.
Folate cycle. Dietary folate becomes tetrahydrofolate (THF), a crucial carrier for one-carbon groups. Folate is crucial for DNA synthesis in red blood cells and neural tube closure. Methionine synthase transfers methyl from THF to the SAM cycle.
Vitamin B12 or cobalamin catalyzes methyl transfer by forming a Co-CH3 bond. It is a metalloenzyme with a cobalt coordination complex.
Vitamin K required to synthesize many clotting factors.
SAM cycle or methionine cycle produces S-Adenosyl methionine. SAM transfers its methyl group and becomes homocysteine (SAH).
Bicarbonate buffer system. CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2CO3 ⇌ HCO3- + H+. Carbon dioxide is transported as carbonic acid.
- Carbonic anhydrase is a zinc metalloenzyme that catalyzes CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2CO3. It helps maintain acid-base homeostasis and transport carbon dioxide. Mainly in the kidney.
Medicine
Medical student 4 years
Resident
- Intern
Fellow
Attending
Admitting or MOD
nurse
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medical_Informatics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clinical_decision_support_system
Diagnosis code: International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Procedure code: Current Procedural Terminology
SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms) covers clinical findings, symptoms, diagnoses, procedures, body structures, organisms and other etiologies, substances, pharmaceuticals, devices and specimens.
US National Library of Medicine NLM
- PubMed.gov, including the MEDLINE journal database indexed on Medical Subject Headings (MeSH).
- RxNorm
Embase
Evidence-based medicine
UpToDate
Merck manual
Cochrane Reviews
Clinical questions: Patient, Population or Problem, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcomes (PICO)
Aging
- Hayflick limit. Differentiated cells can only divide 50 times before their telomeres become too short.
Epidemiology.
Exercise
Pediatrics
- Bassinet or cradle for infants up to 4 months.
- Infant bed or crib contain children up to 1 year old that can climb.
- Baby colic: crying more than three hours a day for most days. Affects 20% of babies around 2-12 weeks old.
- The Happiest Baby on the Block (2002) by Harvey Karp on the 5 S’s to soothe babies: nightly swaddling until baby can roll over, side/stomach position, shushing, swinging, and sucking or pacifier. Argues that human babies are born three months early. Swaddling reduces stimulation and may resemble a hug.
Ophthalmology and Optometry.
Evidence-based practices
Hierarchy of evidence:
- clinical practice guideline
- meta-analysis systematic review
- randomized controlled trial (RCT)
- observational
- cohort studies: prospective, follow cohort
- case control studies: retrospective
- cross-sectional survey
- no design: case report, narrative review, expert opinion
- animal and lab studies
Emergency medicine
- First aid kit
- bandages
- burn dressings
- porous tape
- antiseptic cream
- sterile dressings, triangular dressings, adhesive dressings
- foil blanket
- CAB: Chest compression, Airway, Breathing
- Basic airway management
- Choking but conscious: encourage coughing, back blows, abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver).
- Recovery position on the side with mouth downward and chin up to protect the airway.
- Head tilt/chin lift to clear the airway. Standard if cervical spine injury is not a concern.
- Jaw-thrust maneuver: open the jaw, which pulls the tongue forward.
- Rescue breaths for infants or drowning victims.
- Advanced airway management
- Trachea intubation. Sniffing position with a rolled towel under the head. Laryngoscope helps place the trach between vocal cords.
- Surgical airway: cricothyrotomy cuts the neck and cricothyroid membrane to access the trachea bypassing the upper airway.
- Basic airway management
- CPR: cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Level of consciousness
- Oriented: name, location, and date.
- AVPU: alert, verbal, pain, unresponsive.
- Glasgow Coma Scale rates eye, verbal, and motor responses out of 4, 5, 6. Higher is more responsive.
- Pain stimulus such as a sternal rub
- Activities of daily living (ADL)
- Immobility can cause chest infections, muscle deconditioning, and embolism.
- Prevent pressure ulcers, bed sores, or decubitis through regular turning or alternating pressure in multiple air chambers.
- Bandages and gauze cover wounds. Gloves and disinfectant.
- Tourniquet reduces blood loss
- Sling
- Moldable splint can be used as a neck brace.
External causes
- Hypercapnia. OSHA Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) of 5,000 ppm CO2.
- Russian BIOS-3 (1972) used 8 square meters of Chlorella algae per human.
- heat stroke
- hypothermia or exposure. frostbite.
- altitude sickness
- diving disorders or decompression illness
- Decompression sickness or the bends caused by dissolved gases emerging from solution as bubbles.
- Arterial gas embolism (AGE): perfusion blockage caused by gas bubbles
- Prevent via decompression stops to limit ascent to 10 m/min.
- Treat with 100% oxygen in a hyperbaric chamber to reduce bubbles.
- poisoning
- Antifreeze or ethylene glycol is metabolized to glycolic acid, causing acidosis. Glycolic acid is metabolized to oxalic acid causing AKI.
- sodium thiosulfate treats cyanide poisoning. It is a sulfur donor which converts cyanide to the nontoxic thiocyanate via rhodanase.
- copper toxicity involves liver cirrhosis, kidney necrosis, and irritability. Usually due to Wilson’s disease. Penicillamine is a copper chelating agent.
- Dimercaprol has adjacent thiols that chelate arsenic, mercury, gold, and lead.
- Trauma
- Abbreviated Injury Scale: location, structure affected, level (injury type), and severity (out of 5).
- Emergency bleeding control
- External bleeding: lacerations, incisions and abrasions.
- Internal bleeding.
- blister
- burn: first-degree epidermis, second-degree dermis, and third-degree subcutaneous injury.
- wound care
- crush injury can cause hypovolemic shock, hyperkalemia, compartment syndrome, and acute kidney injury (AKI) from rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown).
- compartment syndrome: increased pressure in an arm or leg causes insufficient blood supply
- can be caused by toxins from a high pressure injection injury.
Endocrine
Hypothalamus
- Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck.
- HP-adrenal axis
- CRH -> anterior pituitary ACTH -> adrenal cortisol
- Low cortisol below 5 mg/dL suggests adrenal insufficiency or crisis, causing hypotension. Addison’s disease is primary adrenal insufficiency.
- Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and increase blood pressure.
- Glucocorticoids produced in the adrenal cortex zona fasciculata.
- cortisol (hydrocortisone), prednisone, dexamethasone. Also nasal fluticasone and mometasone.
- Mineralocorticoids produced in the adrenal cortex zona fasciculata.
- aldosterone causes active sodium reabsorption, passive water reabsorption, and active potassium secretion in the collecting tubule.
- Glucocorticoids produced in the adrenal cortex zona fasciculata.
- HP-thyroid axis.
- TRH -> anterior pituitary TSH -> thyroid thyroxine T4 -> triiodothyronine T3 increases metabolism and growth.
- hyperthyroidism
- Graves’ disease. thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin
- Thiamazole inhibits thyroperoxidase and thyroid hormone synthesis.
- 500 MBq of iodine-131 kills thyroid cells.
- hypothyroidism: primary and secondary. Tiredness, intolerance to cold, hair loss, low blood pressure.
- 130 mg/day potassium iodide blocks thyroid from radioactive iodine.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Radiation_protection
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Antidotes
- HP-somatotropic axis
- GHRH -> anterior pituitary growth hormone GH -> liver IGF-1
- Pituitary tumors can cause acromegaly and gigantism.
- HP-gonadal axis
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone GnRH -> anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone LH and follicle-stimulating hormone FSH -> testes Leydig cell testosterone or ovary estradiol. Testosterone -> spermatogenesis and muscle mass.
- Activin -> FSH. Inhibin -| FSH. TGF-β family.
- Anabolic steroids resemble testosterone. They increase muscle mass causes testicular atrophy and infertility. hCG resembles LH and helps maintain testes testosterone.
- Short and long feedback
- Somatostatin inhibits GH, TSH, prolactin, and ECL cells.
- dopamine -| anterior pituitary prolactin -> milk
- Clomifene depletes estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, increasing GnRH, FSH, and LSH, which induces ovulation and testosterone production.
- Sheehan’s syndrome. Hypopituitarism due to ischemic necrosis usually due to childbirth, causing low prolactin, low gonadotropin and menstral cycles, and hypothyroidism.
Posterior pituitary are axonal projections that secrete:
- oxytocin: uterine contractions and lactation
- vasopressin -> kidney water retention and arteriole contraction -> increase BP
- Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus (DI): excessive activation of hypothalamic thirst
- central DI due to low vasopressin
- Nephrogenic DI: kidneys fail to respond to vasopressin
Adrenal cortex secretes steroids and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), a testosterone or estrogen precursor.
Pancreas. Islets of Langerhans comprise 1-2% of pancreatic cells:
- Beta cells produce insulin.
- Alpha cells produce glucagon.
- Delta cells produce somatostatin.
- Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells aid digestion.
Prostaglandins like PGE1 (alprostadil) causes local vasodilation. Also causes uterus contraction when pregnant.
- PGD2 causes inflammation.
- thrombin, epinephrine, or collagen -> platelet surface receptor -> phospholipase C -> arachidonic acid.
-> cyclooxygenase COX -> prostoglandin, prostacyclin, thromboxane.
-> lipoxygenase -> leukotriene.
body mass index (BMI) approximates body fat percentage
- Obese: 30 kg/m^2
- Overweight: 25 kg/m^2
- Hydrostatic weighing measures density: fat is 0.9 kg/L and nonfat is 1.1 kg/L
- Bariatric surgery: gastric banding or gastric bypass.
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder of blood sugar regulation affecting 500 million people (9%) and causing 1.5 million deaths per year. High glucose levels are excreted in urine causing polyuria, dehydration, thirst, hunger, and weight loss. Long term, high blood sugar can lead to heart disease, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and kidney disease.
- Hyperglycemia causes diabetic coma
- Hypoglycemia or insulin shock.
- High glucose cause advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) which bind to matrix proteins and reduce wound healing, leading to diabetic foot ulcers.
Hemoglobin A1C is hemoglobin with bound glucose, which reflects average sugar levels in the past few months. 5.7% A1C is prediabetes and 6.5% A1C is diabetes (average glucose 145 mg/dL).
In diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), low insulin triggers starvation protection via lipolysis or release of fatty acids. In the liver, beta oxidation converts fatty acids to acetyl CoA, which metabolizes to acidic ketone bodies via ketogenesis. There is a risk of coma and cerebral edema due to osmotic imbalance.
Insulin pump
- Natural insulin works in 30 minutes.
- Fast-acting
- insulin lispro (Humalog, Eli Lilly, 1996). Swaps lysine (K) and proline (P) to B28 and B29 to prevent dimerization. The new order matches IGF-1.
- insulin aspart (Fiasp, Novo Nordisk, 2000) acts within 10 minutes. Absorbed twice as fast due to B28Asp (from proline).
- Long acting
- NPH insulin (Novo Nordisk’s founding drug, 1946): neutral pH, protamine, by Hans Christian Hagedorn. Protamine extends duration to 24 hours. Subcutaneous injection twice a day.
Type II diabetes is 90% of cases. The body doesn’t make enough insulin or becomes insulin resistant.
- metformin (1957). First-line treatment and the second most common medication in the US, at 90 million. Decreases liver glucose production, increases insulin sensitivity, and increases GDF15, which reduces appetite.
- semaglutide
- sitagliptin (Januvia, Merck, 2006). dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP-4) inhibitor, increasing insulin production.
- Jardiance (empagliflozin, Boehringer, 2014): most selective SGLT-2 inhibitor, blocking glucose reabsorption. Third-most sold drug.
- dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca, 2014): SGLT-2 inhibitor. Tenth-most sold.
- dulaglutide (Trulicity, Eli Lilly, 2014): glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) agonist.
Type I diabetes: the immune system attacks beta cells in the pancreas.
- Teplizumab (2022) delays the onset of stage 3 (symptomatic) diabetes. It binds to CD3 and weakly activates T cells, causing cell anergy or apoptosis. It has low affinity to Fc receptors to avoid cytokine release syndrome.
Tirzepetide better for weight loss than semaglutide, has a real indication.
Osteoporosis
- Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measures bone mineral density (BMD). Use two beams with different energy levels to subtract out soft tissue absorption.
ALS
Huntington’s disease
Reproductive system
Oogenesis forms eggs or ova
- Prenatal stage: oogonia (immature germ cells) divide into diploid primary oocytes. These are enveloped in a layer of granulosa cells to form primordial follicles. Primary oocytes arrest after meiosis I (DNA replication) but arrest before meiosis II (chromosome separation).
- Menstrual cycle begins at puberty.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates a few primary oocytes to undergo meiosis II into a haploid secondary oocyte and a tiny polar body containing discarded genetic material. The follicle granulosa cells produce estrogen which thickens the uterine lining.
- High estrogen levels trigger luteinizing hormone (LH) leading to ovulation. The mature ovum is released from the ovary. The corpus luteum (follicle remnants) produces progesterone to prepare the uterus for implantation.
- After fertilization, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis II and releases another polar body.
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF) allows preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
- Trophoblast cells around the embryo produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to ensure maternal recognition of pregnancy and maintain corpus luteum.
- hCG pregnancy strip tests.
- Some cancers produce hCG.
- Without fertilization, the corpus luteum degenerates, progesterone levels drop, and the uterine lining sheds during menstruation.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Vasodilators treat erectile dysfunction by inhibiting PDE5, preventing nitric oxide degradation. Also pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis).
Obstetrics and gynecology
- 1948. Alfred Kinsey founds the Kinsey Institute and writes the Kinsey Reports on human sexuality.
- 1966. Masters and Johnson research sexual behavior through direct laboratory observation.
- Human Sexual Response to stimulation: excitement, plateau, orgasmic, and resolution.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Human_sexuality
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Sex
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Sexual_revolution
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Sexual_orientation
Digestion and gastrointestinal
Digestion
- proteases: pepsin, trypsin, collagenase, and chymotrypsin
- Cytochrome P450 is the main enzyme involved in drug metabolism. It is a monooxygenase, adding hydroxy groups to steroids and fatty acids. It contains a heme cofactor and has peak light absorption at 450 nm.
- P-glycoprotein Pgp actively transports drugs and toxins back into the intestinal lumen, bile ducts, or proximal tubule.
GI tract or alimentary canal
- Esophagus
- Stomach: top fundus, body, and lower antrum makes mucus and ghrelin.
- Enteroendocrine cells
- G cell -> gastrin -> motility and parietal cell gastric acid (HCl).
- Stretch receptors -> vagus nerve -> enteric nervous system.
- -> gastric chief cell secretes pepsinogen and gastric lipase.
- -> parietal cells.
- -> ECL cells -> histamine -> parietal cells.
- -> lumen delta cells -> somatostatin -| parietal cell, ECL cell.
- -| antrum delta cells -> somatostatin -| G cell.
- Pylorus and pyloric sphincter
- Enteroendocrine cells
- Small intestine
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Large intestine or colon
- Cecum and appendix
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon is a 15" curved segment
- Rectum is the final 5" descending portion
- Anal canal has interior and exterior sphincters. Rectal venous plexus includes hemorrhoid cushions, which can prolapse with increased venous pressure.
- Layers
- Mucosa
- Submucosa: submucosal plexus.
- Muscularis Propia: circular and longitudinal muscle, and myenteric plexus
- Serosa or adventitia
- Biliary tract
- Liver. Major site of first-pass metabolism. Second-pass metabolism: venous blood travels through the hepatic portal vein and hepatocytes.
- Pancreas
- Bile ducts secrete bile (bile acids, bilirubin, phospholipids)
Gallbladder
Hepatic portal vein
Peritoneum is mesothelium that lines the abdominal cavity.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Peptic ulcer disease
Antacids relieve heartburn, indigestion, and upset stomach.
- Alka-Seltzer has sodium bicarbonate, citric acid for bubbles, and aspirin.
- Tums is calcium carbonate with sucrose.
H2 receptor antagonists like famotidine (Pepcid) block histamine receptors of stomach parietal cells, reducing stomach acid.
Proton-pump inhibitors like omeprazole (Prilosec) irreversibly inhibit H+/K+ ATPase.
Laxatives treat constipation.
- Bulk-forming like dietary fiber and psyllium (Metamucil) are gentlest.
- stool softeners or emollients like Docusate (dioctyl sulfosuccinate) are surfactants that add water and fat.
- Lubricants like mineral oil.
- Hyperosmotic agents like lactulose and PEG (Miralax) increase water in stool.
- nonabsorbable salines: sodium phosphate, magnesium citrate, magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia), magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt)
- stimulant: senna glycoside and the suppository bisacodyl
- castor oil is hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase to ricinoleic acid.
Antidiarrheal
- Fluid replacement: oral rehydration therapy with volume expander: electrolyte (3 g salt, 3 g sodium citrate, 1.5 g potassium chloride) and 20 g glucose.
- Normal saline is 0.9% or 9 g/L.
- Bulking agents like fiber, guar gum, methylcellulose. methylcellulose can also absorb infectious substances.
- bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) is anti-inflammatory.
Antiemetic
- 5-HT3 receptor antagonists like ondansetron (Zofran) block serotonin receptors and can cause constipation.
- gingerols, shogaols, and galanolactone in ginger
- Antihistamines can reduce nausea.
Appendicitis. A fecal blockage increases pressure, reduces blood flow, increases bacterial growth, and eventually tissue death and rupture.
Kidney
Each kidney contains 1 million nephrons. Each nephrone has a glomerulus, a network of capillaries surrounded by Bowman’s capsule. Afferent arteriole pressure filters water and solutes from the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule. Only blood proteins and cells are not filtered. Adults filter 150 L of fluid a day.
Secretes erythropoietin EPO is a glycoprotein cytokine to increase red blood cell production in the bone marrow. Increases above baseline if there is kidney hypoxia. Performance enhancing at maximal output.
Renal tubule
- Proximal tubule reabsorbs proteins and ions. It can also secrete urea and H+.
- Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 reabsorbs glucose. SGLT2 inhibitors (gliflozins) reduce blood glucose and reduce body weight but can cause ketoacidosis.
- Loop of Henle countercurrent exchange. Juxtamedullary nephrons have a long loop which penetrates deep into the hypertonic renal medulla.
- Descending limb reabsorbs water.
- Ascending limb actively pumps sodium out of the filtrate, producing hypotonic urine.
- Distal tubule uses active transport.
- parathyroid hormone: reabsorb calcium and secrete phosphate.
- aldosterone: reabsorb sodium and secrete potassium.
- atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP): secrete sodium.
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS)
- Kidney juxtaglomerular cells convert blood prorenin into renin in response to low kidney blood flow
- Renin converts liver angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
- Lung angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which converts to angiotensin III, which increases blood pressure and stimulates aldosterone secretion.
Diuretics: alcohol inhibits vasopressin secretion. Caffeine and chocolate theobromine inhibit sodium reabsorption and increase GFR.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) measured via glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Normal is GFR > 90. Kidney failure has GFR < 15, creatinine clearance < 10 mL/min, and uremia. Albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) or proteinuria is also indicative. Renal replacement therapy:
- Hemodialysis filters out urea and creatinine via IV.
- Peritoneal dialysis infuses 3 L of hyperosmotic dialysis fluid containing salt, lactate, bicarbonate, and glucose into the periteneum. After 4 hours, waste fluid is removed.
- Kidney transplant
Urinalysis: leukocyte <10/uL, nitrite, protein <30 mg/dL, pH 5-6, hemoglobin, bilirubin <0.2 mg/dL, glucose.
- Urine test strip
Urology and urinary system
- incontinence
- urinary retention
- Testicular torsion: spermatic cord cuts off blood supply causing severe pain. Treat within six hours.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Urologic_procedures
Nutrition
Malnutrition
Starvation response
Anemia
- Risk factor for restless legs syndrome
Protein: 2 g/kg/day
Vitamins
- Vitamin A, C, E antioxidants.
- Vitamin B12 is anti-inflammatory and improves immune function.
- Vitamin D deficiency in children can cause rickets: weak bones, bowed legs, stunted growth, and scoliosis.
- Zinc reduces inflammation. Brain and immune health.
- Iron helps transport oxygen.
- Soluble fiber from oat or barley has β-glucan, which decreases absorption of LDL cholesterol and reduces the risk of coronary heart disease.
- inulin can be extracted from Jerusalem artichoke.
- Lipid
- monounsaturated fatty acid: omega-9
- polyunsaturated fatty acid: omega-6
- Omega-3 for brain health.
- Liver can convert Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) -> FADS1 and FADS2 -> eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) -> docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). However, <10% of ALA is converted.
Parenteral nutrition is IV nutrition due to a blocked or nonfunctional GI tract.
- Total (TPN)
- Trace elements: zinc 3 mg, copper 0.3 mg, manganese 55 mcg, selenium 60 mcg.
FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols) can cause gas and bloating, especially in people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). They are short-chain carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and ferment in the colon.
Artificial sweeteners. In mice, saccharin, sucralose, or aspartame changed the gut microbiome and degraded glucose response (https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700). There is less data on erythritol or allulose.
Reducing sugars have a reactive carbonyl group.
- Maillard reaction (1912): sugars attack amino acids, creating brown melanoidins.
- Strecker degradation (1862) catalyzed by dicarbonyls: R-CNH2-COOH (amino acid) -> RCOH (aldehyde) + NH3 + CO2.
No-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL): highest exposure without adverse effect
margin of exposure (MOE): ratio of NOAEL to estimated human intake
Acrylamide
- https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/37f97e4d-c080-46d5-a271-0651eda8dc01/content
- BMD: benchmark dose for 10% extra tumor risk
- BMDL: 95% lower confidence limit. 0.3 mg/kg bw/d for mammary tumors in rats.
- margin of exposure of 300 based on 100 ug/day average intake.
- Fried food contains acrylamide, a probable carcinogen that reacts with DNA. Humans have a daily intake of around 1.6 ug acrylamide/kg body weight, detectable as a hemoglobin adduct (bound to hemoglobin). Surprising 1% absolute risk of cancer linearly extrapolated from rat studies.
- Acrylamide: A Cooking Carcinogen? Chem Res Toxicol 2000. Tareke (Stockholm University).
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/chemicals/acrylamide.html
- Daily intake of 100 ug acrylamide. Acrylamide caused by frying at 160 °C or microwaving until fully browned. Water in potato protects against pyrolysis from microwaving.
- Analysis of Acrylamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002. Tareke.
- 700-2300 ug/kg (ppb) acrylamide in potato chips.
- Analysis of acrylamide in cooked foods, The Analyst, 2002. Rosen (Swedish National Food Administration).
- Sugar reduces asparagine to carcinogenic acrylamide at 20 min at 160 °C, and water triples reaction rate. Potato contains 40% asparagine.
- Acrylamide is formed in the Maillard reaction, Nature 2002.
- 300 ppb acrylamide in potato chips, popcorn, french fries, veggie chips. Popchips 3000 ppb. Lay’s, Better Made 1400 ppb.
- At most 50 ppb acrylamide can be used to treat drinking water.
- https://www.epa.gov/nscep
Dry heating of animal-derived food produces inflammatory advanced glycation end-products (AGE). Glycoproteins or glycolipids activate stress receptors -> NF-κB -> inflammation.
- Mount Sinai, J Am Diet Assoc, 2010, 1k citations. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3704564/
Autoxidation is oxidation in air at standard conditions. Unsaturated fatty acids, especially polyunsaturated (PUFA), are most susceptible. Stability can be measured by induction time until rancid.
- Fresh oil has <10 mEq/kg peroxide value, while 30 mEq/kg tastes rancid.
- primary oxidation products are tasteless. Taste comes from secondary oxidation products like alcohols, acids, ketones, lactones and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Pentanal tasted at 1ppb.
- Measured by oxidizing iodide to iodine.
- Warmed-over flavor of meat: cooking releases iron from hemoglobin, which catalyzes oxidation of cell membrane lipids.
Olive oil is the most stable liquid fat. Can measure oxidation via polar compounds
- Oxidative stability of virgin olive oil, Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol 2002. 600 cites.
Canola and grapeseed have high PUFA and thus low stability. Polar compounds start to form at 180 C.
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) (1947) is an antioxidant that prevents fat from going rancid. Possible carcinogen and potential endocrine disruptor based on rat studies.
Seven Countries Study (1978): correlation between cholesterol and heart disease.
Cardiology and circulatory
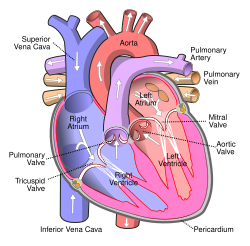
Heart wall
- Pericardium is a sac around the heart. Contains an outer connective tissue layer and an inner serous membrane which secretes serous fluid, a lubricant.
- Pericardial effusion is a buildup of pericardial fluid in the pericardium, causing cardiac tamponade (compression of the heart).
- Myocardium: muscle layer
- Endocardium: inner epithelial layer.
Circulation
- Right atrium -> tricuspid valve
- Right ventricle -> pulmonary valve -> pulmonary artery -> pulmonary vein
- pulmonary artery catheter (PAC) or Swan-Ganz catheter measures pressures.
- Left atrium -> mitral valve
- Left ventricle -> aortic valve -> aorta
- Aortic arch branches into carotid artery and subclavian artery.
- Descending aorta
- celiac artery branches into gastric, hepatic, and splenic arteries.
- two mesenteric arteries supply the intestines.
- two common iliac arteries supply the groin and legs.
- Arterioles have a layer of smooth muscle and provide the main vascular resistance, reducing pressure to the capillaries.
- Capillaries exchange water, oxygen, glucose, urea, lactic acid, creatinine with interstitial fluid. Drain into venules.
- Endothelial cells are a single layer that lines blood and lymph vessels. They from mesoderm, have vimentin filaments, and have tight junctions with CD31.
- Weibel-Palade body storage granules contain Von Willebrand factor (VWF) and P-selectin which promote platelet adhesion.
- Superior vena cava drains the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm
- Internal jugular vein drains the brain.
- Subclavian vein drains the axillary vein (arms) and the external jugular vein.
- Venous access: central venous catheter delivers pressors or other therapies.
- Inferior vena cava. Common iliac veins drain the lower half of the body, including the femoral vein in the groin.
Conduction system and electrocardiogram ECG or EKG
- sinoatrial node at the top of the heart contains pacemaker cells.
- P wave: atrial depolarization and contraction. Bundle of His carries the action potential through the right atrium to the atrioventricular AV node near the center. Bachmann’s bundle carries signal to the left atrium.
- PR interval: AV node delays signal.
- QRS complex: ventricular depolarization. Bundle branches and Purkinje fibers carry signal. Atrial repolarization also occurs but is masked.
- ST segment: ventricular contraction. Isoelectric or flat at baseline.
- elevated ST segment can indicate a heart attack
- depressed ST segment can indicate ischemia
- T wave: ventricular repolarization.
- 12-lead ECG with 10 electrodes: right arm, left arm, right leg, left leg, and V1-6 across the chest. V1-2 are septum leads. V3 and V4 at the anterior wall. V5 at left anterior axillary (armpit) line, V6 at the mid-axillary line.
- Wilson’s central terminal averages RA, LA, and LL.
- Cardiac stress test on a treadmill.
- VO2 max is 80 mL/(kg min) in elite athletes.
- Multi-stage fitness test, beep test, or PACER test (progressive aerobic cardiovascular endurance run)
Cardiac action potential
Blood pressure
- systolic: highest pressure on the artery walls when the ventricles contract (systole). Top reading. 120 mm Hg is normal.
- diastolic (bottom): lowest pressure when the ventricles relax (diastole). 80 mm Hg is normal.
- Blood pressure cuff (sphygmomanometer) and stethoscope.
- Compresses the brachial artery in the elbow.
- Initially fully blocks blood flow. Deflate at 3 mm Hg/s.
- Systolic pressure: first sound heard, caused by turbulent flow of blood.
- Diastolic pressure: last sound heard, when the artery is fully open.
Blood content
- Red blood cells (RBC) do not have a nucleus and have 200 million hemoglobin molecules. Humans produce 500 billion blood cells each day.
- Platelets are sticky cytoplasm fragments used in blood clots.
- Plasma proteins: albumin, glycoprotein, lipoprotein.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) speeds up tissue repair and reduces inflammation. Used for tendon injuries, such as tennis elbow and achilles tendonitis, as well as ligament and muscle injuries.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arterial_blood_gas_test
Vasopressors treat low blood pressure: sympathomimetics, corticosteroids, vasopressin, angiotensinamide. Also positive inotropic agents:
- PDE3 inhibitors: amrinone, enoximone, milrinone.
- Cardiac glycosides inhibit the sodium-potassium pump: digoxin

Coagulation cascade
- Hemostasis prevents bleeding via vasoconstriction, a temporary platelet plug, and coagulation into a thrombus (fibrin mesh clot).
- Extrinsic pathway: tissue factor (III) or thromboplastin is a glycoprotein found outside of blood vessels. Upon vessel injury, tissue factor activates factor X. Tissue factor binds factor VII, which converts to VIIa, a serine protease.
- Intrisic amplification pathway: contact activates factor X.
- prothrombinase cleaves prothrombin to thrombin (IIa). It is a complex of factor Xa and its cofactor, factor Va, which assembles on negatively charged phospholipid membranes in the presence of calcium.
- thrombin polymerizes liver fibrinogen to fibrin (Ia).
- tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) inhibits Xa.
- Endothelial cells produce tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), a serine protease that cleaves plasminogen to plasmin. Plasmin breaks down clots (fibrinolysis). Alteplase or Activase by Genentech is recombinant TPA.
- Wound healing: hemostasis, inflammation, tissue growth, and tissue remodeling.
An embolism is a blood clot or other blockage.
- Pulmonary embolism blocks the pulmonary artery.
- Migrates from a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the legs.
Atherosclerosis is narrowing of arterial walls from atheromatous plaque.
- Simvastatin (Zocor, 1992) is a statin that lowers lipid levels.
- Coronary artery disease is a decrease in blood flow in the coronary arteries.
- Myocardial infarction or heart attack is tissue death.
- ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI): complete block
- NSTEMI: partial block. Can show ST segment depression or T wave inversion.
Shock is insufficient circulation to the tissues.
- Obstructive shock is a physical obstruction in blood flow.
- Cardiogenic shock: inadequate blood flow to the heart.
- heart attack or injury.
- Hypovolemic shock from bleeding, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Distributive shock with normal cardiac output. Septic shock, anaphylactic shock, neurogenic shock (decreased sympathetic stimulation), systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
- FAST: focused assessment with sonography in trauma
Cardiac arrest: heart stops.
- automated external defibrillator (AED)
- Targeted temperature management (TTM) or protective hypothermia. Shivering reflex at 36 °C. Metabolism slows by 5% per degree Celsius.
Heart block: block in heart electrical conduction causing arrhythmias.
Hypertension: blood pressure above 160 / 100 mmHg.
- DASH diet: Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension.
- ACE inhibitors relax blood vessels: lisinopril.
- Angiotensin II receptor blocker: losartan.
- Calcium channel blockers reduce contraction: amlodipine.
Congestive heart failure: weaker heart muscle does not pump blood effectively. Causes shortness of breath, fatigue, and leg swelling.
- sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto, Novartis, 2015).
- Sacubitril -| neprilysin -| natriuretic peptides -> sodium excretion -| ECF volume. Also neprilysin -| adrenomedullin (vasodilator).
- Valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist.
Coronary artery disease involves cardiac ischemia due to buildup of atherosclerotic plaque. Causes angina and myocardial infarction.
- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG or cabbage) restores blood supply.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) deploys a coronary stent through a peripheral artery in the thigh in a catheterization lab.
Arrhythmia
- missed or extra beats
- supraventricular tachycardia
- atrial fibrillation
- ventricular arrhythmia
- bradyarrhythmia
- Antiarrhythmic
- Procainamide is a sodium channel blocker with a small therapeutic window.
- Amiodarone blocks voltage-gated potassium and calcium channels, slowing conduction rate and prolonging the refractory period.
Aortic aneurysm is dilation by 50%. Rupture kills 15,000 Americans per year.
Anticoagulant
- heparin increases antithrombin activity for unstable angina.
- Protamine sulfate 1969 binds with heparin, reversing its activity before surgery.
- warfarin prevents deep vein thrombosis and embolism. Requires monitoring prothrombin time (INR) every four weeks.
- apixaban (Eliquis, BMS, 2012) prevents stroke. No need to monitor. Most sold drug, $9B/year.
- rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer, 2011) prevents deep vein thrombosis and embolism. Blocks clotting factor Xa.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is a pediatric heart defect. The ductus arteriosus is opening between the aorta and pulmonary artery. It is normally open in the womb to allow blood to bypass the lungs, but it should close within a few days. If it stays open (patent), it can cause breathing problems or heart murmur (a whooshing sound caused by abnormal blood flow). It is treated by inserting a catheter through a peripheral artery up to the PDA and using it to place a plug to fill the PDA.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/patent-ductus-arteriosus-pda
Cardiopulmonary bypass circulates blood during heart surgery.
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) provides prolonged cardiac and respiratory support during cardiac arrest.
Raynaud syndrome: fingers turn white or blue when cold due to sympathetic hyperactivity. 4% prevalence.
Amyloidosis: amyloid fibril buildup causes nonspecific symptoms.
- Wild-type transthyretin amyloid (WTTA) or senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA) is the primary cause of death for most supercentenarians.
- Transthyretin amyloidosis is due to a mutation. tafamidis (Vyndaqel, 2019) stabilizes transthyretin.
Lung respiratory pulm
Respiratory tract
- Nasal cavity: nostrils open into the fossae cavities. Divided by the nasal septum. Nasal concha or turbinates send air to the olfactory epithelium.
- Olfactory epithelium contains bipolar olfactory receptor neurons which express odor receptors. 3 in behind the nostrils.
- Pharynx connects to the larynx (laryngeal inlet) and esophagus.
- Epiglottis prevents aspiration of food into the lungs.
- Larynx is the voice box, which opens into the trachea.
- laryngeal skeleton surrounds the trachea
- Cricoid cartilage is the only one that fully encircles the trachea
- Thyroid cartilage is the largest. Includes the Adam’s apple.
- Trachea or windpipe branches into the bronchi and bronchioles. Bronchioles are 1 mm diameter. Cilia to remove mucus and irritants.
- Alveoli or air sacs for gas exchange. Emphysema is enlarged alveoli.
The pleurae are two layers of serous (smooth tissue) membrane around each lung.
- Pneumothorax or collapsed lung is air in the pleural space. Typically involves sharp chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Tension pneumothorax if it forms a one-way valve putting pressure on the lungs.
- Thoracentesis removes fluid or air from the pleural space using a cannula (hollow needle).
Breathing decreases carbon dioxide concentration.
Inhalation reduces chest cavity pressure, drawing blood into the lungs.
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: inhalation increases heart rate.
- Also, deep, slow breathing can temporarily lower blood pressure
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): shortness of breath or cough due to bronchitis or emphysema.
Sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) where the airway is blocked by tonsils or soft palate. Causes snoring and hypoxia causing excessive daytime sleepiness. Obesity is a risk factor. Central sleep apnea involves a loss of breathing effort.
Respiratory failure causes hypoxemia (arterial PaO2 < 60 mmHg) or hypercapnia (PaCO2 > 50 mmHg).
- Monitor with pulse oximetry
- supplemental oxygen therapy via via nasal cannula, face mask, or endotracheal intubation.
- Mechanical ventilation with a ventilator
Cystic fibrosis: accumulation of thick mucus in the lungs.
- Caused by a recessive mutation in the CFTR protein.
- Trikafta (elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor). Fourth most-sold drug.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF): nintedanib (Ofev, Boehringer, 2020)
Orthopedics and musculoskeletal system
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Fibroblasts produce ECM and antiviral IFN-β. Critical for wound healing.
- Collagen and elastin fibers
- Lubricating ground substance with water-absorbing glycosaminoglycans (GAG) like hyaluronic acid, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and chondroitin sulfate.
- Extracellular fluid (ECF).
Connective tissue: blood and lymph from mesenchyme.
- Dense connective: regular oriented collagin fibers in tendons and ligaments. Irregular is not oriented.
- Loose connective
- Fat or adipose tissue.
- Adipocytes store energy and secrete leptin, estrogen, resistin, and inflammatory TNF-α.
- White adipose tissue have one big lipid droplet.
- Brown adipose tissue: non-shivering thermogenesis. Darker due to iron from mitochondria needed to burn fatty acids. Thermogenin uncouples ATP synthesis from the production of protons.
- Reticular connective tissue has type III collagen. Mononuclear phagocyte system.
- Fat or adipose tissue.
- Cartilage
- Chondrocytes produce cartilage.
- Hyaline Cartilage: Type II collagen fibers. Hyaline means glass-like.
- Elastic Cartilage in ear, epiglottis, and larynx. Has elastic fibers.
- Fibrocartilage: shock absorber. Type I collagen fibers.

Joint
- A synovial joint joins bones with a fibrous joint capsule continuous with the bone periosteum. Filled with lubricating synovial fluid. Most common joint.
- A cartilaginous joint or synchondrosis allows limited movement.
- A fibrous joint or synarthrosis is immobile. Consists of fibrous tissue.
- Ligaments are collagen fibers that connect bones and stabilize joints.
- Tendons connect muscle to bone.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Joints
Soft tissue injury
- sprained ligament.
- Sprained ankle
- strained muscle or tendon
- Ergonomics to improve posture and prevent Repetitive strain injury (RSI) and tendinitis
- computer vision syndrome and eye strain (asthenopia) of ciliary muscles and extraocular muscles
- pulled hamstring
- joint dislocation like dislocated shoulder: X-ray diagnosis, and reduction to its normal position quickly to restore blood flow.
- Achilles tendon rupture: surgical sewing or rehab.
- RICE: rest, ice, compression, elevation. Rest delays healing. Ice constricts vessels and delays healing.
- Immobilization with a splint, bandage, cast, or walking boot. Surgical wires, nails, screws, rods, or plates in severe cases.

Bone tissue
- Osteoblasts build bone. Produce hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate), collagen, osteocalcin, and osteopontin.
- Osteoclasts consume bone. Derives from HSC and fuses into big multinucleated cells.
- Osteoblasts, T cells, and macrophages -> RANKL (TNF family) -> RANK -> osteoclast differentiation and activation.
- An osteon is a unit of bone, 3 cm diameter. A central Haversian Canal with nerves and blood vessels is surrounded by up to 20 lamellae or bone rings.
- Osteocytes are mature osteoblasts. They live in lacunae, small spaces in the lamellae, which interconnect via canaliculi. Humans have around 40 billion.
- Compact bone or cortical bone is dense and hard.
- Spongy bone or cancellous bone. Lattice of trabeculae (“small beams”). High surface area.
- Bone marrow produces blood cells. 5% of body weight.
- Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) increases in osteoporosis and obesity.
- Periosteum membrane covers the outer surface of all bones
- Adults have 206 bones. Femur is the largest and stapes is the smallest.
- Bone fracture
- avulsion fracture
- a comminuted fracture is broken into fragments.
Muscle
Muscle tissue
- Skeletal muscle: voluntary control, long muscle fibers, a third of body weight.
- Cardiac muscle cells are joined by intercalated discs, with gap junctions to allow a wave of depolarization. Some autorhythmic cells are pacemakers which do not contract. Rest are contractile cardiomyocytes.
- Smooth muscle is non-striated, without sarcomeres. The whole muscle contracts. Many gap junctions between cells to propogate action potential.
- Myocytes are 2 cm long multinucleated cells, 100 μm in diameter, and surrounded by the sarcolemma cell membrane. MSC-derived.
- Myogenesis is the fusion (syncytium) of myoblasts.
- Myocytes contain myofibrils, long chains of sarcomeres.
- Muscle consists of fascicles, bundles of muscle fibers. Each fiber is surrounded by fascia connective tissue.

- Sarcomeres are the basic contractile unit:
- Very dark Z line at the ends.
- Isotropic I band near the ends is lighter with mostly actin.
- Anisotropic A band is darker with mostly myosin. H zone in the center has no actin/myosin overlap and has the dark M-line in the middle.
- Myofilament consists of:
- Thick filaments of myosin II motor protein, 15 nm in diameter.
- Thin filaments of actin, tropomyosin, and troponin.
- Elastic filaments of titin anchor thick filament to the Z line.
- Excitation-contraction coupling
- Axon terminal releases acetylcholine across the synaptic cleft, which depolarizes the sarcolemma causing an action potential across the muscle fiber.
- T-tubules are folds in the sarcolemma at the Z-line that extend deep into the muscle cell. They carry the impulse via dihydropyridine receptors (DHPR), voltage-gated calcium channels. T-tubule associates closely with two terminal cisternae (sacs) of the SR.
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) releases calcium ions via ryanodine receptors, causing muscle contraction.
- Summation: when another action potential arrives before the complete relaxation of a muscle twitch, then more fibers will fire, and larger motor units will activate, which can produce 50x more force.
- Tetanus is sustained contraction due to high rate of motor nerve stimulation.
- In muscle relaxation, acetylcholinesterase removes stimulation. Active transport moves calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

Sliding filaments and the crossbridge cycle.
- Binding of ATP detaches the pair of myosin heads from actin.
- Myosin hydrolyzes ATP and moves to cocked position, which weakly binds actin, with the rest of the binding site blocked by tropomyosin.
- Calcium ions bind troponin C on the actin, moving the tropomyosin to expose myosin binding sites on actin.
- Power stroke: myosin pulls with 2 pN force and releases the phosphate. Thick filaments slide in.
Cramps are caused by lactic acid buildup, possibly from low water or salt.
Neuromuscular diagnostics
- Electromyography
- Evoked potential
Electrical muscle stimulation prevents atrophy.
Microcurrent electrical neuromuscular stimulator (MENS)
Anatomy
intrinsic, extrinsic, and stabilizing and rotating muscles
Dental
Mandible lower jaw
Maxilla is the fixed upper jaw
Tooth: white enamel, dentin, pulp and root canal with nerves and blood vessels.
Gums or gingiva surround the teeth
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gunshot_wound#Neck
Clavicle or collarbone is the only horizontal long bone.
Shoulder blade is a flat bone at the back.Deltoid muscle on the shoulder.
Rib cagesternum is a long flat bone which connects to the ribs via cartilage.
- the xiphoid process is the tip of the sternum
12 ribs with intercostal spaces in between.
Leggastrocnemius muscle in the back of the lower leg.
Physical therapy PT
cardio, strength, mobility
Core: proximal stiffness enables distal athleticism.
Short walk every hour.
Twice per day.
Curl with one knee bent, 2 sides x 5x10 s. Hands under back for lumbar support. Strengthens the front of the spine.
side plank 60 s. strengthens the quadratus lumborum and oblique muscles.
bird dog, 2 sides x 10 reps x 10 s. strengthen small lumbar muscles behind the spine.
superman
Ultimate Back Fitness and Performance: suitcase carry and bottoms-up kettlebell carry.
Lumbar Instability: excessive movement between two vertebrae
Prone Instability Test: check for weak stabilization. Apply pressure to vertebra and check for pain in resting position.
Dermatology and skin
Skin layers
- Epidermis
- rete pegs project into the papillary dermis.
- Basement membrane
- Dermis
- papillary dermis has fingerlike dermal papillae with capillaries or tactile Meissner’s corpuscles (fingerprints).
- reticular dermis
- Subcutis
mucous membrane or mucosa: epithelium, basement membrane, lamina propria (dermis analogue), and muscularis mucosa (GI smooth muscle).
- Goblet cells secrete mucins.
Adnexa or appendages
- Eccrine sweat gland
- Sebaceous or oil gland secretes lubricating sebum.
- Hair follicle
- Matrix produces the actual hair and the skin root sheath
- Hair shaft consists of medulla, cortex, and cuticle.
- Vellus hair (“peach fuzz”) and thick terminal hair.
- Arrector pili muscle causes goose bumps
Widow’s peak: a sharp dip in the hairline in the center of the forehead.
Ear, nose, and throat ENT
Audiology
- Cochlear implant directly stimulates the auditory nerve.
Immune system
Lymphatic system
- Spleen.
- White pulp (25%) makes antibodies.
- periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths (PALS). T cells surround central arteries.
- Lymph follicles: B cells make IgM and IgG2 which opsonize bacterial capsules.
- Marginal zone contains APCs.
- Red pulp (75%). Macrophages remove aged blood cells and pathogens.
- Efferent lymph vessels with filtered lymph.
- White pulp (25%) makes antibodies.
- Thymus behind the sternum in front of the heart. Efferent lymph vessels with filtered lymph.
- Lymph nodes. Lymph filter lymph via afferent and efferent vessels.
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) for mucosal immunity
- Microfold cells uptake antigens to antigen-presenting cells.
- Tonsils: adenoid, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. Swell during infection.
- Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
- Peyer’s patches in the small intestine
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) produce blood cells in red bone marrow.
- Differentiates into CLP and common myeloid progenitor (CMP). The latter differentiates into RBC, platelets, and myeloblasts.
- Derives from angioblastic mesenchyme.
- Express CD34+, a cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein.
White blood cells or leukocytes. Includes lymphocytes.
- Myeloblasts becomes monocyte and granulocyte.
- Monocyte: antigen-presenting cells. Largest cells.
- Macrophages are phagocytes. They digest pathogens and cellular debris and promote inflammation and healing.
- IFN-γ and TLR ligands -> M1 phenotype -> inflammatory IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6. Metabolizes arginine to nitric oxide.
- IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, TGF-β -> M2 phenotype -> anti-inflammatory IL-10, TGF-β, IL-4. Also IGF-1 for healing. Metabolizes arginine to ornithine.
- Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) creates macrophages.
- Tumor-associated macrophages promote tumors and inflammation.
- Adipose tissue macrophages are almost half of all immune cells.
- Liver Kupffer cells and tissue histiocytes.
- Dendritic cells present antigens to T cells. Found in epithelial tissue.
- Langerhans cells are immature dendritic cells in the skin.
- Macrophages are phagocytes. They digest pathogens and cellular debris and promote inflammation and healing.
- Granulocyte contain specific granules, secretory vesicles with cytotoxic enzymes and antimicrobial peptides. Mostly characterized by stain.
- Neutrophils are phagocytes. They contain alkaline phosphatase, lactoferrin, lysozyme, NADPH oxidase, and myeloperoxidase (MPO).
- Eosinophils contain cathepsin and major basic protein.
- Basophils contain heparin and histamine.
- Mast cells contain heparin and histamine.
- Colony-stimulating factor (CSF) increases white blood cell production.
- Many cells express Fc receptors such as CD32, which binds to antigen-antibody complexes.
- Fas ligand is a transmembrane protein which binds with Fas receptor (CD95) to cause apoptosis.
- Immune cells produce IL-25, which activates NF-κB and IL-8.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interleukin
Lymphocytes
- Common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) migrates to lymphoid organs, where they differentiate into ILC and T cells.
- Cellular immunity
- Type 1: intracellular microbes
- NK, ILC1, Th1 produce IFN-γ and TNF, which activates macrophages. Also IL-22 which promotes proliferation and wound healing, as well as antimicrobials like S100 and defensins.
- ILC1 and NK cells differentiate via IL-15.
- Type 2: extracellular parasites like helminths.
- Th2 activate B cells which mediate type 2 inflammation. Differentiates via IL-4 and produces IL-4. IL-4 promotes M2 tissue repair.
- ILC2 and ILC3 differentiate via IL-7.
- IL-13 is the main regulator for allergic inflammation and asthma. Activates STAT6. Causes mucus production and wound repair.
- IL-5 activates eosinophils and increases B cell IgA.
- Type 3: phagocytosis of extracellular microbes via ILC3.
- Type 1: intracellular microbes
- Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) CD127+
- Natural killer (NK) cells (CD56+, CD3-) are granular and kill infected or cancerous cells.
- T cells recognize and kill cancer.
- Helper T cells (CD4+) kill infected or cancerous cells. Secrete cytokines.
- CD4 binds to MHC as a coreceptor of the T cell receptor complex and recruits the Lck kinase which phosphorylates CD3 immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs), and the Lck SH2 domain binds ZAP-70, which becomes phosphorylated and activates the T cell.
- Th cells activate APCs via CD40.
- Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+) kill infected or cancerous cells by apoptosis.
- Activated T cells -> IL-2 -> T cells multiply, B cells produce antibody.
- Regulatory T cells (Treg, CD4+) suppress autoimmunity, producing inhibitory cytokines TGF-β, IL-10 (Jak1 and Tyk2), IL-35. They express FOXP3 master regulator.
- Memory T cells live for many years.
- Central memory T cells T_CM live in the lymph nodes and spleen. They proliferate into many effector T cells upon re-exposure to antigen.
- Effector memory T cells T_EM in skin and lungs can directly attack the pathogen.
- Helper T cells (CD4+) kill infected or cancerous cells. Secrete cytokines.
- T cells develop in the thymus
- Start as immature T cells or thymocytes. 2% mature and the rest die.
- β-selection: make new T cell receptors via V-D-J recombination until it forms a functional TCR β-chain.
- Positive selection ensures it can bind MHC.
- Central tolerance is negative selection of self-reactive B and T cells.
- Mature as naive T cells, which are activated by APCs into cytotoxic or helper cells in the thymus and lymph nodes.
- MHC: major histocompatibility complex presents antigens to T cells.
- MHC class II is expressed in antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as monocytes and B cells.
- MHC class I or human leukocyte antigen (HLA) is expressed in all cells and presents cytosolic protein fragments for T cell receptor.
- B cells (CD19+) produce antibodies to destroy pathogens. In bone marrow, naive B cells have IgD dimers that recognize antigens and also activate basophils and mast cells.
- Plasma cells secrete antibodies.
- Immunoglobulin class switching changes the constant region, while the variable region stays the same.
- Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL)
- CAR-T immunotherapy harvests T cells and infuses them with added chimeric antigen receptor against cancer.
- CD38 expressed on B cells and natural killer cells.
- Binds to CD31 on T cells, causing them to produce cytokines.
- Binds to CD31 on endothelium.
- Catalyzes NAD+ -> ADP ribose, which is calcium-releasing.
Immunity
- Humoral immunity is based on molecules in blood and lymph
- Innate immune system is nonspecific: skin and mucous membranes, inflammatory responses, complement system, antimicrobial cathelicidin and defensin, phagocytes, granulocytes, innate lymphoid cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes.
- Toll-like receptors recognize conserved pathogen features like LPS, flagellin, dsRNA, unmethylated CpG islands. Pattern recognition receptors were the first immune system to evolve.
- Dying cells release damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) or alarmins, which promote inflammation.
- Defensins are small cationic peptides that disrupt negatively charged microbial membranes, attract immune cells, and promote macrophage phagocytosis. β-defensin is widespread. α-defensin in neutrophils and small intestine.
- Plasmacytoid dendritic cells secrete high IFN-α against viruses.
- CD14 and LPS-Binding Protein help detect LPS.
- Endotoxin or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) forms the cell envelope of Gram-negative bacteria. Consists of lipid A and O-antigen, a long glycan.
- Adaptive immune system: antibodies and lymphocytes.
Complement system.
- Classical complement pathway: one IgM or several IgG antibodies bind to an antigen, forming a C1 complex, which generate C3 convertase which cleaves the component 3 protein. C3b binds to C3 convertase to generate C5 convertase which cleaves C5. These assemble the membrane attack complex (MAC), creating a pore on the target cell membrane. They also act as opsonins which activate phagocytes.
- Alternative complement pathway: C3b directly binds a microbe and generates alternative C5 convertase.
Antibodies
- Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins with a crystallisable fragment Fc base and two antigen-binding fragments Fab. They consist of two heavy chains (spanning both Fab and Fc) and two light chains (Fab only) connected by disulfide bonds.
- Antibodies are produced by B cells through V(D)J recombination. B cell observe allelic exclusion, where each B cell produces only one type of variable chain. B cells proliferate rapidly when activated by antigen, and undergo somatic hypermutation of about one mutation per variable gene per cell division. In affinity maturation, B cells with lower affinity die by apoptosis.
- V(D)J recombination: RAG1 endonuclease excises DNA. Cuts are joined in a hairpin, and the Artemis protein complex ligates the cut DNA. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) adds random nucleotides without a template.
- IgA is the main antibody in mucus. It agglutinates and neutralizes pathogens, preventing adhesion to the mucus.
- IgG is the most abundant antibody, at 10 g/ml. It provides long-term immunity and takes several weeks to emerge. It can activate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
- IgM is the first antibody produced in response to a new infection, active within days. It is pentameric and agglutinizes pathogens. It also activates the complement system and opsonizes pathogens, activating phagocytes.
- IgE triggers the allergic response, via histamine release from mast cells. It is least abundant.
- The ABO gene encodes a glycosyltransferase that modifies red blood cell surface proteins, which determines ABO blood type.
Hygiene hypothesis: early childhood exposure to microorganisms improves immune tolerance and prevents allergies.
Anaphylaxis
Antihistamine
- First-generation: diphenhydramine (DPH, Benadryl), promethazine, and doxylamine are sedative. Chlorpheniramine is less sedative.
- Second-generation is selective for peripheral receptors. Cetirizine (Zyrtec), fexofenadine (Allegra), loratadine (Claritin), acrivastine
Rheumatoid arthritis
- TNF inhibitor. Infliximab or Remicade (1998), Adalimumab or Humira (2002), and golimumab or Simponi suppresses inflammation. Etanercept or Enbrel (1998) is a decoy TNF receptor that reduces TNF levels.
- glucocorticoid: dexamethasone
- upadacitinib (Rinvoq, 2019): JAK inhibitor
Celiac disease: allergy to gluten found in wheat, barley, and rye.
- dermatitis herpetiformis rash
ulcerative colitis
Crohn’s disease
- Mesalazine (1987)
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease. An inflammatory cascade causes white blood cells to move from the dermis to the epidermis and release cytokines such as interleukins and TNF-α. The cytokines cause keratinocytes to proliferate and skin cells to be replaced every 3-5 days rather than the normal 28-30 days, resulting in the formation of well-defined, erythematous (red) plaques with silvery scales usually on the elbows, knees, and back. Stress can worsen symptoms.
- Deucravacitinib is a tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor. Three hydrogen atoms are replaced by deuterium on an amide methyl group.
- ustekinumab (Stelara, Janssen, 2009) blocks IL-12 and IL-23.
Dermatitis or eczema affects 10% in the US.
- atopic dermatitis: itchy red patches.
- Dyshidrosis: small clear itchy vesicles on the fingers that disappear in a few weeks. 1% incidence.
sarcoidosis forms granulomata (clumps of macrophages)
asthma
alopecia
vitiligo
rosacea
acne
- antibacterial or exfoliating: benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, salicylic acid (keratolytic). glycolic acid is more gentle.
- retinoids speed cell turnover: adapalene, retinol. In some night creams. Isotretinoin (Accutane) is strongest with serious side effects.
- avoid coconut oil and cocoa butter, which are comedogenic and clog pores.
dandruff
Sunscreen should be broad-spectrum and SPF 30 or more. Reapply every two hours.
- Chemical: oxybenzone and octinoxate
- Physical: titanium dioxide and zinc oxide.
Moisturizers: hyaluronic acid, ceramides, petroleum jelly. CeraVe and Cetaphil.
Infectious disease
Infection can cause fever and enlarged lymph nodes.
Bloodstream infection diagnosed with blood culture.
Sepsis or septic shock is when infection triggers systemic inflammation and coagulation, which can lead to hypovolemia, hypoperfusion, and organ failure.
Antifungal treats Candida, etc.
- Polyenes disrupt the cell membrane by binding to ergosterol. Amphotericin B is IV (poorly absorbed) and hurts kidneys. Nystatin is topical.
- Azoles inhibit ergosterol synthesis by lanosterol 14α-
demethylase.- Imidazoles like ketoconazole, miconazole, clotrimazole treat topical infections like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and vaginal yeast infections.
- Triazoles like fluconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole are more potent.
- Terbinafine is an allylamine that inhibits synthesis of squalene, an ergosterol precursor. Butenafine is a similar benyzlamine. Topical.
- Echinocandins inhibit synthesis of beta-glucan, a cell wall component.
- Intracellular action
- Griseofulvin (1939) binds to tubulin and treats ringworm.
- Flucytosine (1957) is a pyrimidine analogue and thymidylate synthase inhibitor.
- selenium sulfide is keratolytic, interfering with hydrogen bonds and loosening skin flakes. It is antimitotic, decreasing epidermal cell turnover.
- Whitfield’s ointment is 3% salicylic acid and 6% benzoic acid.
Antihelminthics treat parasitic worms.
- Mebendazole, Praziquantel (1982).
Protozoan infections
- metronidazole (1960) and tinidazole
- Pyrimethamine treats toxoplasmosis
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protozoan_infection
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_parasites_of_humans
Viruses
HIV/AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus) is a retrovirus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). It uses CCR5 and CD4 receptors to infect T cells. CCR5 is a chemokine receptor, which signals the T cell to migrate to sites of infection.
- Emtricitabine/tenofovir (Truvada, 2004). Emtricitabine is a cytidine analogue. Multiple drugs = highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).
- Efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir (Atripla, 2006). Efavirenz (by BMS) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
- Elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir (Quad pill, Gilead, 2012). Elvitegravir is an HIV integrase inhibitor. Cobicistat inhibits cytochrome P450 3A4 and intestinal transport proteins that metabolize elvitegravir.
- Bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir (Biktarvy, Gilead, 2018). Second-most sold retail drug.
- dolutegravir (Tivicay, GSK, 2013). Eleventh-most sold retail drug. HIV integrase inhibitor.
Antiviral
- DNA virus
- dsDNA: herpes simplex and shingles.
- Purine analogue: valacyclovir and aciclovir. Inhibits DNA synthesis when activated by thymidine kinase (TK).
- dsDNA: herpes simplex and shingles.
- Retrovirus
- Hepatitis B
- Tenofovir (Viread, 2001) is an adenosine analogue that inhibits reverse transcriptase.
- Entecavir (Baraclude, 2005) is a deoxyguanosine analogue that inhibits reverse transcriptase.
- Hepatitis B
- RNA virus
- Flu: Tamiflu (seltamivir, 1999) is an oral neuraminidase inhibitor. Neuraminidase cleaves host sialic acid. Inhibition prevents release of viral particles.
- Hepatitis C
- Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi, Gilead, 2013) is a nucleotide analogue that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase NS5B. Replaced IFN, which causes fever side effects.
- ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni, 2014). Ledipasvir inhibits NS5A.
- ProTide delivers nucleotide prodrugs into the cell
- Daclatasvir inhibits replication via NS5A.
Bacteria
Impetigo: yellowish crusts on the skin caused by staph or strep.
Protein synthesis inhibitors.
- 30S
- Tetracycline is a polyketide that bind tRNA. Doxycycline, minocycline.
- Aminoglycosides inhibit protein synthesis initiation in Gram-negative bacteria. Contain an amino-modified glycoside.
- Streptomycin was the first antibiotic active against tuberculosis. Neomycin (1952). Neosporin is neomycin/polymyxin B/bacitracin triple ointment. Gentamicin.
- 50S
- Macrolides bind to the ribosome and inhibit translation.
- azithromycin and clarithromycin
- erythromycin
- Clindamycin is used for acne and other infections. It is ineffective against most aerobic Gram-negative bacteria. Technically a lincosamide.
- Linezolid blocks initiation of protein synthesis.
- chloramphenicol binds to the bacterial ribosome and inhibits peptidyl transferase activity.
- Macrolides bind to the ribosome and inhibit translation.
- Fusidic acid (1962) binds to and prevents release of elongation factor G (EF-G) from the ribosome.
- mupirocin (1971) inhibits isoleucine-tRNA ligase.
Cell wall and envelope.
- Beta-lactams inhibit penicillin-binding proteins (PBP). PBP is a transpeptidase crucial for crosslinking in peptidoglycan layer synthesis.
- Penicillin. Augmentin is penicillin and clavulanic acid, a β-lactamase inhibitor. Second-generation like oxacillin is β-lactamase resistant. Amoxicillin and ampicillin are third generation. Piperacillin/tazobactam adds a β-lactamase inhibitor.
- Cephalosporins like ceftriaxone: first generation like cefalexin targeted gram-positive cocci, while newer generations like ceftaroline targets extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing gram-negative bacteria.
- Carbapenems are reserved for multidrug-resistant (MDR) infections. Imipenem and meropenem for hospital-acquired pneumonia and ertapenem for abdominal infections.
- Bacitracin inhibit bactoprenol, which carries peptidoglycan building blocks outside the inner membrane.
- Vancomycin and teicoplanin are glycopeptides that inhibits peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase chain elongation. Last resort for serious antibiotic-resistant Gram-positive infections.
- Isoniazid inhibits mycolic acid synthesis in mycobacteria like tuberculosis.
Inhibit nucleic acids
- Fluoroquinolones inhibit topoisomerase ligase activity, causing breakdown of DNA: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin.
- Antifolates: folate is needed to make thymine.
- 1932. Sulfonamides like sulfadiazine inhibit dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). Gerhard Domagk wins the 1939 Nobel Prize for prontosil.
- Trimethoprim or Bactrim (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (DHRI).
- Rifampicin, rifapentine, and rifabutin treat tuberculosis by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
- Only work when reduced, in anaerobic bacteria:
- Metronidazole forms nitroso radicals which disrupt DNA synthesis
- Nitrofurantoin attacks DNA.
Oncology
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemotherapy#Treatment_strategies
Immune checkpoints suppress immune activity, and immune checkpoint inhibitor drugs improves immune activity against cancers.
- PD-1 inhibitors target the programmed cell death protein. Cancer cells express the ligand PD-L1.
- Nivolumab (2014) treats melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urothelial carcinoma, colon cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, and gastric cancer.
- Pembrolizumab or Keytruda (2014) treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer.
Tumor angiogenesis. Tumors release vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) digest the extracellular matrix to make room. PDGF recruits blood vessel support cells.
- Metaplasia: replacement of one mature cell type with another mature cell type, often in response to chronic irritation, such as squamous metaplasia in smokers
- Hyperplasia: abnormal increase in number of cells
- Dysplasia: abnormal cell size, shape, or organization
- Neoplasm or tumor: uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells
- benign neoplasm
- in situ neoplasm: neoplasm with cells growing in their normal place
- cancer or malignant neoplasm
Types
- Blood
- Lymphoma incl. Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Leukemia
- myeloma: proliferation of clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow
- lenalidomide (Revlimid, BMS, 2006) is first line.
- pomalidomide (Pomalyst, 2013) inhibits angiogenesis.
- Carcinoma: epithelial cells
- Endocrine cancer
- Head, oral, sinus, nasal, neck
- Esophageal, gastric, colon cancer, rectal, anal
- Gastrointestinal stomach tumor (GIST)
- pancreatic, liver, bile duct, gallbladder
- Lung cancer
- osimertinib (Tagrisso, 2015) EGFR TKI for non-small-cell lung carcinoma.
- Breast cancer
- Gynecologic: cervical, vaginal, vulvar, uterine, endometrial
- BRCA+ ovarian cancer: olaparib (Lynparza, 2014) inhibits poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), which is involved in DNA repair.
- germ cell tumor like seminoma: pluripotent cells
- testicular, urethral, penile, kidney
- Prostate
- enzalutamide (Xtandi, Pfizer, 2012): nonsteroidal antiandrogen
- Adenocarcinoma: glandular
- Merkel cell carcinoma: rare and aggressive skin cancer
- Sarcoma: connective tissue like soft tissue, bone, and muscle.
- Melanoma and glioma is neural crest-derived
- Blastoma mostly in kids
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_hematologic_conditions
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_cancer_types
Treatment
- Medical
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy
- hormonal therapy
- Radiation
- Surgical
Leukemia
- chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The Philadelphia chromosome is a reciprocal translocation that creates the fusion gene BCR-ABL1 where tyrosine kinase ABL1 is always on, causing uncontrolled cell division.
- Imatinib (2001) by Novartis is a competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
- Ibrutinib (Imbruvica, AbbVie, 2013) covalently binds Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), part of the B-cell receptor pathway. $5B/year.
- Rituximab (1997) binds to the CD20 surface antigen and kills B cells.
Breast cancer usually overexpresses estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). 20% of cases are triple negative.
- KISS1 gene encodes kisspeptin, which binds to GPCR and activates MAPK, which suppresses MMP-9 and melanoma and breast cancer metastasis. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9) are crucial for metastasis.
- Antiestrogen therapy for ER+ like tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator.
- palbociclib (Ibrance, 2015) for hormone receptor+, HER2-. CDK4/6 inhibitor.
- abemaciclib (Verzenio, Eli Lilly, 2017) for hormone receptor+, HER2-. CDK4/6 inhibitor.
paclitaxel, vinblastine, and eribulin target microtubules.
Paxol
Gemcitabine is a nucleoside analog that causes anemia, leukopenia, and nausea.
Cisplatin is a platinum coordination complex that interferes with DNA replication and causes kidney damage, ear damage, and nausea.
Methotrexate (1947) treats cancer and autoimmune disease.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies carcinogens as Group 1 (proven), Group 2A probable (sufficient evidence in animals), Group 2B possible (limited evidence in humans), Group 3 (limited evidence in animals)
Neuroscience and neurology
Neuroimaging
- EEG: electroencephalography
- alpha (8-13 Hz), beta (13-30 Hz) prominent during intense thinking
- delta (0.5-4 Hz), and theta (4-7 Hz) only appear in sleep.
- Electromyography (EMG) measures the electric potential generated by skeletal muscles
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- highly uniform 1.5 T magnetic field oscillates at the resonance frequency to polarize hydrogen nuclei spins of water.
- Excite atoms with a strong RF pulse to detect polarization by tipping the magnetization in the direction of the receiver coil.
- Gradient coils vary the local magnetic field, causing a loud hum as the windings move slightly in magnetostriction.
- Relaxation realigns magnetization with the magnetic field via molecular rotations matching the nuclear spin resonance.
- T1 relaxation time measures spin-lattice relaxation, the longitudinal component of the nuclear magnetic moment vector parallel to the field.
- repetition time (TR) is the time magnetization is allowed to recover.
- T2 relaxation time measures spin-spin relaxation, the transverse component. Inhomogeneous effects cause decoherence of the transverse nuclear spin magnetization which can be reversed by an inversion pulse. The refocused transverse component creates a spin echo.
- echo time (TE) is the time magnetization is allowed to decay.
- Repetition time is the amount of time for relaxation
Can image , which differs by tissue type.
- T1 relaxation time measures spin-lattice relaxation, the longitudinal component of the nuclear magnetic moment vector parallel to the field.
- Gadolinium(III) contrast shows lesions since hydrophilic Gd chelates do not cross the BBB. Gd reduces T2* in nearby water protons.
- fMRI blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal
- positron emission tomography (PET)
- Tc-99m exametazime shows brain blood flow and energy use.
- Perfusion CT uses iodinated contrast to image blood flow to assess stroke
electrophysiological recordings
lesion studies - Cortical stimulation mapping uses electrodes to directly stimulate and map the cortex.
- Connectome maps neural connections.
- Animal models
Nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system operates internal organs, smooth muscle, and glands.
- Sympathetic: quick “fight or flight” response. Sympathetic trunk from the spinal cord to the organs.
- Parasympathetic: slower “rest and digest” dampening, plus sexual arousal.
- Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord
- preganglionic nerve fibers to the ganglia. Cholinergic and myelinated.
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS): ganglia, nerves, and enteric nervous system in the digestive tract.
- TRPV1 burning sensation activated by heat above 109 °F, capsaicin, and allyl isothiocyanate.
Brain
- Brainstem
- pons
- cochlear nucleus -> superior olivary complex -> lateral lemniscus (includes a crossing)
- principal sensory nucleus of trigeminal nerve -> dorsal and ventral trigeminal tract
- midbrain continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon
- retina -> reticular activating system (RAS) regulates wakefulness.
- retina -> superior colliculus controls saccades, directed head turns, arm-reaching, and spatial attention.
- lateral lemniscus -> inferior colliculus (auditory)
- cranial nerves -> spinal trigeminal nucleus -> ventral trigeminal tract
- medulla oblongata
- cardiovascular center regulates heart rate.
- vasomotor center regulates blood pressure.
- respiratory center generates breathing.
- dorsal respiratory group (DRG) initiates inhalation.
- ventral respiratory group (VRG)
- pons
- diencephelon
- thalamus is a relay
- amygdala -> medial dorsal nucleus -> orbitofrontal cortex.
- optic tract -> lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) <-> optic radiation <-> primary visual cortex. Decorrelation in time and color channels (opponent process).
- parasol ganglion -> two magnocellular layers
- midget ganglion -> four parvocellular layers
- inferior colliculus -> medial geniculate nucleus -> auditory cortex. attention.
- output to the primary somatosensory cortex:
- trigeminal tract -> ventral posteromedial nucleus
- skin -> medial lemniscus -> ventral posterolateral nucleus -> spinothalamic tract for touch, pain, and warmth.
- ventral posterior nucleus: third-order neuron cell body
- hypothalamus including posterior pituitary
- epithalamus including pineal gland which produces melatonin
- thalamus is a relay
- cerebellum
- meninges
- pia mater
- arachnoid membrane
- Primary brain vesicles
- prosencephalon (forebrain) divides into the telencephalon (cerebrum) and diencephalon (thalamus)
- mesencephalon (midbrain)
- rhombencephalon (hindbrain) divides into the metencephalon (pons and cerebellum) and myelencephalon (medulla oblongata)
Cerebrum
- Left and right hemispheres joined by the corpus callosum below the longitudinal fissure.
- Cerebral cortex is the outer layer. Gyrus (fold or ridge) and sulcus (groove).
- Olfactory bulb
- Electroolfactography measures electric potentials in the olfactory epithelium.
- 1957. Electroantennography measures the response of an insect antenna to a given odor. Helps screen for insect pheromones.
- Limbic system in the temporal lobe.
- Amygdala processes emotion. It also processes emotional facial expressions, especially fear. More emotional arousal increases memory retention and modulates visual perception.
- Direct thalamus input allows early fear response to crude sensory elements, without cognition. Input via cortex for finer processing with slower response time.
- anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is a key correlate of emotional feeling. BA24,32,33.
- dorsal ACC does reward-based decision-making
- perigenual ACC processes emotional stimuli and autonomic responses to emotions
- Papez circuit
- downward projection allows top-down cortical regulation of emotion
- cingulate cortex → hippocampus → hypothalamus
- bottom-up perception: hypothalamus → anterior thalamus → cingulate cortex
- downward projection allows top-down cortical regulation of emotion
- Hippocampus helps form new memories.
- Reciprocal connections to the temporal cortex.
- 1971. Place cells fire in a spatial location by John O’Keefe. Half of the 2014 Nobel Prize.
- parahippocampal gyrus
- entorhinal cortex (EC)
- 2005. Grid cells fire in a regular hexagonal pattern. Edvard Moser and May-Britt Moser. Half of the 2014 Nobel Prize.
- 2005. Grid cells fire in a regular hexagonal pattern. Edvard Moser and May-Britt Moser. Half of the 2014 Nobel Prize.
- parahippocampal place area which encodes environmental scenes.
- entorhinal cortex (EC)
- dentate gyrus
- Trisynaptic circuit
- entorhinal cortex (EC) → perforant path →
- dentate gyrus (DG) → mossy fibres →
- pyramidal neurons in CA3 → schaffer collaterals →
- pyramidal neurons in CA1
- posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) involved in self-reflection and emotional salience.
- Amygdala processes emotion. It also processes emotional facial expressions, especially fear. More emotional arousal increases memory retention and modulates visual perception.
- Temporal lobe: language and high-level vision. It is folded on the side creating the lateral sulcus or lateral fissure.
- Auditory cortex
- Wernicke’s area: speech comprehension. -> arcuate fasciculus -> Broca’s area.
- Temporal pole <-> uncinate fasciculus <-> orbitofrontal cortex. Face patch for face recognition. Role in semantic memories.
- The insular cortex is folded deep in the lateral sulcus
- anterior insular cortex processes disgust and nausea.
- basal ganglia: motor control
- striate nucleus
- dorsal striatum: caudate nucleus and putamen
- ventral striatum: nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle
- substantia nigra
- striate nucleus
- Frontal lobe
- Prefrontal cortex (PFC): emotion, reward, and goal-oriented behavior
- ventromedial PFC (vmPFC): regulates the amygdala and self-control. present in all mammals.
- ventral PFC or orbitofrontal cortex: decision-making. BA14,13,11.
- medial prefrontal cortex: dorsal nexus. Includes the ACC, BA25, BA12.
- lateral PFC (LPFC): only in primates
- ventrolateral PFC or inferior frontal gyrus: motor inhibition and uncertainty. BA44,47,45.
- inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) > Broca’s area: speech production.
- dorsolateral (DLPFC) or dorsomedial PFC: executive function and highest level of motor planning. Highly connected. BA46,10,9,8.
- frontal eye fields
- ventrolateral PFC or inferior frontal gyrus: motor inhibition and uncertainty. BA44,47,45.
- precentral gyrus for motor function
- ventromedial PFC (vmPFC): regulates the amygdala and self-control. present in all mammals.
- motor cortex
- premotor cortex
- supplementary motor area
- primary motor cortex
- Prefrontal cortex (PFC): emotion, reward, and goal-oriented behavior
- Parietal lobe behind the frontal lobe, separated by the central sulcus
- primary somatosensory cortex
- inferior parietal lobule
- supramarginal gyrus: lesions cause receptive aphasia.
- angular gyrus -> Wernicke’s area
- precuneus: self-awareness, episodic memory, visuospatial attention.
- Occipital lobe at the back
- primary visual cortex (V1): visual field projects to the retinotopic map, six distinct layers, edge detection.
- secondary visual cortex (V2): texture, depth, and color. Reciprocal feedback to V1!
- lingual gyrus for letter recognition.
- dorsal stream (where). V3A motion processing, V5 motion detection.
- superior longitudinal fasciculus -> DLPFC.
- ventral stream (what). V4 color center, LO large object recognition.
- fusiform gyrus: high-level vision includes fusiform face area and visual word form area (VWFA).
- inferior longitudinal fasciculus
- vertical occipital fasciculus
- 1909. Brodmann areas mapped based on cytoarchitecture or histology

Vertebral column
- Cervical C1-7. The axis (C2) has a dens or odontoid process peg that articulates with the anterior arch of the atlas (C1).
- Thoracic T1-12 have facets on the sides to articulate with the heads of the ribs.
- Lumbar L1-5
- Sacrum is the back of the pelvis, fused from 5 sacral vertebrae.
- Coccyx or tailbone.
- The cervical and lumbar region curves in (lordosis), while the thoracic and sacral region curves out (kyphosis). Lordosis positions mass over the pelvis, allowing an efficient gait.
- intervertebral disc is a symphysis or fibrocartilaginous fusion between vertebrae. A fibrous ring surrounding a gel-like center.
- spinal disc herniation: protrusion or prolapse of the inner gel can compress the nerve root.

Spinal cord
- Cranial nerves: olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear (one eye muscle), trigeminal, abducens (outward gaze), facial (face muscles and taste), vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal (taste), vagus, accessory (sternocleidomastoid and trapezius), hypoglossal (tongue muscle)
- Trigeminal nerve: face sensation via ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. The latter also handles chewing.
- Vagus nerve: parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestion (enteric nervous system). Activated in vagal maneuvers: holding breath, cold water, coughing, singing, bowel movement.
- Spinal nerves
- dorsal root: afferent sensory neuron
- first-order neuron: cell body in the dorsal root ganglion. pseudounipolar neuron where the axon has two branches.
- second-order neuron: cell body in the spinal cord or brainstem. Axon crosses to the other side
- ventral root: efferent motor neuron
- sciatic nerve is the longest and widest human nerve.
- sciatica: pain going down the leg from the lower back.
- dorsal root: afferent sensory neuron
- Nerve compression or entrapment: chronic pressure on a nerve causes radiculopathy (pain).
- Local anesthesia: nerve block reduces pain by preventing depolarization.
- Lidocaine and benzocaine.
- Adjuvant: epinephrine increases duration by decreasing blood flow via vasoconstriction
- Spinal cord injury
- quadriplegia
Pupillary response
Gag reflex or pharyngeal reflex.
Blink reflex or corneal reflex.
Dyslexia
Seizures
Epilepsy
Memory
- Episodic
- Declarative
- Procedural
Neuron
- afferent sensory and efferent motor.
- interneurons are mostly inhibitory via GABA. aspiny dendrites, can receive both excitatory and inhibitory synapses
- spiny stellate cell (SSC) is an excitatory glutamatergic interneuron with many spines around its soma but without an apical dendrite. receive excitatory thalamic nuclei. only in layer IV of primary sensory areas.
- multipolar neuron has many dendrites and one axon.
- Long-term potentiation.
- pyramidal neurons have a conic body and a large apical dendrite.
- Myelin sheats insulate axons and increase signal speed.
- CNS oligodendrocytes and PNS Schwann cells add myelin sheaths.
- Glial cells
- CNS: astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia macrophages.
- PNS: satellite cells.
- https://sci-hub.st/10.1038/nrn1519
Ionotropic glutamate receptors
Hodgkin-Huxley model simulates neuron responses
Neurotransmitters
- Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels.
- Metabotropic receptors are GPCRs.
- CB1 receptor is the most abundant.
- Serotonin or 5-HT regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and memory. Tryptophan can metabolize to serotonin.
- Acetylcholine is crucial for arousal, memory, and motor neurons.
- nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) is a ligand-gated pentameric ion channel in the neuromuscular junction that causes an excitatory postsynaptic potential.
- muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) is a GPCR.
- atropine is an antimuscarinic used to treat slow heart rate and nerve agent and pesticide poisoning.
- scopolamine is an antimuscarinic that treats nausea.
- acetylcholinesterase inhibitor: Rivastigmine (1997) treats Alzheimer’s.
- Catecholamine is a monoamine with a catechol (benzene double alcohol).
- beta adrenergic receptors: β1 in heart and kidneys, β2 in lungs, GI, liver, muscle, and β3 in fat cells.
- Sympathomimetics
- Dopamine is derived from tyrosine. It is crucial for reward and movement.
- L-dopa or levodopa is a dopamine agonist and precursor.
- Epinephrine or adrenaline triggers the fight-or-flight response. It binds to alpha and beta-adrenergic GPCR receptors and increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar. Epipen treats allergic shock.
- Norepinephrine binds to alpha-adrenergic receptors in blood vessels, causing vasoconstriction. Synthesized from dopamine.
- Ephedrine increases norepinephrine activity.
- Beta agonists like dobutamine relax airway muscles, widens the airway, and increase blood pressure.
- Dopamine is derived from tyrosine. It is crucial for reward and movement.
- Beta blockers like propranolol, atenolol, and sotalol manage arrhythmia and angina and protect from a second heart attack by decreasing sinus node output.
- GABA-A is a ligand-gated ion channel causing a fast influx of chlorine ion. GABA-B is a metabotropic receptor open potassium channels, causing a −100 mV inhibitory postsynaptic potential.
- glutamate activates AMPA, NMDA, and Kainate ionotropic glutamate receptors, as well as metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease.
Neurodegenerative disease
- Alzheimer’s disease is the main cause of dementia.
- Reduced acetylcholine synthesis leads to the loss of cholinergic neurons in the limbic system and cerebral cortex.
- Misfolded amyloid beta peptide forms toxic amyloid plaques. Tau protein forms neurofibrillary tangles.
- Parkinson’s. Low dopamine.
- Insoluble alpha-synuclein aggregates form Lewy body inclusions in nerve cells in the midbrain and cortex.
- MPTP induces Parkinson’s by killing dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Lipophilic and can cross the blood-brain barrier. Its metabolite MPP+ inhibits oxidative phosphorylation complex I, causing cell death. MPTP can form as a side reaction from opioid MPPP synthesis.
- Huntington’s is genetic.
Concussion can cause fencing response, loss of consciousness, memory loss, headache, difficulty thinking, nausea, and blurred vision. Total tau is an axonal injury biomarker and S-100 calcium-binding protein B is an astroglial injury biomarker.
- 5100 BC Trepanning for cranial trauma
Hydrocephalus: accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain.
Stroke. Poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. Can be ischemic or hemorrhagic. Symptoms include hemiplagia (weakness on one side), aphasia (language difficulty), dizziness, and loss of vision on one side. Reperfusion injury from inflammation.
Intracranial bleed or hematoma or hemorrhage.
- Intracerebral bleed inside brain tissue (parenchyma) or ventricles.
- Subarachnoid bleed between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater.
- Subdural bleed between the arachnoid mater and the dura mater.
- Epidural bleed between the dura mater and the skull.
- Can increase intracranial pressure, causing Cushing reflex of high blood pressure, irregular breathing, and bradycardia. Pressure can also cause brain herniation and decorticate posturing.
Large-scale brain networks
- Default mode network (DMN) is active in wakeful rest, daydreaming, mind wandering, and internal attention. Deactivates during externally directed attention. Dorsal medial prefrontal cortex, PCC, precuneus, angular gyrus.
- Salience network filters salient stimuli.
- Frontoparietal network (FPN) or central executive network in complex problem-solving.
- Dorsal attention network (DAN) is active in goal-directed attention.
https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/
Sleep cycle
- Stage 1: relaxed wakefulness. Alpha waves disappear, theta wave appears.
- Hypnic jerk: sudden involuntary muscle constraction associated with a feeling of falling.
- Stage 2
- sleep spindles: short bursts of high frequency activity
- K-complex: large positive and negative peaks. Suppresses arousal to safe stimuli.
- Slow-wave sleep: delta waves. Consolidation of declarative memory.
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
- PGO waves: pons -> LGN -> occipital lobe.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronotype
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sleep_onset_latency
- Time in bed and total sleep duration
- Sleep study
- Polysomnography (PSG) combines brain EEG, eye EOG, muscle EMG, heart ECG.
- Actigraphy uses an accelerometer to measure movement
- 2-3 Hz band pass filter to ignore external vibrations.
Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Apnea-hypopnea index (AHI). 5 events/h causes 4% oxygen desaturation.
- Sleep disruption: respiratory effort-related arousals (RERA) of the cortex.
- Adequate
- oximeter
- respiratory: airflow (nasal pressure transducer and oral thermistor) and effort sensor
- cardiac: ECG or heart rate
- body position
- also adequate: Peripheral Arterial Tonography (PAT), actigraphy, oximetry
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5337595/
Eye

Eye
- Anterior segment in front of the lens contains aqueous humor, produced by the ciliary body and drained through the trabecular meshwork.
- The iris is a pigmented circle, due to fibrous stroma and epithelia cells. Sphincter pupillae and dilator pupillae contract and enlarge the stroma.
- The pupil lets in light. A black hole in the iris.
- The cornea is the clear cover over the iris. Most of the eye’s focusing power, at 43 dioptres (reciprocal of focal length meters).
- LASIK or laser eye surgery reshapes the cornea.
- Lens
- Accommodation: ciliary muscles change lens optical power by 15 dioptres.
- Posterior cavity contains vitreous humor.
- The sclera is the fibrous outside of the eyeball.
- The conjunctiva is a mucous membrane that covers the sclera. Highly vascularized.
- The uvea is a pigmented layer between the retina and sclera. Absorbs reflected light and light through the sclera, and has blood vessels.
- The fundus is the back of the eye.
- corneo-retinal standing potential (CRSP): retina is 0.5 mV more negative than the cornea.
- Electrooculography (EOG): measures eye movement using the CRSP using two electrodes placed on two sides of the eye.

Retina is the light-sensitive back of the eye.
- Fovea centralis is a dense pit of cones that provide sharp central vision. 5.5 mm or 18 degrees. Surrounded by the macula.
- rods and cone cell photoreceptors
- horizontal cells: lateral center-surround inhibition for spatial decorrelation, contrast, and edge detection
- bipolar cells
- amacrine cells: lateral inhibition
- ganglion cells have a long axon. Forms the optic disc, optic nerve, optic chiasm (crossing), and optic tract.
Mydriasis (pupil dilation)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pupillary_light_reflex
- Relative afferent pupillary defect: decreased pupillary response to light in the affected eye due to a lesion of the optic nerve.
- Diagnosed with the swinging light test.
- Relative afferent pupillary defect: decreased pupillary response to light in the affected eye due to a lesion of the optic nerve.
- tropicamide eyedrops allow a better view for the back of the eye
Visual Acuity Test usually measures far acuity, which is reduced in myopia (nearsightedness)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eye_chart
- 1862. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snellen_chart
- 20/20 vision: numerator is the distance to the chart (20 ft), and denominator is the distance that a person with normal vision would be able to read the chart. Higher denominator is worse.
- Normal vision is considered 1 arc minute, or 1.75 mm at 6 m.
- The limit of acuity is 20/10, 0.5 arc minutes, 0.01 degree, or 150 mm at 1 km. 128 pixels per degree (ppd).
Eye exam
- 1851. Ophthalmoscope magnifies the back of the eye (fundus). By Hermann von Helmholtz. Monocular view, 10x magnification.
- color vision
- field of vision
- refraction test

Slit lamp magnifies the anterior segment and posterior segment. Binocular view.
Red eye
- Conjunctivitis: infection
- Subconjunctival bleeding caused by pressure or trauma.
Glaucoma: high intraocular pressure (IOP) damages the optic nerve.
- open-angle glaucoma: draining is impeded
- closed-angle glaucoma: acute blockage and sharp increase in pressure.
- Normal IOP is 10-21 mmHg.
- Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) is the gold standard. Place prism against the eye.
- applanation tonometry: IOP = contact force / contact area.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetic_retinopathy
Psychiatry
Psychosis and schizophrenia involve a break from reality, including delusions, hallucinations, and incoherent speech and behavior. Antipsychotics are sedative.
- Schizophrenia: episodes of psychosis, disorganized thinking, and flat affect.
- Second-generation or atypical antipsychotics block dopamine and serotonin
- olanzapine (Zyprexa, 1996)
- risperidone
- paliperidone (Invega, 2006)
- First-generation or typical antipsychotics like chlorpromazine and haloperidol (Haldol) block dopamine. Can cause extrapyramidal side effects like muscle spasms. Blocking dopamine also reduces nausea.
Mood and neurotic disorders
- Depression
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI): venlafaxine (Effexor) and paroxetine (Paxil)
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI)
- Prozac (fluoxetine) (1986), citalopram (Celexa), and fluvoxamine (Luvox).
- First-generation:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) like imipramine (Tofranil).
- atypical antidepressants are sedative.
- mirtazapine (Remeron) (1996) is a tetracyclic antidepressant (TCA).
- trazodone (1981) is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor. Sedative.
- Serotonin syndrome: high blood pressure and fast heart rate. Severe cases involve high fever which can be fatal.
- Anxiety
- CNS depressants like benzodiazepines
- Nonbenzodiazepines or Z-drugs. Zolpidem (Ambien) increase GABA receptor activity via allosteric binding.
- An internalizing disorder, where people tend to keep their problems to themselves, which can cause the problems to grow into larger burdens.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Counterphobic_attitude
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Mania
- Bipolar, treat with mood stabilizers
- lithium at 1 mEq/L
- anticonvulsants like valproate, lamotrigine, and carbamazepine.
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder: persistent unwanted intrusive thoughts that cause anxiety or discomfort and leads to compulsions like excessive hand washing, cleaning, counting, ordering, repeating, avoiding triggers, hoarding, neutralizing, seeking assurance, praying, and checking things.
- Dissociative disorder: loss of identity.
- Somatoform disorder: physical symptoms with no physical basis.
- Hypochondriacal disorder: preoccupation with having a disease.
- Body dysmorphia
- Eating disorders: anorexia and bulimia.
- Insomnia
- Hypersomnia
- Sleep duration correlates with mortality.
- Night terrors
- Sexual dysfunction: loss of sexual desire
Personality disorders
- Schizoid: withdrawal from social interaction.
- Histrionic (self-dramatization) and narcissism
- Antisocial personality disorder: limited capacity for empathy, impulsivity, and aggression. Psychopathy and sociopathy are not recognized DSM-5 diseases.
- Borderline personality disorder: emotional dysregulation, distorted sense of self, and long-term relationship instability.
- Dependence on others and feelings of incompetence.
Neurodevelopmental disorders emerge during childhood
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): executive dysfunction including inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and emotional dysregulation
- Autism: deficits in social interaction, repetitive patterns of behavior (stimming), restricted interests, and resistance to changes. Stimming protects against overstimulation and reduces anxiety.
Psychosurgery treats depression and OCD via the limbic system
- 1936 transorbital “ice pick” lobotomy
- phineas gauge
Addiction and substance use disorder
Pain management
- nociceptive pain
- neuropathic pain
- chronic pain
Electrical brain stimulation and electroanalgesia
- Deep brain stimulation
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
- Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) using external noninvasive magnets.
- Electroconvulsive therapy or electroshock therapy induces seizure without muscular convulsion via 800 mA at 100 V for 1 s. Only 1% of the current reaches the brain.
Analgesics
- Acetaminophen or paracetamol (Tylenol): CNS cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist.
- Can cause liver failure due to the toxic metabolite NAPQI which binds to mitochondria.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid and ibuprofen (Advil) are COX inhibitors. Reduces fever. Reduces clotting and can cause GI bleeds.
- gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin treat neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia by blocking voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCC) with an α2δ subunit.
- opioids are analgesics and depressants. Endorphins. Usually causes miosis or pupil constriction.
- opium dens
- codeine is 10% as potent as morphine. Cough syrup often contains codeine/promethazine, abused as lean.
- Dextromethorphan (Robitussin) is a NMDA antagonist and cough suppressant. It is dissociative at high doses and has no opioid activity.
- Tramadol is 10% as potent as morphine.
- hydrocodone is equally potent as morphine.
- Pethidine or meperidine (Demerol) has neurotoxic metabolite norpethidine and can trigger serotonin syndrome. Reduces shivering and decreases intestinal intraluminal pressure.
- Oxycodone (OxyContin) is 1.5x as potent as morphine. Combined with paracetamol in Percocet.
- Heroin is 3x as potent as morphine. Black tar heroin is an impure mix of morphine derivatives due to acetylation without a reflux apparatus. Reflux condenses vapor and returns the condensate.
- Hydromorphone (Dilaudid) by IV is 5x stronger than morphine. Used in labor.
- Fentanyl is 100x more potent than morphine.
- GPCR opioid receptors. In the brain there is high concentration in the Periaqueductal gray, Locus coeruleus, and the Rostral ventromedial medulla.
- Laudanum is a tincture of 10% powdered opium in alcohol.
- naloxone is an antagonist that treats overdose.
- Treatment: buprenorphine is a partial agonist. Methadone treats opioid withdrawal. Naltraxone is an antagonist that blocks opioid effects.
- Narcan reverses overdose. Patients drop straight into withdrawal and can get very cranky.
- Injection can cause venous sclerosis (narrowing).
- Lacing or cutting agents add bulk or substitute cheaper drugs.
General anesthesia
- etomidate: rapid, short-duration GABA agonist and imidazole derivative. 0.5 mg/kg.
- ketamine is an analgesic glutamate NMDA receptor antagonist. Dissociative k-hole feeling. 2 mg/kg.
- propofol is an injected GABA agonist. 1.5 mg/kg.
- midazolam (Versed) lipophilic benzodiazepine GABA agonist that rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier. 0.6 mg/kg for sedation. 2 mg to reduce anxiety and induce anterograde amnesia.
- Sevoflurane is a rapid inhaled GABA agonist. Desflurane is the fastest. Isoflurane can cause airway irritation. Halothane can cause immune hepatitis.
- Chloroform incapacitates after ten minutes of inhalation and requires continuous administration.
- GHB is a colorless and odorless GABA-B precursor.
- volatile solvents or inhalants
- nitrous oxide or laughing gas is a NMDA antagonist. Euphoria and anesthetic. Used to pressurize whipped cream.
- alkyl nitrite poppers are nitric oxide prodrugs and euphoric vasodilators
- Ether is flammable. Causes a long excitation stage before anesthesia.
- Clonidine and xylazine (tranq) is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist.
- carfentanil is a large animal opioid tranqulizer.
- Dexmedetomidine is a α2-adrenergic receptor agonist.
- remifentanil is an opioid sedative.
Depressants: hypnotics and sedatives or sleeping pills.
- Cannabinoids including cannabis (marijuana, weed, hashish).
- Cannabidiol (CBD) is calming.
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is psychoactive and antiemetic.
- Head shops. Associated with 420 after a high school group would smoke at 4:20 pm.
- Rolled into a joint or blunt and smoked.
- A bong or water pipe guides cannabis smoke through a bowl of water and up a stem. A bowl holds cannabis for smoking. A carburetor hole at the lower part of the stem allows air through the stem.
- Gravity bong: light the bowl and move it up, filling a jar of smoke. A waterfall bong drains water to pull smoke through the bowl.
- alcohol
- Metabolized as alcohol dehydrogenase -> aldehyde -> aldehyde dehydrogenase -> carboxylic acid.
- alcohol is a hangover remedy: “hair of the dog that bit you”
- methaqualone (Quaalude)
- Nonbenzodiazepine (z-drugs) are sedative GABA agonists.
- Zolpidem (Ambien)
- Zaleplon (Sonata)
- Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
- Zopiclone (Imovane)
- benzodiazepines (tranquilizers) are addictive GABA agonists.
- lorazepam (Ativan) is calming and sedative, and metabolized through glucuronidation or conjugation, reducing risk of drug accumulation.
- diazepam (Valium) is calming and long-lasting.
- alprazolam (Xanax) is calming.
- flunitrazepam (Rohypnol or roofies).
- temazepam (Restoril) is hypnotic
- Chlordiazepoxide treats alcohol withdrawal.
- clonazepam (Klonopin) treats parasomnia.
- Clobazam treats epilepsy.
- treatment: flumazenil is a GABA antagonist
- Barbiturates are obsolete addictive GABA agonists. Phenobarbital is long-lasting. Sodium thiopental impairs memory and thought and was used as a truth serum.
- Baclofen is a GABA-B agonist that treats epilepsy.
- Chloral hydrate is an obsolete GABA agonist.
- Melatonin is a sedative.
- Belsomra and Quviviq are nonaddictive orexin receptor antagonists that block wakefulness signals.
Stimulants
- Catecholamines
- caffeine is an alkaloid
- Nicotine or tobacco is a an alkaloid and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. It becomes sedative at high dose.
- A hookah is a heated bowl with a hose or pipe which conducts smoke through a jar of water.
- methamphetamine or crystal meth releases dopamine by binding to sigma receptor. It is neurotoxic.
- methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a dopamine reuptake inhibitor and treats ADHD.
- Cocaine is a stimulant and dopamine reuptake inhibitor, blocking dopamine transport from the synaptic cleft into the pre-synaptic axon terminal. It also blocks serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake.
- Crack cocaine is a smokable free base. A love rose is a glass tube used as a crack pipe.
- Powder cocaine is cocaine hydrochloride.
- Benzylpiperazine (BZP) is a serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
Hallucinogens
- MDMA (ecstasy tablets or molly crystals) is an empathogen and substituted methamphetamine.
- LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) is a serotonin agonist. Fluorescent.
- mescaline and psilocybin are serotonin agonists.
- PCP (phenylcyclohexyl piperidine) or angel dust is a NMDA receptor antagonist. Also phencyclidine.
Paralytics or neuromuscular-blocking drugs (NMB) affect skeletal muscle.
Depolarizing blockers like succinylcholine 2 mg/kg resemble ACh and activate the motor end plate. Muscle pain side effects.
Nondepolarizing blockers like rocuronium 1 mg/kg are competitive antagonists. Long-acting with sugammadex used as a reversal agent.
1970 Controlled Substances Act
1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs treaty
Recovery model: personal journey to restore hope, secure base, sense of self, supportive relationships, empowerment, social inclusion, coping skills, and meaning
A trap house is an abandoned house used for drugs.
Psychology
See also: sociology.
Consciousness
- 1988. Global workspace theory: spotlight of attention in a theater of consciousness, with many subconscious cognitive processes occurring behind the scenes.
- Mindstream 心相续 is the moment-to-moment continuum of sense impressions and mental phenomena in Buddhism.
- stream of consciousness: thoughts seem to flow one at a time in sequence
- train of thought and inner speech are more cognitive.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Philosophy_of_mind
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binding_problem
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neural_correlates_of_consciousness
Emotion
- James-Lange theory: emotion is embodied
- stimulus causes a physiological response that causes an emotion.
- weaker version: bodily feedback modulates the experience of emotion
- Cannon-Bard theory: thalamus receives a stimulus and sends signals at the same time to the amygdala for emotional experience and the autonomic nervous system for physical reaction.
- Papez circuit
- thought stream: thalamus -> cingulate cortex -> cingulum pathway -> hippocampus -> fornix -> hypothalamus mammillary bodies -> mammillothalamic tract -> anterior thalamus
- feeling stream: thalamus -> mammillary bodies
- delayed gratification
- Emotional self-regulation
- Stanford marshmallow experiment
- Ego depletion, decision fatigue, analysis paralysis
- Fixation
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Emotion_navbox
William James
Perception
- perceptual set or perceptual expectancy: predisposition to perceive things in a certain way
- Priming
- image schema
- Gestalt psychology: patterns and configurations
- Principles of grouping: proximity, similarity, closure, symmetry, continuity, past experience, common fate (motion trend)
- Figure-ground: figures are convex, symmetric, small, and enclosed.
- Reification of illusory contours
- Multistable perception
- The absolute threshold is around 5 photons in a completely dark room, and 0 dB for sound.
- The equal-loudness contour shows that hearing is most sensitive around 3 kHz.
- The just-noticeable difference is the maximum sensory resolution. 1 dB. Tonal resolution is 10 cents, or around 1,400 total tones.
- Weber’s law states that perceptible difference is proportional to the existing intensity. Perceived sensation as the log of the stimulus intensity.
- Halo effect
Perceptual illusions
- Ebbinghaus illusion (1901): relative size perception
- Multistable perception
- Necker cube
- Schroeder stairs
- Tritone paradox
- Euler’s Disk
- Barberpole illusion and Shepard tone
- Fechner color is an illusion of color when looking at rapidly changing or moving black-and-white patterns.
- impossible object: Penrose triangle, Escher’s impossible cube, Penrose stairs, impossible trident or devil’s tuning fork, Borromean rings, Impossible waterfall.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_illusion
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Optical_illusions
Memory
- Sensory memory
- Iconic memory is very brief (< 1 s), high capacity, fragile, unable to be actively maintained, precategorical store.
- causes change blindness and continuity of experience during saccades
- Visual short-term memory lasts several seconds and only stores 4 chunks
- visuospatial sketchpad
- phonological loop (acoustic store, articulatory loop)
- Iconic memory is very brief (< 1 s), high capacity, fragile, unable to be actively maintained, precategorical store.
- Working memory or short-term memory holds around 4 chunks decays over 20 seconds without rehearsal.
- Chunking organizes material into meaningful groups
- Primacy effect and recency effect
- Free recall: recall items in any order
- n-back test
- Intermediate-term memory lasts for several hours.
- Long-term memory
Child development
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Developmental_psychology
- Attachment
- Young children need a relationship with a primary caregiver to develop healthy social and emotional functioning.
- Ainsworth “strange situation” experiments.
- Piaget’s theory of cognitive development
- Sensorimotor stage to 2 years: learn language
- Preoperational stage to 7 years
- Concrete operational stage to 11 years: logic
- Formal operational stage to 15 years: symbols, abstract concepts, hypotheticals
- Erik Erikson: psychosocial stages of development
- Trust, autonomy, initiative, industry, identity, intimacy, generativity, ego integrity
- Critical period
- Imprinting
- Konrad Lorenz shows that baby ducks follow the first moving stimulus they see in a critical period after hatching, which can include inanimate objects like boots or balls.
- Sexual imprinting: animals prefer mates that appear like their parents. Chi Chi sexually presented (Lordosis) to zookeepers over another giant panda.
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
- Harlow: comfort and security is more important than food.
- McGuire’s Motivations
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model_of_hierarchical_complexity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Sociolinguistics
Learning
- Non-associative learning: habituation and sensitization
- Classical conditioning is associative learning of stimuli. Normal unconditioned stimulus causes a reflexive response such as salivating at food. Pairing food with a neutral stimulus conditions the stimulus, so Pavlog’s dog salivates when a bell rings.
- Operant conditioning is reinforcement learning.
- Skinner box
- Law of effect by Thorndike: responses that produce a satisfying effect in a situation are more likely to occur.
- Observational learning
- Latent learning
- Categorization
- Prototype theory: new stimulus compared to a single prototype
- Exemplar theory: new stimulus compared to multiple known examplars.
Personality
- Big Five personality traits: extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, openness to experience
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: poor validity
Cognition
- Schema organizes categories of information and their relationships, mental framework, way of perceiving new information
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Framing_(social_sciences)
- cultural schema theory
- social cognition
- Rigidity
- Functional fixedness
- Intelligence
- IQ test: Stanford-Binet Intelligence Test by Alfred Binet and Lewis Terman.
- Social intelligence
Persuasion, advertising, marketing
- Inoculation theory
- Gruen transfer: confuse shoppers to make them forget their original goal and more likely to impulse buy.
- Facing, fronting, or zoning to be more neat and full with better selection.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Argument_from_authority
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appeal_to_tradition
Problem solving
- Gordian Knot
- Egg of Columbus
- Lateral thinking
- Oblique Strategies game by Brian Eno
- Thinking outside the box and the nine-dots puzzle
Therapy
1885. Freud develops psychoanalysis, studying the unconscious through dreams and free association. He discovers transference and popularizes repression. He develops a model of id, ego and superego.
Carl Jung
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classical_Adlerian_psychotherapy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rational_emotive_behavior_therapy
Cognitive biases
2011. Thinking, Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman: instinctive emotional reactions and heuristics vs. slower logical thought.
Mental defense mechanisms
- Binary/black-and-white/all-or-nothing thinking or splitting: tendency to view people as all good or all bad.
- Repression: the conscious mind avoids bringing up ideas that cause anxiety.
- Denial of painful facts, such as death.
- Isolation: minimize associative connections to an unpleasant or threatening thought.
- Avoidance of anxiety-causing ideas or situations.
- Antiprocess: marginalization of undesired information
- Regression: ego reverts to an earlier stage of psychosexual development in reaction to an overwhelming problem.
- Displacement
- Transference: shift feelings connected with one person (like a parent) to some other person. Vent angry feelings on unrelated people.
- Projection and blame shifting: transfer negative parts of the self to others.
- Undoing: try to cancel out a past action by engaging in contrary behavior.
- Reaction formation: suppress a current unwanted impulse by expressing its opposite, such as being nice to someone you’re jealous of, condemning a kink that you secretly share, or laughing to hide the pain.
- Sublimation: channel libido into socially useful disciplines.
- Introjection: take on others’ beliefs and attitudes to maintain a relationship or avoid conflict.
- Rationalization
- Choice-supportive bias: our perception biases in favor of our choices or purchases.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_dissonance
Fundamental attribution error: we attribute others’ bad behavior, such as being late, to their disposition or personality, while we excuse our negative actions due to the situation.
- Just-world fallacy: people get what they deserve.
- Principle of charity: consider what other people say in the best possible interpretation
- Hanlon’s razor: never attribute to malice that which is adequately explained by stupidity.
Representativeness heuristic
- Extension neglect: we tend to ignore sample size even when it is relevant
- Base rate fallacy
- Insensitivity to sample size
- Scope neglect: we don’t scale our perception of a problem proportional to its size
- Duration neglect and the peak-end rule: we evaluate painful experiences mostly by the peak and how quickly the pain diminishes. Our judgment depends little on the duration.
- Conjunction fallacy
- Gambler’s fallacy: if an event occurred less frequently than expected, it is more likely in the future.
- Illusion of validity
- Regression fallacy
- Illusory correlation
- Clustering illusion: humans see patterns in random data.
Availability heuristic: events that are easier to picture are judged more likely to occur.
Anchoring
- framing effect
- Less-is-better: we value an overfilled ice cream serving with 7 oz of ice cream more than an underfilled serving with 8 oz of ice cream.
- Observer-expectancy effect
- Clever Hans. A trainer believed that his horse could do arithmetic, when in fact, the horse was responding directly to his subconscious body language.
- Placebo effect
- Blinded experiment
- Hawthorne effect and watching-eye effect: people behave differently when aware of being observed
- Novelty effect
- Sophomore effect
Path of least resistance, psychological inertia, cognitive inertia and belief perseverance: resistance to perspective, change problem solving approach, or belief.
Loss aversion and prospect theory.
- status quo bias
- omission bias: people judge harm of comission more negatively than harm of omission
- Daniel Kahneman, 2002 Nobel Prize in Economics.
- Sunk cost, plan continuation bias, Ovsiankina effect
- mere ownership effect: people who own an object develop an attachment to it and evaluate it more positively than people do not own it.
- endowment effect or divestiture aversion: people’s willingness to accept (WTA or price to sell) something they own is higher than their willingness to pay (WTP or price to buy).
- “what belongs to us, and what we give away, always seems very precious to us” -Aristotle
- Negativity bias: unpleasant thoughts, emotions, or events have a greater effect than positive events.
- Risk perception: emotion, framing, etc
Confirmation bias: we seek out, interpret, favor, and recall information that confirms our beliefs. Includes selective perception, cherry-picking, motivated reasoning, wishful thinking, Barnum effect, overconfidence and illusory superiority.
- Naive realism: we believe that we see the world objectively.
- Dunning-Kruger effect: people with lower competence tend to overestimate their ability.
- False consensus effect: we believe that our behavior is normal.
- Curse of knowledge: we tend to assume that others share our background and understanding.
- Spotlight effect: we overestimate how much others care about us.
- Hindsight bias: we overestimate our ability to predict past events.
Positive illusions: unrealistically favorable beliefs.
- Self-serving bias: our perception is biased in ways that maintain our self-esteem.
- Hedonic treadmill: people have a happiness set point.
- Positivity offset: on average, people are mildly satisfied with their lives.
- Fading affect bias and Pollyanna principle: people are more likely to remember happy events
- Optimism bias
- Illusion of control: humans overestimate their control over events
- Depressive realism: realistic viewpoints correlate with depression.
Questionable cause
- Post hoc ergo propter hoc (“after this, thus because of this”)
- correlation implies causation
- association fallacy
- Texas sharpshooter fallacy
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IKEA_effect
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_cognitive_biases
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_effects
Radiology
- X-ray fluoroscopy
- chest X-ray
- Barium sulfate suspension is an oral contrast for the gastrointestinal tract.
- Radiocontrast agents
- CT scan: computed tomography
- Contrast CT images shortly after a bolus of iodinated contrast.
- CT pulmonary angiogram used to diagnose pumonary embolism.
- PET scan (positron emission tomography) or 2D scintigraphy
- fludeoxyglucose traces glucose metabolism
- Ventilation/perfusion lung scan measures V/Q ratio using Tc-99m. Lower ventilation causes lower arterial partial pressure of oxygen (pO2), while a shunt has no ventilation. High V/Q is associated with embolism since a dead space has no perfusion.
Histology and pathology
- Fix with 10% formalin for 24 hours. Can form methylene bridges or amino crosslinking.
- Antigen retrieval reduces fixing by heating or alkaline solution.
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) anionic surfactant used to lyse cells and denature proteins.
- Section with a microtome.
Lab analysis and biotech techniques
- See also: Microscopy
- Identify via color, flame test, odor, solubility, weight, volume, pH indicator, melting point, reactivity, chemical tests, calorimetry.
- Immunofluorescence with fluorophores or green fluorescent protein (GFP).
- Separation processes
- Wet chemistry: recrystallization, precipitation, distillation.
- Extraction using solvents, acid-base, etc.
- Decant immiscible liquids
- Filtration.
- Add flocculant to form clumps.
- Chelation forms coordinate covalent bonds with metal ion.
- Bead beating
- Centrifuge
- Silica membrane binds DNA at high salt concentration.
- Chromatography separates molecules based on how they bind to a stationary phase. Used to purify proteins.
- High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Field-flow fractionation uses a centrifugal, electric, or thermal field instead of a stationary phase.
- Gel electrophoresis. Smaller, more negatively charged molecules move faster in agarose gel.
- Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
- TAE buffer contains Tris amine base, acetic acid, and EDTA, which chelates divalent cations (iron and calcium). LB buffer is lithium borate.
- Wet chemistry: recrystallization, precipitation, distillation.
- Flow cytometry counts and sorts cells, potentially with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Cells are charged and deflected in an electric field.
- Bradford protein assay quantifies total protein using Coomassie blue.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) quantifies specific proteins using antibodies.
- A Western blot detects a specific protein using antibodies.
- A Northern blot detects a specific messenger RNA (mRNA).
- A Southern blot detects a specific DNA fragment.
- Quality control
- Positive control, negative control
- Calibration curve or standard curve determines concentration from raw signal.
- Limit of detection, limit of quantification, limit of linearity.
- Standard addition spikes the sample to quantify concentration with an unknown matrix.
DNA sequencing
- small subunit ribosomal RNA is universally conserved.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifies DNA by cycling heating and polymerase.
- DNA microarray measures expression for thousands of specific genes using probes. Suspension array technology (SAT) uses tagged 5.6 um diameter beads with probes to multiplex 100 assays on a single sample.
- Sanger sequencing uses nucleotides with markers that permanently block elongation, and gel electrophoresis to sort DNA by length.
- Illumina dye sequencing uses DNA polymerase to add nucleotides modified with a reversible fluorescent blocker. Next-gen sequencing (NGS) technique.
- A contig is a sequence of overlapping reads.
- A scaffold assembles contigs separated by gaps of known length.
- CRAM: Compressed Reference-oriented Alignment Map
- De Bruijn graph uses overlap graphs to assemble short reads.
- Nanopore sequencing uses a bias voltage to drive ssDNA through an alpha hemolysin (αHL) or MspA (Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A) nanopore. It has lower resolution and accuracy but longer reads.
- Shotgun sequencing of whole-community DNA.
- RNA-Seq or RT-PCR quantifies RNA expression or transcriptome. Reverse transcriptase (RT) generates complementary DNA (cDNA) from RNA.
- Expressed sequence tags (EST) were short cDNA fragments used to prove exon expression before whole genome sequencing.
- Acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction (AGPC or Trizol) extracts RNA.
- Centrifuge with phenol and chloroform to dissolve proteins and lipids respectively.
- Nucleic acids partition into a clear upper aqueous phase and proteins into a lower organic phase. DNA stays in the lower phase in pH 4-6.
- Add guanidinium thiocyanate, a chaotropic agent that disrupts hydrogen bonding, to denature RNases and remove ribosomal proteins. 2-mercaptoethanol or sarcosine also works.
- Precipitate RNA with 2-propanol.
- DNase removes DNA contamination.
- Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) or ChIP-seq sequences DNA bound to a specific protein. DNA and proteins are crosslinked with formaldehyde, sheared into 200-500 bp fragments via sonication or nuclease, immunoprecipitated with a antibody for the protein, and sequenced.
- DNA footprinting. DNA regions with bound protein are protected from DNase I. After gel electrophoresis, the footprints show up as gaps in the ladder.
- FAIRE-Seq: Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements uses formaldehyde crosslinking to preserve protein-DNA bindings, producing more reads in open chromatin regions. It replaces DNase-seq, which uses DNase to preferentially cleave DNA in open regions.
- ChIP-on-chip produces genome-wide protein binding maps.
- DNA adenine methyltransferase identification (DamID) modifies the protein of interest and then runs methyl PCR.
- Methyl PCR sequences methylated DNA. DpnI only methylated DNA. DpnII cuts non-methylated DNA.
- Forward genetics seeks to find the genetic basis of a phenotype.
- Reverse genetics finds the phenotypes controlled by a gene using gene knockout.
- Promoter bashing studies promoter activity: mutate part of the promoter, ligate it to a reporter gene, and measure transcription rate.
- Single-cell transcriptome
- Laser capture microdissection uses a microscope-guided laser to cut individual cells.
- Genome-wide association study (GWAS) finds SNPs associated with disease.
Gene editing
- Transformation: use a plasmid vector to insert genes into a cell.
- Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific restriction sites and leave sticky ends with overhangs, which can be joined using DNA ligase to produce recombinant DNA. Enables bioreactors.
- CRISPR template are used by Cas9 to cut the complementary DNA sequence. Cas9 originally targeted bacteriophage DNA.
- RNA editing: ADAR (adenosine deaminase acting on dsRNA) converts adenosine to inosine, which is interpreted as guanosine.
- RNA interference (RNAi). Dicer cleaves dsRNA and ssRNA with hairpin loops into small interfering siRNA and microRNA. These activate the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which produces a guide strand to degrade the target mRNA.
- Knockdown is also possible with synthetic antisense Morpholino RNA.
Bioreactor
- Good manufacturing practice (GMP) uses a quality management system (QMS).
- Site Master File (SMF) documents pharmaceutical manufacturing operations.
- A fed-batch culture has continuous nutrient input but batch product output. Useful to overcome substrate inhibition, Crabtree effect (yeast produce ethanol instead of biomass at high glucose concentrations), catabolite repression (high glucose inhibits other catabolic pathways).
- A chemostat is a continuous flow bioreactor.
- Hollow fiber bioreactor increases surface area.
- E. coli and yeast used to produce simpler molecules.
- Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell is the most common host for therapeutic proteins and antibodies, producing 10 g protein per liter of culture. It can produce complex glycosylations.
- HEK 293 cells (human embryonic kidney) are easy to culture and transfect.
High-throughput screening finds molecules with nanomolar binding affinities.
Fragment-based lead discovery grows 200 Da molecules to increase their affinity.
- Lipinski’s rule of five: oral drugs have at most five H-bond donors and 10 H-bond acceptors, mass less than 500 daltons, and octanol-water partition coefficient Clog P < 5.
Pharmacology
- Pharmacodynamics (PD): dose-response relationship
- Pharmacokinetics (PK): absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion ADME. Affected by plasma protein binding.
- A pharmacophore is a drug blueprint that defines the essential steric and electronic features needed to bind to a target. Hydrophobic centroids fit into hydrophobic pockets. Aromatic rings are slightly electron rich and can interact through pi-pi stacking with receptor aromatic residues or with cations.
- Binding requires high lipophilicity.
- Kinetic isotope effect: deuterated drugs are heavier and have a higher activation energy in the transition state, leading to a longer half-life.
- Strong C-F bond resists oxidative metabolism
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rational_design
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biomedical_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biomolecular_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molecular_engineering
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_engineering
Devices
A pulse oximeter measures peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rate.
- Use wavelenghths for bound (oxygenated) and unbound (non-oxygenated) hemoglobin. Ratio = percentage of bound hemoglobin.
- Isobestic point: wavelength where absorbance does not change with pH.
- oxyhemoglobin 586 nm, deoxyhemoglobin 808 nm.
- transmissive pulse oximetry: requires a thin section of the body.
- reflectance pulse oximetry: photodetector on the same surface as the illumination.
- compute change in absorbance due to arterial blood, excluding unchanging absorbance due to venous blood, skin, bone, muscle, fat, and nail polish.
- works better for white people.
Plethysmography (PG) measures volume changes with two distinct uses:
- Lung effort sensor: respiratory rate, tidal volume, etc in the thorax and abdomen.
- Respiratory inductance PG (RIP). Breathing changes the self-inductance of wire coils placed in elastic bands.
- piezoelectric respiration (PZT) sensor gives a voltage pattern over time. Does not directly measure actual volume.
- Blood flow: pulse waveform can be captured with a fingertip sensor. The foot of the wave is the beginning of systole, chosen since it is free of reflections.
- Pulse wave velocity (PWV) and arterial stiffness can be measured with two tonometers.
- piezoelectric PG
- photoelectric PG (PPG)
- near-diastolic pressure to reduce interference from respiration and movement
- veno-arteriolar reflex vasoconstriction
- Peripheral Arterial Tonography (PAT) measures finger artery stiffness
Companies
- Health insurance: UnitedHealth Group (500B), Elevance fka Anthem (120B), Cigna (100B).
- pharmacy benefit managers (PBM) pay pharmacies, collect manufacturer rebates, and process prescription drug claims. Cigna Express Scripts, CVS Caremark, and UHG OptumRx have 80% market share.
- GoodRx provides consumer prices from different PBMs and allows comparing between pharmacies. But it also helps set PBM pharmacy payment rates leading to algorithmic collusion.
- Eli Lilly (800B) mainly earns money from diabetes drugs.
- Novo Nordisk (450B) is the world’s largest charity, founded to make insulin by August Krogh.
- Johnson & Johnson (400B).
- AbbVie (300B) makes Humira (adalimumab) for autoimmune diseases.
- Merck (300B).
- Roche (250B) bought Genentech.
- Thermo Fisher (200B).
- Novartis (200B).
- AstraZeneca (200B).
- Pfizer (150B).
- Amgen (150B) makes Enbrel for arthritis.
- Vertex (120B) makes Trikafta for cystic fibrosis.
- Regeneron (110B)
- Dupixent (dupilumab) for atopic dermatitis $12B revenue at $37k/year.
- Eylea (aflibercept) for wet macular degeneration $6B revenue at $20k/year.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb BMS (100B) owns Celgene.
- Sanofi (100B).
- Gilead (80B).
- Life sciences: Danaher (200B).
- Medical devices: Abbott (200B), Intuitive Surgical (150B), Stryker (130B), Boston Scientific (110B), Medtronic (110B).
- Contract research organisations (CROs) and contract manufacturing organisations (CMOs) are commodities at $40B total.
History of medicine
The National Institutes of Health funds 30% of medical research in the US with a budget of $50 billion.
- 400 BC. Hippocrates is the father of medicine.
- The Hippocratic Oath includes “first do no harm”.
- Professionalism: physicians be well-kempt, honest, calm, understanding, and disciplined.
- Importance of clinical observation and documentation. Complexion, pulse, fever, pains, movement, excretions, family history, and environment.
- Acute, chronic, endemic and epidemic categories of illness. Exacerbation, relapse, resolution, crisis, paroxysm, peak, and convalescence.
- Describes nail clubbing (swelling) associated with lung and heart disease.
- Describes Hippocratic face, a sign of impending death with sunken eyes and temples, pale color, and stretched skin.
- Treated diabetes with diet and exercise.
- Treated hemorrhoids with ligation and burning.
- On the Nature of Man.
- Miasma theory holds that disease is caused by bad air.
- Humoral theory that disease is caused by an imbalance (“dyscrasia”) of bodily fluids: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. Leads to bloodletting.
- 335 BC. Aristotle describes spontaneous generation of life or abiogenesis.
- 165. Antonine Plague of smallpox or measles kills a quarter (5 million) of Rome. Smallpox will continue to kill 10% of people for a millenium.
- 165. Galen discusses: venous and arterial blood, motor and sensory nerves, agonists and antagonists, muscle tone, larynx as the source of voice.
- On the Temperaments: sanguine, choleric, melancholic and phlegmatic.
- 200. Charaka shapath is a medical oath.
- 541. Plague of Justinian is a bubonic plague that kills around 20 million.
- 1027. Avicenna writes The Book of Healing, which favors experimentation over induction.
- 1242. Ibn al-Nafīs describes pulmonary circulation in Commentary on Anatomy in Avicenna’s Canon.
- 1347. Black Death is a bubonic plague that kills half (50 million) of Europe’s population.
- 1492. Columbian Exchange kills 90% of Native Americans (50 million).
- 1543. Andreas Vesalius writes the anatomy textbook De Humani Corporis Fabrica.
- 1579. China develops innoculation or variolation against smallpox using a strain with 1% mortality (versus 30% mortality for the deadly strain).
- 1668. Francesco Redi shows that maggots come from eggs and claims that omne vivum ex ovo (“every life comes from an egg”), against the theory of spontaneous generation.
- 1795. Romantic medicine. Erhard calls for a new medicine based on a real understanding of disease.
- 1780. Brunonian system of medicine believes disorders are caused by excessive excitation.
- 1807. Samuel Hahnemann invents homeopathy. Similia similibus curentur or “like cures like”: things that cause symptoms of disease in healthy people can cure similar symptoms in sick people. Dilutes drugs to reduce their toxic effects while shaking them to maintain potency.
- 1790. John Hunter carries out the first artificial insemination.
- 1796. Edward Jenner proves the vaccine, cowpox pus, by showing that his gardener’s son was immune to smallpox.
- 1800. Xavier Bichat pioneers histology, describing 21 different tissue types without a microscope.
- 1804. Friedrich Sertürner isolates morphine.
- Cell theory
- 1827. Francois-Vincent Raspail asserts that every cell arises from another cell.
- 1831. Scottish botanist Robert Brown discovers the plant cell nucleus.
- 1838. all plants are composed of cells
- 1839. Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden state that the cell is the fundamental component of living organismus. Published as Accordance in the structure and growth of animals and plants. He also shows that heat prevents fermentation.
- 1855. Robert Remak asserts that new cells are generated by division of the existing ones. He also discovers the three germ layers of the embryo (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) (1842), discovers nonmedullated nerve fibres (1838), and Remak’s ganglia in the heart (1844). Became the first Jew to teach at the University of Berlin.
- 1855. Rudolf Virchow popularizes the theory that all cells come from cells.
- 1856. Carl Ludwig: Textbook of Human Physiology. Plots blood flow and pressure.
- 1859. Darwin.
- 1860. Florence Nightingale founds nursing as a profession with better hygiene standards. She trained nurses during the Crimean War and founds a nursing school in London. She also popularizes infographics with the pie chart. She becomes a pop icon as “the lady with the lamp” making rounds on wounded soldiers.
- Germ theory
- 1837. Charles Cagniard de la Tour argues that yeast causes fermentation in mémoire sur la fermentation vineuse.
- 1837. Friedrich Traugott Kützing aruges that yeast causes fermentation.
- 1865. Joseph Lister is the father of modern surgery, using phenol disinfectant and sterile technique.
- 1870. Louis Pasteur invents pasteurization and proves germ theory over the theory of spontaneous generation. He also develops live attenuated vaccines for chicken cholera and rabies.
- 1876. Robert Koch is the father of microbiology. He discovers anthrax bacterium and is the first to show that a specific microorganism causes a specific disease. He invents bacterial staining with methylene blue and Bismarck brown Y; and the Petri dish with agar, a clear solid medium not degraded by bacteria (unlike gelatin).
- 1897. John Abel isolates epinephrine.
- 1910. Flexner Report promotes evidence-based medicine, but also restricts opportunities for women and people of color.
- 1918. Spanish flu pandemic (H1N1) kills around 50 million people. It triggers a cytokine storm which increases mortality in young adults. The press freely reported on the pandemic in neutral Spain whereas wartime censors in other countries suppressed the news.
- 1921. Frederick Banting and John Macleod discover insulin.
- 1928. Alexander Fleming discovers penicillin.
- 1955. Jonas Salk develops the polio vaccine.
- 1957. Asian flu pandemic (H2N2) kills around 2 million.
- 1960. FDA medical officer Frances Kelsey blocks thalidomide, saving thousands of lives.
- 1968. Hong Kong flu pandemic (H3N2) kills around 2 million.
- 1977. Smallpox is the only human disease to be eradicated.
- 1981. HIV/AIDS epidemic kills around 30 million.
- 2020. Covid pandemic kills around 10 million. It is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
- Seasonal flu kills up to half a million people per year.
- Tuberculosis kills over a million people per year.
- Malaria kills over half a million people per year.
- Hepatitis B kills around 800,000 people per year from cirrhosis and liver cancer.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Major_drug_groups
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gold_standard_(test)
https://guide.berkeley.edu/departments/molecular-cell-biology/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cisplatin
quantum https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=35222029
https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx
Sabrexane
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WHO_Model_List_of_Essential_Medicines
https://sites.arizona.edu/njardarson-lab/top200-posters/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Ethology